 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 12 Linux terminal commands that will blow your mind
12 Linux terminal commands that will blow your mind
12 Linux terminal commands that will blow your mind
The Linux command line provides a simpler, easier, and cross-version method to complete common tasks than the graphical interface. Today we share with you 12 Linux terminal commands that will shock you.
##CTRL U: Delete text from the cursor Until the beginning of the line.
CTRL K: Delete text from the cursor to the end of the line.
CTRL Y: Paste text.
CTRL E: Move the cursor to the end of the line.
CTRL A: Move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
ALT F: The cursor moves to the next word
ALT B: The cursor moves to the previous word A word
ALT Backspace: Deletes the previous word.
CTRL W: Cut Cut the character before the cursor to the previous space.
Shift Insert: Pastes text into the terminal.
In order to illustrate that the above command is helpful to us, let’s look at an example:
sudo apt-get intall vlc
In this command There is a typo and in order for the command to work, intall needs to be changed for installation.
Imagine that the cursor is at the end of the line. There are several ways to get back to the word "install" to make changes.
You can press ALT B twice, which will place the cursor at the following location (indicated by the ^ symbol):
sudo apt-get^install vlc
Then, press the cursor keys and insert s into install.
另一个有用的命令是Shift + Insert,尤其是在需要将文本从浏览器复制到终端的情况下。
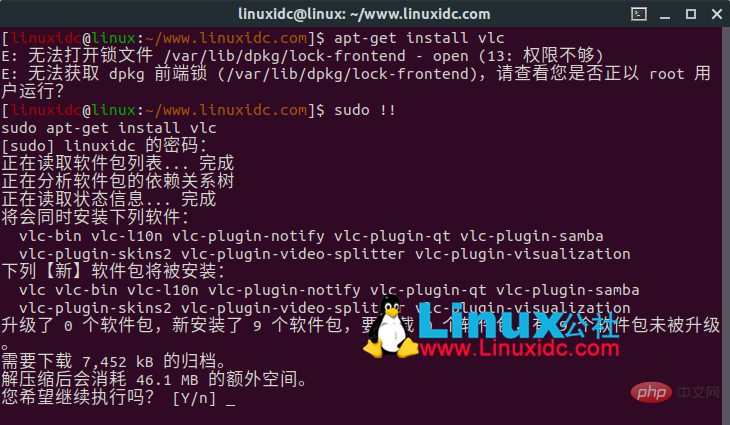
2、SUDO !!
每当您输入一个命令,并且出现权限不够的时候,您都会感谢有这个命令。
怎么使用sudo !!呢?假设您输入了以下命令:
apt-get install vlc
除非您以root权限登录,否则将出现权限不够提示。
sudo !!以sudo的形式运行前面的命令。因此,前面的命令现在变成:
sudo apt-get install vlc
如图:
3、暂停命令并在后台运行命令
要在后台运行终端命令,请按:
CTRL+Z:暂停应用程序
fg:返回到应用程序
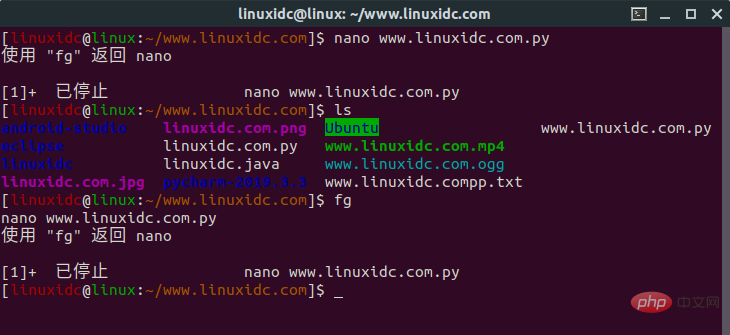
假设你在nano中打开了一个文件,如下所示:
sudo nano www.linuxidc.com.py
在文件中键入文本的过程中,您意识到希望在终端中键入另一个命令,但是您不能这样做,因为您在前台模式下打开了nano。
现在当您按下CTRL+Z时,前台应用程序将暂停,将返回到命令行。然后,您可以运行任何您喜欢的命令,完成后,再通过在终端窗口中输入fg并按回车键回到您之前暂停的会话。
如图:
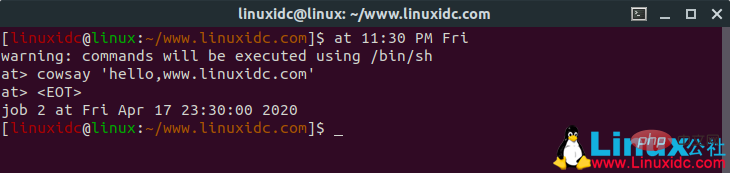
4. Run Linux commands at a specific time
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ at 11:30 PM Fri warning: commands will be executed using /bin/sh at> cowsay 'hello,www.linuxidc.com' at> CTRL+D
export PAGER=most
export MANWIDTH=80
man -H <command>
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ htop
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ ranger

[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ shutdown -c
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ pkill shutdown
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ XKill

[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ sl

[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ fortune
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ fortune | cowsay
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ fortune | xcowsay

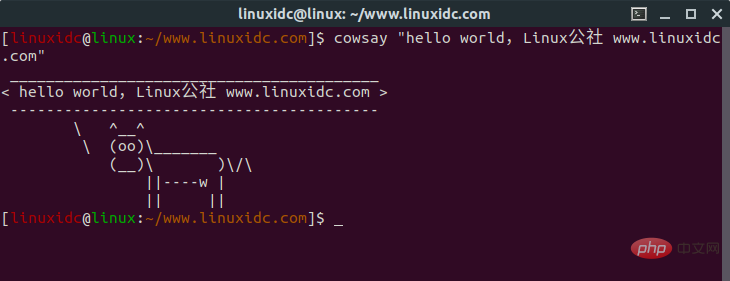
[linuxidc@linux:~/www.linuxidc.com]$ cowsay "hello world,Linux公社 www.linuxidc.com"
The above is the detailed content of 12 Linux terminal commands that will blow your mind. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
How to restart the apache server
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:12 PM
To restart the Apache server, follow these steps: Linux/macOS: Run sudo systemctl restart apache2. Windows: Run net stop Apache2.4 and then net start Apache2.4. Run netstat -a | findstr 80 to check the server status.
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud
 Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
The Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.
 How to fix apache vulnerability
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to fix apache vulnerability
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Steps to fix the Apache vulnerability include: 1. Determine the affected version; 2. Apply security updates; 3. Restart Apache; 4. Verify the fix; 5. Enable security features.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP



