Explore the dynamic convergence of AI and IoT
The integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things brings new dimensions of efficiency, automation, and intelligence to our daily lives. At the same time, artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way machines learn, reason, and make decisions. When combined, AI in IoT opens up a realm of possibilities, enabling intelligent, autonomous systems to analyze large amounts of data and act on its insights.
The Internet of Things refers to a network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, appliances and other objects embedded with sensors, software and network connections. These devices collect and exchange data, creating a vast ecosystem that connects the physical and digital worlds. Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning technologies, IoT devices can analyze and interpret data in real time, enabling them to make informed decisions and take autonomous actions. This combination enables IoT devices to adapt to changing environments, optimize their operations and provide users with personalized experiences.
The importance of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things cannot be overstated. It has the potential to unlock unprecedented opportunities in various sectors including healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, agriculture and smart cities. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence in IoT, we can create intelligent ecosystems where devices communicate seamlessly, collaborate, and make informed choices to improve our lives.
The intersection of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things forms a powerful combination, pushing the functionality of IoT devices to new heights. Let’s explore the fascinating intersection of these two technologies and learn how artificial intelligence can enhance the capabilities of the Internet of Things.
The relationship between artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things revolves around connecting physical objects and enabling them to collect and share data. Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, focuses on creating intelligent systems that can learn, reason, and make decisions. When AI and IoT converge, we witness the synergy of AI providing advanced analytics, automation, and intelligent decision-making to IoT devices.
By integrating artificial intelligence with the Internet of Things, devices are able to interpret and analyze large amounts of data collected from sensors and other sources. This enables it to extract valuable insights, identify patterns and make informed decisions in real time. AI algorithms can discover hidden correlations in IoT data, enabling predictive analytics and proactive actions.
How does artificial intelligence enhance the capabilities of IoT devices?
Artificial intelligence provides enhanced functions for IoT devices, making them smarter and more efficient. Here are some ways artificial intelligence can enhance IoT devices:
Advanced Data Analysis
Artificial intelligence algorithms can process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by the IoT. By leveraging technologies such as machine learning and deep learning, IoT devices can identify trends, anomalies, and patterns in data. This analysis provides valuable insights into optimizing processes, predicting maintenance needs, and detecting potential risks or failures.
INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION
Artificial intelligence enables IoT devices to intelligently automate tasks and processes. By learning historical data and user behavior, IoT devices can automate daily operations, adjust settings, and optimize energy consumption. For example, smart thermostats can learn an occupant's temperature preferences and adjust heating or cooling accordingly, allowing for energy savings and personalized comfort.
Real-time decision-making
With artificial intelligence, IoT devices can make decisions in real-time based on the data they collect and analyze. This allows it to respond quickly to changing conditions or events. For example, in smart grid systems, AI algorithms can analyze power usage patterns and adjust power distribution to ensure efficient use and prevent blackouts.
Practical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things
The integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things has stimulated numerous practical applications across industries. Here are some examples:
Smart Healthcare
IoT devices powered by artificial intelligence enable remote patient monitoring, personalized healthcare recommendations, and early detection of health issues. Wearable devices equipped with sensors and artificial intelligence algorithms can continuously monitor vital signs, detect abnormalities and alert healthcare providers in emergencies.
Autonomous Vehicles
The artificial intelligence-driven Internet of Things plays a vital role in the development of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles rely on artificial intelligence algorithms to interpret sensor data, make real-time decisions and navigate complex road conditions. The convergence of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things enables autonomous vehicles to optimize routes, avoid collisions and improve passenger safety.
INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION
Artificial intelligence in IoT is revolutionizing industrial processes by enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing supply chains and improving operational efficiency. IoT devices equipped with artificial intelligence algorithms can monitor machine performance, detect potential failures and schedule maintenance activities before failure occurs. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and reduces maintenance costs.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things
The integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things brings numerous benefits and revolutionizes the way we interact with technology and the world around us. Let’s delve into the benefits of integrating artificial intelligence into IoT systems.
Using artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things to improve data analysis and decision-making
One of the significant benefits of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things is its ability to analyze large amounts of data and extract meaningful insights. With the help of AI algorithms, IoT devices can process and interpret data in real-time, enabling accurate decision-making and actionable intelligence. Here are some of the key benefits:
Augmented Predictive Analytics
AI-powered IoT devices can predict future outcomes and behaviors based on historical data patterns. By leveraging machine learning and predictive modeling, IoT systems can predict maintenance needs, optimize resource allocation, and anticipate customer preferences. This proactive approach enables organizations to make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency and deliver a better customer experience.
Real-time monitoring and alerting
Artificial intelligence algorithms enable IoT devices to monitor key parameters in real-time and trigger alerts. For example, in a smart home security system, AI-powered cameras can detect unusual activity or intrusions and immediately notify the homeowner or security personnel. This real-time monitoring enhances security and enables rapid response to potential threats.
Contextual decision-making
Artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things enables devices to make situational decisions based on a deep understanding of the environment. For example, in smart city applications, AI-driven traffic management systems can analyze real-time traffic data, weather conditions and historical patterns to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. This increases traffic efficiency and reduces travel time for commuters.
Enhancing automation and efficiency through the integration of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence provides intelligent automation for IoT devices, optimizing processes and improving overall efficiency. Here’s how AI can enhance automation in IoT systems:
INTELLIGENT ENERGY MANAGEMENT
IoT devices powered by AI help optimize energy consumption by intelligently managing power usage. For example, smart thermostats can learn user preferences, automatically adjust temperature settings and optimize energy efficiency. By integrating artificial intelligence algorithms, IoT systems can dynamically adjust energy consumption patterns to minimize waste and reduce costs.
Autonomous Operation
AI-driven IoT devices can operate autonomously, reducing the need for manual intervention. For example, in industrial settings, AI robots can perform complex tasks, adapt to changing conditions, and work seamlessly with humans. This automation increases productivity, reduces human error, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Simplify Processes
Artificial Intelligence in IoT streamlines business processes by automating daily tasks and optimizing workflows. For example, an AI-powered inventory management system can analyze demand patterns, predict inventory needs and automatically place orders for replenishment. This reduces inventory holding costs, ensures products are available on time, and improves supply chain efficiency.
Predictive maintenance and fault detection through IoT artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence enhances the predictive maintenance and fault detection capabilities of IoT devices, thereby saving costs and improving reliability. Benefits include:
Proactive Maintenance
Artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze data from IoT sensors to identify potential equipment failures before they occur. By detecting early warning signs such as abnormal vibration or temperature changes, IoT systems can proactively schedule maintenance activities. This approach to predictive maintenance minimizes downtime, extends equipment life and reduces maintenance costs.
Anomaly Detection
AI-powered IoT devices are good at detecting anomalies in data streams. By establishing baseline patterns, AI algorithms can identify deviations that indicate potential failures or anomalies. This early anomaly detection enables timely intervention, preventing costly failures and ensuring continuous operations.
Condition Monitoring
Artificial intelligence-driven IoT systems can monitor the condition of assets and equipment in real time. By collecting and analyzing data from various sensors, IoT devices can assess the health and performance of machinery. For example, in manufacturing environments, AI-driven IoT sensors can monitor factors such as temperature, vibration, and energy consumption to detect signs of equipment degradation or imminent failure. This real-time condition monitoring enables timely maintenance and minimizes unplanned downtime.
Personalization and intelligent user experience enabled by artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things
Artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things enables personalized and intuitive user experiences, enhancing the way we interact with connected devices. Benefits include:
Customized Recommendations
Artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze user behavior, preferences and historical data to provide personalized recommendations and customized experiences. For example, an AI-driven IoT platform can recommend personalized content, products or services based on personal preferences, resulting in a more engaging and satisfying user experience.
