How to use Selenium for automated web testing
How to use Selenium for Web automated testing
Overview:
Web automated testing is a vital part of the modern software development process. Selenium is a powerful automated testing tool that can simulate user operations in a web browser and implement automated testing processes. This article will introduce how to use Selenium for web automation testing, and come with code examples to help readers get started quickly.
- Environment preparation
Before starting, you need to install the Selenium library and web browser driver. Selenium can be installed through the command line:
1 |
|
In addition, you also need to download the corresponding browser driver. The driver download addresses for different browsers are as follows:
- Chrome: https://sites.google.com/a/chromium.org/chromedriver/downloads
- Firefox: https: //github.com/mozilla/geckodriver/releases
- Edge:https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-edge/tools/webdriver/
- Safari:https ://webkit.org/blog/6900/webdriver-support-in-safari-10/
Choose the browser driver that suits you, download it and save it locally.
- Create a test script
The first step in using Selenium for automated web testing is to create a test script. First, we need to import the selenium library and set the path of the browser driver:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Next, we can access the web page and perform operations through the WebDriver instance. For example, get the page title:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
- Location element
During the test, we need to interact with elements on the Web page, such as clicking buttons, entering text, etc. Therefore, accurately locating elements is an important part of web automation testing. Selenium provides a variety of methods for locating elements, including ID, class name, tag name, link text, CSS selector, XPath, etc. Here are a few examples:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
- Perform operations
Once we locate the element that needs to be operated, we can perform the corresponding operation. For example, click a button, enter text, etc.:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
- Assertion and Verification
After passing the operation and input, we usually need to verify the results on the page. Selenium provides a variety of assertion and verification methods, such as determining whether an element exists, determining whether the element text matches, etc. Here are a few examples:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
- Close the browser
After the test execution is completed, it is best to close the browser to release resources. For example:
1 2 |
|
Summary:
This article introduces how to use Selenium for web automation testing, and comes with code examples. By learning these basic methods and techniques, readers can use Selenium to carry out automated testing in actual projects. I hope this article can be helpful to everyone.
The above is the detailed content of How to use Selenium for automated web testing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
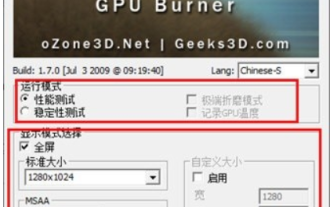 What do you think of furmark? - How is furmark considered qualified?
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:25 AM
What do you think of furmark? - How is furmark considered qualified?
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:25 AM
What do you think of furmark? 1. Set the "Run Mode" and "Display Mode" in the main interface, and also adjust the "Test Mode" and click the "Start" button. 2. After waiting for a while, you will see the test results, including various parameters of the graphics card. How is furmark qualified? 1. Use a furmark baking machine and check the results for about half an hour. It basically hovers around 85 degrees, with a peak value of 87 degrees and room temperature of 19 degrees. Large chassis, 5 chassis fan ports, two on the front, two on the top, and one on the rear, but only one fan is installed. All accessories are not overclocked. 2. Under normal circumstances, the normal temperature of the graphics card should be between "30-85℃". 3. Even in summer when the ambient temperature is too high, the normal temperature is "50-85℃
 Learn to install Selenium easily using PyCharm: PyCharm installation and configuration guide
Jan 04, 2024 pm 09:48 PM
Learn to install Selenium easily using PyCharm: PyCharm installation and configuration guide
Jan 04, 2024 pm 09:48 PM
PyCharm installation tutorial: Easily learn how to install Selenium, specific code examples are needed. As Python developers, we often need to use various third-party libraries and tools to complete project development. Among them, Selenium is a very commonly used library for automated testing and UI testing of web applications. As an integrated development environment (IDE) for Python development, PyCharm provides us with a convenient and fast way to develop Python code, so how
 Join a new Xianxia adventure! 'Zhu Xian 2' 'Wuwei Test' pre-download is now available
