CentOS 7 system optimization script

1. Introduction
As an operation and maintenance person, we often deploy operating systems for various purposes. However, in these tasks, we will find that many tasks are actually repetitive labor, and the content of the operations is similar. Based on this type of work, In this case, we can make the same operation into a script for unified execution, and different things can be entered manually as variables. Can’t the time saved be used to do more meaningful things?Recently, I found a relatively easy-to-use shell source code based on the recommendation of fans. I adapted it based on this and shared it with everyone.
2. Menu
Main menu:
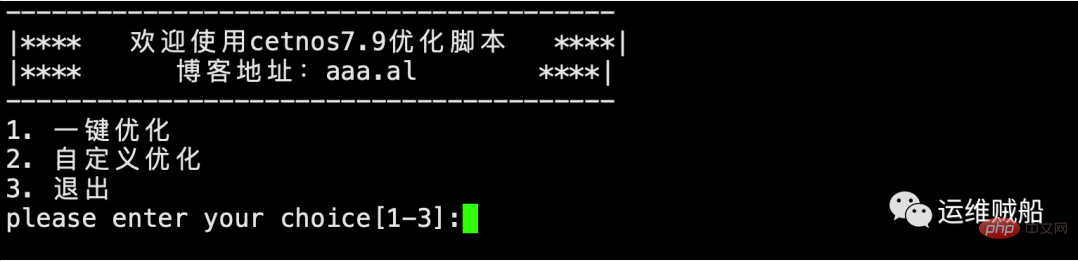
Secondary menu:
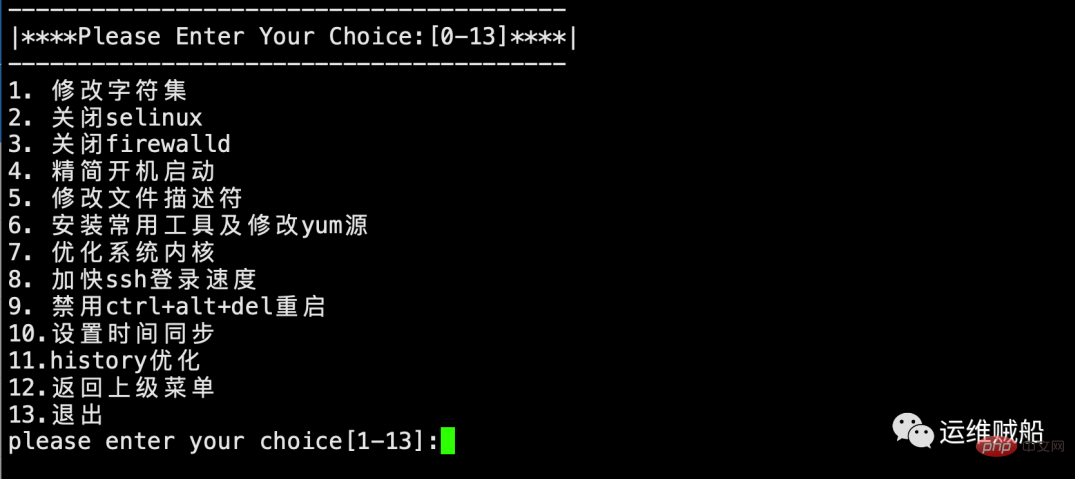
# Mainly realizes various optimizations of the system, such as commonly used functions such as modifying character sets, turning off selinux, turning off firewalls, installing commonly used tools, and accelerating SSH login. .
1 |
|
3. Source code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 |
|
Save it as init.sh, then grant execution permission and execute it.
1 |
|
If it is troublesome to copy and paste back and forth like this, you can also execute it through my one-click command, which can also achieve the above effect:
1 |
|
Finally, if you have any functions you want to implement, It can also be modified and implemented based on the original script.
The above is the detailed content of CentOS 7 system optimization script. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Steps to configure IP address in CentOS: View the current network configuration: ip addr Edit the network configuration file: sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 Change IP address: Edit IPADDR= Line changes the subnet mask and gateway (optional): Edit NETMASK= and GATEWAY= Lines Restart the network service: sudo systemctl restart network verification IP address: ip addr
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS Platform Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) Performance Optimization Guide Optimizing HDFS Performance is a multi-faceted issue, and multiple parameters need to be adjusted for specific situations. The following are some key optimization strategies: 1. Memory management adjusts the NameNode and DataNode memory configuration: reasonably configure the HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS and HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS environment variables according to the actual memory size of the server to optimize memory utilization. Enable large page memory: For high memory consumption applications (such as HDFS), enabling large page memory can reduce memory page allocation and management overhead and improve efficiency. 2. Disk I/O optimization uses high-speed storage
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro




