 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 RISC-V Linux startup page table creation analysis
RISC-V Linux startup page table creation analysis
RISC-V Linux startup page table creation analysis
The previous article analyzed the assembly startup process of RISC-V Linux, which mentioned that relocate redirection requires turning on the MMU. Today we analyze the page table creation of RISC-V Linux.
Note: This article is based on the linux5.10.111 kernel
##sv39 mmu
RISC-V Linux supportssv32, sv39, sv48 and other virtual address formats, which respectively represent 32-bit virtual address, 38-bit virtual address and 48-bit virtual address. address. RISC-V Linux also uses the sv39 format by default. The virtual address, physical address, and PTE format of sv39 are as follows:
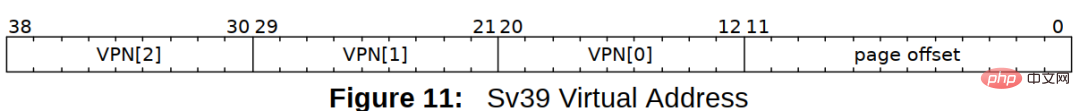


The physical address is represented by 56 bits, the lower 12 bits represent the page offset, and the higher bits are the physical pages PPN[0], PPN[1] and PPN[2]
PTE saves the physical page PPN[0] , PPN[1] and PPN[2], corresponding to the PPN in the physical address; the lower 10 bits of the PTE represent the access rights of the physical address. When RWX is all 0, it means that the address stored in the PTE is The physical address of the next level page table, otherwise it means that the current page table is the last level page table .
Look at the page table format of sv39. sv39 uses a three-level page table, PGD, PMD and PTE, each The level page table is represented by 9 bits, that is, each level page table has 512 page table entries.
In the code, create an array with 512 elements to represent a page table. A PTE has 512 page table entries, each page table entry occupies 8 bytes, 512*8=4096 bytes, so a PTE represents 4K. A PMD also has 512 page table entries, each entry can represent a PTE, 512 *4 K=2M, so a PMD represents 2M. By analogy, one PGD represents 512 * 2M = 1G.
Important conclusion: PGD represents 1G, PMD represents 2M, and PTE represents 4K. The default page size of sv39 is 4K.
Schematic diagram of the process of converting the virtual address of the third-level page table to the physical address: 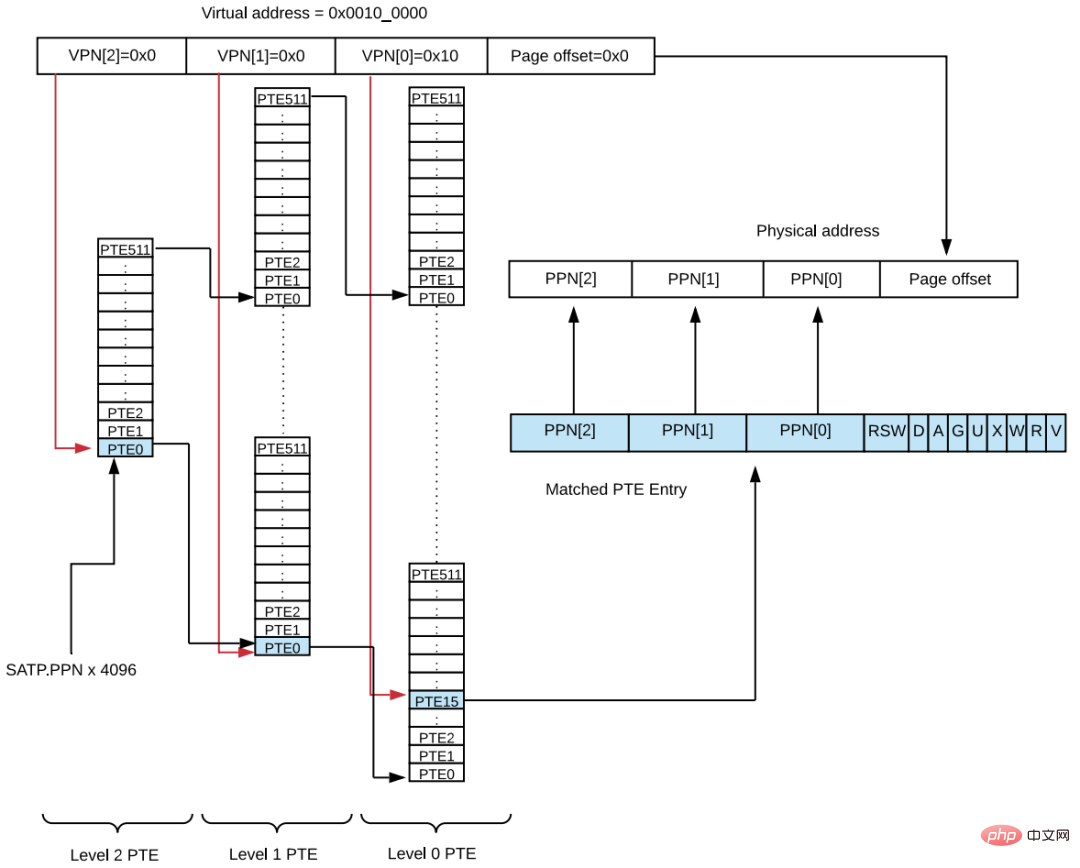
sv39 The process of converting the virtual address of the third-level page table to the physical address:
MMU passes satp The register obtains the physical address of PGD, and combines it with the PGD index (i.e., V PN[2]) to find the PMD; after finding the PMD, it then combines it with the PMD index (i.e., V PN[1]) to find the PTE, and then combines it with the PTE index (i.e., V PN[0] ]) Get the value of VA in the PTE index to get the physical address.