Apr 22, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
Join a new Xianxia adventure! 'Zhu Xian 2' 'Wuwei Test' pre-download is now available
Apr 22, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
The "Inaction Test" of the new fantasy fairy MMORPG "Zhu Xian 2" will be launched on April 23. What kind of new fairy adventure story will happen in Zhu Xian Continent thousands of years after the original work? The Six Realm Immortal World, a full-time immortal academy, a free immortal life, and all kinds of fun in the immortal world are waiting for the immortal friends to explore in person! The "Wuwei Test" pre-download is now open. Fairy friends can go to the official website to download. You cannot log in to the game server before the server is launched. The activation code can be used after the pre-download and installation is completed. "Zhu Xian 2" "Inaction Test" opening hours: April 23 10:00 - May 6 23:59 The new fairy adventure chapter of the orthodox sequel to Zhu Xian "Zhu Xian 2" is based on the "Zhu Xian" novel as a blueprint. Based on the world view of the original work, the game background is set
 Database testing skills in Golang
Aug 10, 2023 pm 02:51 PM
Database testing skills in Golang
Aug 10, 2023 pm 02:51 PM
Database testing skills in Golang Introduction: Database testing is a very important link when developing applications. Appropriate testing methods can help us discover potential problems and ensure the correctness of database operations. This article will introduce some common database testing techniques in Golang and provide corresponding code examples. 1. Testing using an in-memory database When writing database-related tests, we usually face a question: How to test without relying on an external database? Here we can use memory
 How to use MTR to conduct reliability testing of MySQL database?
Jul 13, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
How to use MTR to conduct reliability testing of MySQL database?
Jul 13, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
How to use MTR to conduct reliability testing of MySQL database? Overview: MTR (MySQL Test Runner) is a testing tool officially provided by MySQL, which can help developers conduct functional and performance testing of MySQL databases. During the development process, in order to ensure the reliability and stability of the database, we often need to conduct various tests, and MTR provides a simple, convenient and reliable method to conduct these tests. Steps: Install MySQL test runner: First, you need to download it from the MySQL official website
 What are the differences between function testing and coverage in different languages?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:30 AM
What are the differences between function testing and coverage in different languages?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:30 AM
Functional testing verifies function functionality through black-box and white-box testing, while code coverage measures the portion of code covered by test cases. Different languages (such as Python and Java) have different testing frameworks, coverage tools and features. Practical cases show how to use Python's Unittest and Coverage and Java's JUnit and JaCoCo for function testing and coverage evaluation.
 The new king of domestic FPS! 'Operation Delta' Battlefield Exceeds Expectations
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:37 AM
The new king of domestic FPS! 'Operation Delta' Battlefield Exceeds Expectations
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:37 AM
"Operation Delta" will launch a large-scale PC test called "Codename: ZERO" today (March 7). Last weekend, this game held an offline flash mob experience event in Shanghai, and 17173 was also fortunate to be invited to participate. This test is only more than four months away from the last time, which makes us curious, what new highlights and surprises will "Operation Delta" bring in such a short period of time? More than four months ago, I experienced "Operation Delta" in an offline tasting session and the first beta version. At that time, the game only opened the "Dangerous Action" mode. However, Operation Delta was already impressive for its time. In the context of major manufacturers flocking to the mobile game market, such an FPS that is comparable to international standards
 How to use Selenium for automated web testing
Aug 02, 2023 pm 07:43 PM
How to use Selenium for automated web testing
Aug 02, 2023 pm 07:43 PM
Overview of How to Use Selenium for Web Automation Testing: Web automation testing is a vital part of the modern software development process. Selenium is a powerful automated testing tool that can simulate user operations in a web browser and implement automated testing processes. This article will introduce how to use Selenium for web automation testing, and come with code examples to help readers get started quickly. Environment preparation Before starting, you need to install the Selenium library and web browser driver






