 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What is the difference between ${} and $() in Bash
What is the difference between ${} and $() in Bash
What is the difference between ${} and $() in Bash
GNU-based operating systems like Linux rely on a command language interpreter or shell called Bash to accomplish most of their computing tasks and goals .

Bash is the abbreviation of Bourne Again Shell. Bunne Again Shell is a pun name that pays tribute to Bourne Shell (invented by Steven Bourne). In terms of compatibility, Bash and sh are a perfect match. Useful features evident in the C shell ( csh ) and Korn shell ( ksh ) are also included in this shell language interpreter.
In terms of implementation, Bash aims to conform to the tools portion of the IEEE POSIX specification (IEEE Standard 1003.1) and the IEEE POSIX Shell. Therefore, as an interactive and programming tool, Bash provides functional improvements over those in sh.
Users of Linux and other GNU-based operating systems do not have to rely solely on Bash as their primary command language interpreter, since versions of shells like csh are also pre-packaged on these systems. Due to its unique shell properties such as portability, Bash is only configured to be used as the default Linux shell.
Comparing $() with ${} in Bash
In order to compare these two properties related to the Bash environment, we must reiterate $() to$(command) and ${}to ${parameter}. So we can try to define these two Bash entities.
Understanding $(command)
$(command)Involves command substitution in Bash. More specifically, the command part in$(command) is executed and its output is captured and printed on standard output. The syntax behind
牛逼啊!接私活必备的 N 个开源项目!赶快收藏
$(command) is token level. Consider executing the following command, which is designed to print out the current date on the terminal.
echo "今天是 $(date). LinuxMi.com 又是美好的一天。"
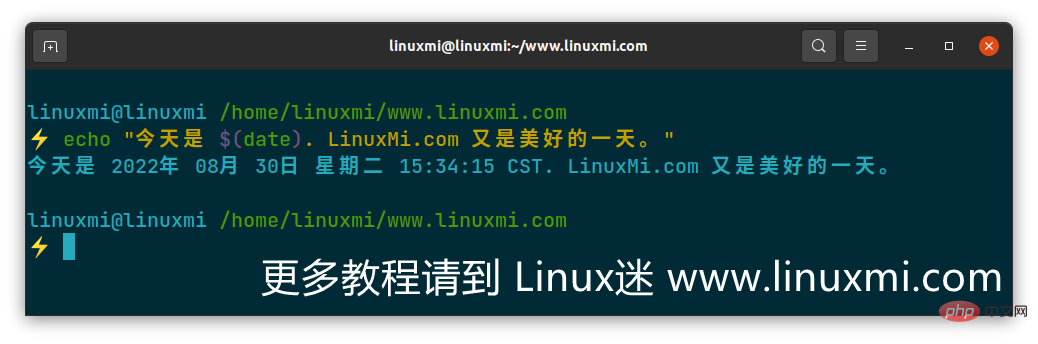
在 Linux 中打印日期
上述执行可以用以下方式解释。首先,执行 date 命令并将其输出作为参数包含在 echo 命令中。
在这里,我们可以假设命令替换在重新包含在主 shell 之前在单独的子 shell 中执行。
了解 ${parameter}
${parameter}在Bash中涉及参数替换。根据 Bash 手册页,参数是一个值存储实体。参数实体可以与名称、数字或特殊字符相关联。
大括号{}暗示我们在处理位置参数,或者在使用的参数(参数值)后面是一个与参数名称不相关的非解释性字符,例如${animal}s。
至于位置参数,可以用一个或多个数字来表示(单个数字 0 除外)。因此,如果我们有一个名为$variable_name的变量,则可以使用参数 替换${parameter}来检索关联的变量值。
考虑以下变量声明命令:
$ animal=lion
让我们调用 animal 变量以尝试将变量值复数:
$ echo $animals
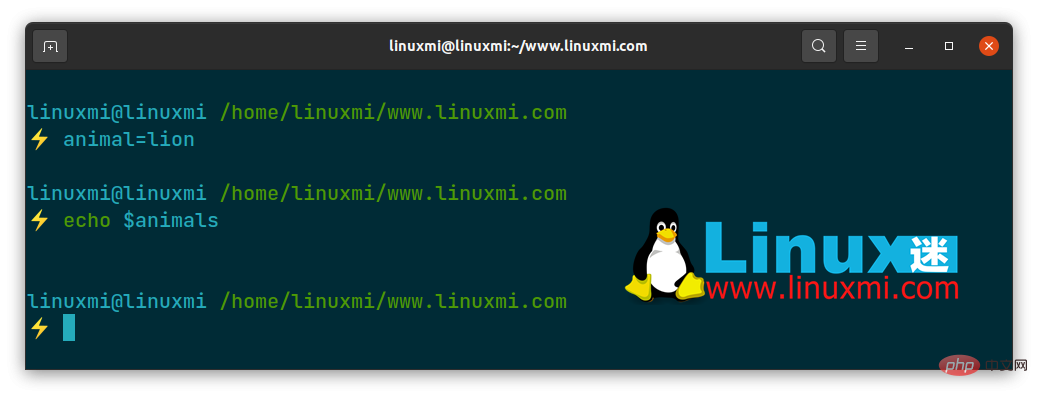
在命令中声明变量
在标准输出中不会打印任何内容,因为 Bash 不理解变量$animals。但是,我们可以通过如下方式使用参数替换方法成功调用我们的$animals变量:
$ echo ${animal}s
在命令中调用变量
在某些情况下,感叹号可能会在参数替换实现的第一个左大括号之后出现。在这种情况下,就会出现变量间接的概念。另外,搜索公众号Linux就该这样学后台回复“猴子”,获取一份惊喜礼包。
变量值优先于参数值,如下所示:
$ animal=lion
$ echo $animal
$ lion=rafiki
$ echo $lion
$ echo ${!animal}
参数值的优先级
希望本文能够说明 Bash 中$()和${}之间的区别。
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between ${} and $() in Bash. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Different ways to run shell script files on Windows
Apr 13, 2023 am 11:58 AM
Different ways to run shell script files on Windows
Apr 13, 2023 am 11:58 AM
Windows Subsystem for Linux The first option is to use Windows Subsystem for Linux or WSL, which is a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables natively on Windows systems. It works for most scenarios and allows you to run shell scripts in Windows 11/10. WSL is not automatically available, so you must enable it through your Windows device's developer settings. You can do this by going to Settings > Update & Security > For Developers. Switch to developer mode and confirm the prompt by selecting Yes. Next, look for W
 Ubuntu Bash performance comparison: Ubuntu vs. Win10 Anniversary Edition
Jan 04, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
Ubuntu Bash performance comparison: Ubuntu vs. Win10 Anniversary Edition
Jan 04, 2024 pm 09:36 PM
At the beginning of this year, when Microsoft and Canonical released Windows 10 Bash and Ubuntu user space, I tried to do some preliminary performance tests on Ubuntu on Windows 10 compared to native Ubuntu. This time I published more about the benchmark comparison between native pure Ubuntu and Windows 10. The Linux subsystem test for Windows completed all tests and was released with the Windows 10 Anniversary Update. The default Ubuntu user space is still Ubuntu14.04, but it can be upgraded to 16.04. So the test is first tested on 14.04, and after completion, the system will be upgraded to 16.04
 Five Little-Known Modern Bash Scripting Techniques
Jun 26, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
Five Little-Known Modern Bash Scripting Techniques
Jun 26, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
Programmers often use the Bash command language to create shell scripts to automate manual tasks. For example, they create Bash scripts for various configurations, file operations, generating build results, and various DevOps-related activities. Almost all Unix-like or Unix-based operating systems provide users with a pre-installed Bash interpreter, so we can use Bash to write more portable automation scripts. As we already know, Bash scripting refers to writing a series of commands using the syntax of the Bash command language, built-in Bash commands, and core operating system CLI programs such as GNU Core Tools. A standard and old-fashioned Bash script usually executes some commands and displays plain text on the terminal
 Bash program to find A raised to the power B?
Aug 30, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
Bash program to find A raised to the power B?
Aug 30, 2023 pm 09:01 PM
Here we will see how to get the number A raised to the power B using a bash script. The logic is simple. We have to use the "**" operator or the power operator to do this. Let us see the following program to understand this concept clearly. Example#!/bin/bash#GNUbashScripta=5b=6echo "$(($a**$b))" output 15625
 Example analysis of bash vulnerability recurrence
May 19, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Example analysis of bash vulnerability recurrence
May 19, 2023 am 11:13 AM
BourneAgainShell (BASH for short) is the most popular SHELL implementation on GNU/Linux. It was born in 1980. After decades of evolution, it has evolved from a simple terminal command line interpreter into a multi-functional interface deeply integrated with the GNU system. . Bash, a type of Unix shell. The first official version was released in 1989. It was originally planned to be used on the GNU operating system, but it can run on most Unix-like operating systems, including Linux and MacOSXv10.4, which use it as the default shell. It has also been ported to Cygwin and MinGW on Microsoft Windows, or can be used on MS-
 Today is the last day you can get Windows 11 Bug Bash stickers
May 13, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
Today is the last day you can get Windows 11 Bug Bash stickers
May 13, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
Last week Microsoft announced BugBash, a campaign designed to engage Windows insiders with tasks to (hopefully) improve Windows 11 development in the long and short term. Originally on March 16, there were around 26 missions available to complete, but that has now grown to a staggering 75. Here's the kicker, though: BugBash will end on March 22nd, along with the opportunity to earn BugBash-specific stickers that will appear in your Feedback Hub. To participate in the Windows11 BugBash, you need to grab the latest Windows 11 preview build from the Dev channel, which is build2
 Eight Shell commands to make you a Linux command line master in no time
Jun 17, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Eight Shell commands to make you a Linux command line master in no time
Jun 17, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Having a solid foundation in programming is obviously an essential quality for a good software engineer. Whether it's an interpreted language like Python or a compiled language like C++, it's crucial to master at least one programming language. However, this is only one aspect of becoming a truly well-rounded engineer. If you lose your way in the shell environment, those basic knowledge will be useless. Flexible use of commands in Bash will take you to areas that traditional programming languages cannot reach. Sometimes, you don't actually need to use a more powerful programming language. By using just the Shell, you can accomplish the tasks you need faster and easier, and without the need for additional dependencies. In this article, we will explore some very useful Bash commands
 Make web-safe colors using Bash
Jul 07, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
Make web-safe colors using Bash
Jul 07, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
When computer monitors have a limited color palette, web designers often use a set of web-safe colors to create websites. While modern websites displayed on newer devices can display more colors than the original web-safe palette, I sometimes like to refer to web-safe colors when creating web pages. This way I know my page will look good everywhere. You can find the Web Safe Palette online, but I wanted to have my own copy for easy reference. You can also create one using a for loop in Bash. Bashfor loop The syntax of a for loop in Bash is as follows: for variable in collection; do statement; done For example, suppose you want to print all numbers from 1 to 3. You can quickly use Bas



