 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 How to use thinkorm to implement database data sharding and partitioning
How to use thinkorm to implement database data sharding and partitioning
How to use thinkorm to implement database data sharding and partitioning
How to use thinkorm to implement data sharding and partitioning of the database
Introduction:
As the amount of data continues to increase, higher requirements are placed on the performance and scalability of the database. Data sharding and partitioning are an effective way to horizontally divide data in a database, thereby improving database performance and scalability. This article will introduce how to use the thinkorm framework to implement database data sharding and partitioning, and give relevant code examples.
1. The concept of data sharding
Data sharding is to divide the data in the database into multiple smaller data sets, and distribute these data sets to multiple database nodes to achieve data Parallel processing and load balancing. Data sharding can be divided into two methods: vertical sharding and horizontal sharding.
Vertical sharding is to divide the tables in the database according to different columns, and store different columns in different database nodes. This method is suitable for situations where there are a large number of redundant fields in the data table.
Horizontal sharding is to divide the tables in the database according to different rows, and store different rows in different database nodes. This method is suitable for situations where there are a large number of rows in the data table and there are not many correlations between each row of data.
2. Introduction to thinkorm framework
Thinkorm is a lightweight ORM (Object Relational Mapping) framework based on PHP language, which provides convenient database operation methods and supports multiple database types. Thinkorm has simple syntax and powerful query capabilities, allowing us to easily operate the database.
3. How thinkorm implements data sharding and partitioning
- Database configuration
First, in the thinkorm configuration file, we need to add the configuration of multiple database nodes , each node corresponds to a database instance. You can refer to the following code example:
return [
'connections' => [
// 主节点
'master' => [
'type' => 'mysql',
'host' => '127.0.0.1',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => 'root',
'database' => 'shard_db',
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
],
// 分片节点1
'shard1' => [
'type' => 'mysql',
'host' => '127.0.0.1',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => 'root',
'database' => 'shard1_db',
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
],
// 分片节点2
'shard2' => [
'type' => 'mysql',
'host' => '127.0.0.1',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => 'root',
'database' => 'shard2_db',
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
],
// ...
],
];- Sharding strategy definition
Next, we need to define the data sharding strategy, which is the rule that determines which database node the data will be distributed to. You can refer to the following code examples:
class UserShardPolicy extends ThinkORMShardingPolicyAbstractPolicy
{
public function findNode($params)
{
// 获取用户ID
$userId = $params['id'];
// 根据用户ID的奇偶来决定将数据存储在哪个节点
if ($userId % 2 == 0) {
return 'shard1';
} else {
return 'shard2';
}
}
}- Implementing data sharding and partitioning
Finally, in our code, we can implement data sharding and partitioning in the following ways:
// 创建数据表模型
class User extends ThinkORMORM
{
protected $connection = 'master';
// 指定分片策略
protected $shardPolicy = UserShardPolicy::class;
}
// 新增用户
$user = new User();
$user->id = 1;
$user->name = 'Tom';
$user->save();
// 查询用户
$user = User::find(1);
echo $user->name; // 输出: TomIn the above code, we created a User class to map the user table in the database. By setting the $connection property, we specify the primary database node, the node where user metadata is stored. By setting the $shardPolicy attribute, we specify the data sharding policy, which determines which shard node the user data is stored in based on the parity of the user ID.
Conclusion:
Through the thinkorm framework, we can easily implement data sharding and partitioning of the database. Through the technology of data sharding and partitioning, we can improve the performance and scalability of the database to better meet the needs of applications.
Summary:
This article introduces how to use the thinkorm framework to implement data sharding and partitioning of the database. We first introduced the concept of data sharding, and then briefly introduced the basic features of the thinkorm framework. Next, we introduced in detail the method of using thinkorm to implement data sharding and partitioning, and gave corresponding code examples. I hope this article can help readers better understand and apply data sharding and partitioning technology.
The above is the detailed content of How to use thinkorm to implement database data sharding and partitioning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Solve the problem that the reserved partition of win11 system cannot be updated
Dec 26, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
Solve the problem that the reserved partition of win11 system cannot be updated
Dec 26, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
After updating win11, some users encountered the problem that the partition reserved by the system cannot be updated, resulting in the inability to download more new software. So today I brought you the solution to the partition reserved by the system cannot be updated by win11. Come and download it together. Try it. What to do if win11 cannot update the partition reserved by the system: 1. First, right-click the start menu button below. 2. Then right-click the menu and click Run. 3. During operation, enter: diskmgmt.msc and press Enter. 4. You can then enter the system disk and check the EFI system partition to see if the space is less than 300M. 5. If it is too small, you can download a tool to change the system reserved partition to larger than 300MB. 450M is recommended.
![[Linux system] fdisk related partition commands.](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/170833682614236.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) [Linux system] fdisk related partition commands.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
[Linux system] fdisk related partition commands.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
fdisk is a commonly used Linux command line tool used to create, manage and modify disk partitions. The following are some commonly used fdisk commands: Display disk partition information: fdisk-l This command will display the partition information of all disks in the system. Select the disk you want to operate: fdisk/dev/sdX Replace /dev/sdX with the actual disk device name you want to operate, such as /dev/sda. Create new partition:nThis will guide you to create a new partition. Follow the prompts to enter the partition type, starting sector, size and other information. Delete Partition:d This will guide you to select the partition you want to delete. Follow the prompts to select the partition number to be deleted. Modify Partition Type: This will guide you to select the partition you want to modify the type of. According to mention
 Solution to the problem of unable to partition after win10 installation
Jan 02, 2024 am 09:17 AM
Solution to the problem of unable to partition after win10 installation
Jan 02, 2024 am 09:17 AM
When we reinstalled the win10 operating system, when it came to the disk partitioning step, we found that the system prompted that a new partition could not be created and the existing partition could not be found. In this case, I think you can try to reformat the entire hard disk and reinstall the system to partition, or reinstall the system through software, etc. Let’s see how the editor did it for the specific content~ I hope it can help you. What to do if you cannot create a new partition after installing win10. Method 1: Format the entire hard disk and repartition it or try plugging and unplugging the USB flash drive several times and refreshing it. If there is no important data on your hard disk, when it comes to the partitioning step, delete all the data on the hard disk. Partitions are deleted. Reformat the entire hard drive, then repartition it, and then install it normally. Method 2: P
 Detailed explanation of how to set up Linux Opt partition
Mar 20, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Detailed explanation of how to set up Linux Opt partition
Mar 20, 2024 am 11:30 AM
How to set up the Linux Opt partition and code examples In Linux systems, the Opt partition is usually used to store optional software packages and application data. Properly setting the Opt partition can effectively manage system resources and avoid problems such as insufficient disk space. This article will detail how to set up a LinuxOpt partition and provide specific code examples. 1. Determine the partition space size. First, we need to determine the space size required for the Opt partition. It is generally recommended to set the size of the Opt partition to 5%-1 of the total system space.
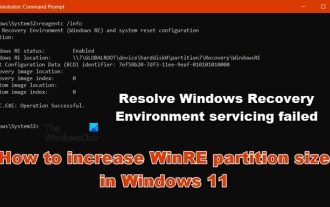 How to increase WinRE partition size in Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
How to increase WinRE partition size in Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
In this article, we will show you how to change or increase WinRE partition size in Windows 11/10. Microsoft will now update Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) alongside monthly cumulative updates, starting with Windows 11 version 22H2. However, not all computers have a recovery partition large enough to accommodate the new updates, which can cause error messages to appear. Windows Recovery Environment Service Failed How to Increase WinRE Partition Size in Windows 11 To increase WinRE partition size manually on your computer, follow the steps mentioned below. Check and disable WinRE Shrink OS partition Create new recovery partition Confirm partition and enable WinRE
 Integer calculation solution for win10 partition defragmentation
Dec 30, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Integer calculation solution for win10 partition defragmentation
Dec 30, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
When partitioning Windows, if you simply enter the calculated value as 1GB=1024MB, you will always get a result like 259.5GB/59.99GB/60.01GB instead of an integer. So how is the integer calculated for the win10 partition? Woolen cloth? Let’s take a look with the editor below. The formula for calculating the integer of win10 partition: 1. The formula is: (X-1)×4+1024×X=Y. 2. If you want to get the integer partition of Windows, you must know a formula. The value calculated through this formula can be recognized by Windows as an integer GB value. 3. Among them, X is the value of the integer partition you want to get, the unit is GB, and Y is the number that should be entered when partitioning.
 Deepin Linux hard disk partitioning and installation tutorial: step by step to achieve efficient system deployment
Feb 10, 2024 pm 07:06 PM
Deepin Linux hard disk partitioning and installation tutorial: step by step to achieve efficient system deployment
Feb 10, 2024 pm 07:06 PM
Before installing Deepin Linux, we need to partition the hard disk. Hard disk partitioning is the process of dividing a physical hard disk into multiple logical areas. Each area can be used and managed independently. The correct partitioning method can improve the performance and performance of the system. Stability, so this step is very important. This article will provide you with detailed and in-depth Linux hard disk partitioning and installation tutorials. Preparation 1. Make sure you have backed up important data, as the partitioning process will erase all data on the hard drive. 2. Prepare a Deepin Linux installation media, such as a USB flash drive or CD. Hard disk partition 1. Boot into the BIOS settings and set the boot media as the preferred boot device. 2. Restart the computer and boot from the boot media to enter the system installation interface. 3.Select
 How to partition hard disk in Win11? Tutorial on how to partition the hard disk in win11 disk
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
How to partition hard disk in Win11? Tutorial on how to partition the hard disk in win11 disk
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
Many users feel that the default partition space of the system is too small, so how to partition the hard disk in Win11? Users can directly click on the management under this computer, and then click on the disk management to perform operation settings. Let this site give users a detailed tutorial on how to partition a hard drive in Win11. Tutorial on how to partition a hard disk in win11 1. First, right-click this computer and open Computer Management. 3. Then check the disk status on the right to see if there is available space. (If there is free space, skip to step 6). 5. Then select the amount of space you need to free up and click Compress. 7. Enter the desired simple volume size and click Next. 9. Finally, click Finish to create a new partition.