Finally, take out PPN[2], PPN[1] and PPN[0] from the PTE, and then add them to the low 12-bit offset of the virtual address to get the final physical address.
Temporary page table analysis
Before starting the MMU, you need to create kernel, dtb, trampoline and other page tables. So that after the MMU is turned on and before the memory management module is run, the kernel can be initialized normally and the dtb can be parsed normally. This part of the page table is a temporary page table, and the final page table is created in setup_vm_final().
Temporary page table creation sequence:
First create early PGD and PMD for fixmap. At this time, PGD uses early_pg_dir. Then create a secondary page table for the first 2M of memory starting from the kernel. At this time, PGD uses trampoline_pg_dir. The page table created for these 2M is also called superpage. Then, create a secondary page table for the entire kernel. At this time, PGD uses early_pg_dir. Finally, reserve 4M size for dtb to create a secondary page table.
Page table creation function
1
2
3
void __init create_pgd_mapping(pgd_t *pgdp,
uintptr_t va, phys_addr_t pa,
phys_addr_t sz, pgprot_t prot)
Copy after login
1 2 3 |
|
pgdp: PGD page table
va: virtual address
pa: physical address
sz:映射大小,PGDIR_SIZE或PMD_SIZE或PTE_SIZE
prot:PAGE_KERNEL_EXEC/PAGE_KERNEL表示当前是最后一级页表,否则pa代表下一级页表的物理地址
create_pmd_mapping()
1 2 3 |
|
pmdp:PMD页表
va:虚拟地址
pa:物理地址
sz:映射大小,PMD_SIZE或PAGE_SIZE
prot:权限,PAGE_KERNEL_EXEC/PAGE_KERNEL表示当前是最后一级页表,否则pa代表下一级页表的物理地址
create_pte_mapping()
1 2 3 |
|
ptep:PTE页表
va:虚拟地址
pa:物理地址
sz:映射大小,PAGE_SIZE
prot:权限,PAGE_KERNEL_EXEC/PAGE_KERNEL表示当前是最后一级页表,否则pa代表下一级页表的物理地址
使用举例
例如,将虚拟地址PAGE_OFFSET映射到物理地址pa,映射大小为4K,创建三级页表PGD、PMD和PTE:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
这样创建后,MMU就会根据PAGE_OFFSET在PGD中找到PMD,然后再PMD中找到PTE,最后取出物理地址。
页表创建源码分析
RISC-V Linux启动,经历了两次页表创建过程,第一次使用C函数setup_vm()创建临时页表,第二次使用C函数setup_vm_final()创建最终页表。
具体细节参考代码中的注释,下面的代码省略了一些不重要的部分。
setup_vm()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
|
setup_vm()在最开始就进行了kernel入口地址的对齐检查,要求入口地址2M对齐。假设内存起始地址为0x80000000,那么kernel只能放在0x80000000、0x80200000等2M对齐处。为什么会有这种对齐要求呢?
我猜测单纯是为给opensbi预留了2M空间,因为kernel之前还有opensbi,而opensbi运行完之后,默认跳转地址就是偏移2M,kernel只是为了跟opensbi对应,所以设置了2M对齐。
那opensbi需要占用2M这么大?实际上只需要几百KB,因此opensbi和kernel中间有一段内存是空闲的,没有人使用。这个问题我们下篇再讲。
setup_vm_final()
在该函数中开始为整个物理内存做内存映射,通过swapper页表来管理,并且清除掉汇编阶段的页表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 |
|
说明:
在setup_vm_final()函数中,通过swapper_pg_dir页表来管理整个物理内存的访问。并且清除汇编阶段的页表fixmap_pte和early_pg_dir。(本质上就是把该页表项的内容清0,即赋值为0)
最终把swapper_pg_dir页表的物理地址赋值给SATP寄存器。这样CPU就可以通过该页表访问整个物理内存。
切换页表通过如下实现:
csr_write(CSR_SATP,PFN_DOWN(_pa(swapper_pg_dir))|SATP_MODE);
在swapper_pg_dir管理的kernel space中,其虚拟地址与物理地址空间的偏移是固定的,为va_pa_offset(定义在arch/riscv/mm/init.c中的一个全局变量)
注意:swapper_pg_dir管理的是kernel space的页表,即它把物理内存映射到的虚拟地址空间是只能kernel访问的。user space不能访问,用户空间如果访问,必须自行建立页表,把物理地址映射到user space的虚拟地址空间。kernel线程共享这个swapper_pg_dir页表。
Summary
The page table creation when RISC-V Linux starts is relatively easy to understand. They are all created in C language, and the code is relatively small. The main two page table creation functions are setup_vm() and setup_vm_final(). After understanding some of the address formats of sv39, it will be easier to analyze the source code. However, the codes of different kernel versions are different and require detailed analysis of specific situations.
This article mentioned that setup_vm() will check whether the kernel entry address is 2M aligned. If it is not aligned, the kernel cannot start. But in fact, we can lift this 2M alignment restriction and make use of this part of the space. The next article will teach you Optimize this part of memory.
The above is the detailed content of RISC-V Linux startup page table creation analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.