Voice and Gesture Recognition
AI-powered IoT devices can understand and respond to natural language commands and gestures. Voice assistants, such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, use artificial intelligence algorithms to interpret speech and perform tasks such as playing music, setting reminders, or controlling smart home devices. Gesture recognition technology powered by artificial intelligence allows users to interact with IoT devices through intuitive gestures, enhancing user convenience and accessibility.
Contextual Adaptation
Artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things enables devices to adapt their behavior based on the environment and user preferences. For example, smart lighting systems equipped with artificial intelligence algorithms can automatically adjust lighting levels and color temperature based on time of day, occupancy or user preference. This contextual adaptation creates a comfortable and personalized environment for users.
Integrating artificial intelligence into the IoT brings numerous benefits, including improved data analysis, enhanced automation, predictive maintenance and personalized user experiences. These benefits have a transformative impact across industries and sectors. Below, we explore the challenges and limitations associated with AI in IoT, as well as the key technologies and techniques driving this convergence.
Challenges and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things
While the integration of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things provides many benefits, it also brings certain challenges and limitations. Understanding and addressing these issues is important to ensure the successful deployment and utilization of AI in IoT systems. Let’s explore some of the key challenges:
Security and Privacy Issues in AI-Powered IoT Systems
Increased connectivity and data exchange in AI-driven IoT devices raises concerns about security and privacy issues. Here are the main challenges:
Data Privacy
Artificial intelligence algorithms need access to large amounts of data in order to learn and make informed decisions. However, ensuring the privacy and protection of sensitive user data becomes critical. Organizations must implement strong data encryption, secure data transfer protocols, and strict access control mechanisms to protect user information and prevent unauthorized access.
CYBERSECURITY RISKS
The interconnected nature of IoT devices expands the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. AI-enabled IoT systems can be targets of malicious activities, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, or manipulation of critical operations. Implementing strong security measures, including intrusion detection systems, encryption and regular security updates, is critical to mitigating these risks.
Ethical Considerations
Artificial intelligence algorithms in IoT devices make decisions based on data analysis and learning. However, ensuring the ethical use of AI is critical to preventing bias, discrimination or unethical decision-making. Organizations must adhere to ethical principles, principles of fairness, and transparent AI practices to avoid unintended consequences and maintain trust among users.
Data management and scalability issues in IoT artificial intelligence applications
The massive data generated by IoT devices brings challenges to data management and scalability. Consider the following challenges:
Data Storage and Processing
Artificial intelligence algorithms require massive amounts of computing power and storage capacity to process and analyze the data generated by the IoT. As the number of connected devices increases, managing the sheer volume of data becomes a daunting task. Organizations must invest in scalable infrastructure and efficient data storage solutions to handle the growing flow of data.
Bandwidth and Network Limitations
Transmitting large amounts of IoT data to the cloud for AI processing can strain network bandwidth and cause latency issues. This becomes especially challenging in scenarios that require real-time decision-making. Edge computing is performing artificial intelligence calculations closer to the data source, helping to alleviate bandwidth constraints and reduce latency.
Integration with legacy systems
Integrating AI capabilities into existing IoT systems or legacy infrastructure can be complex. Traditional systems may lack the compatibility or processing power needed to handle artificial intelligence algorithms effectively. Organizations must carefully plan and execute integration strategies to ensure seamless interoperability between AI-driven IoT systems and legacy infrastructure.
Ethical Considerations and Human-Computer Interaction in IoT Artificial Intelligence
Advances in artificial intelligence technology have given rise to ethical considerations and highlighted the importance of human-computer interaction. Consider the following challenges:
Transparency and Explainability
AI algorithms can be complex and difficult to explain. Ensuring transparency and explainability of AI-driven decisions in IoT systems is critical for user trust and accountability. Organizations must strive to develop AI models that provide clear explanations for their decisions, especially in critical scenarios such as healthcare or autonomous vehicles.
human-machine collaboration
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into IoT systems, striking the right balance between human control and artificial intelligence autonomy becomes critical. Organizations must design interfaces and interactions to facilitate effective collaboration between humans and AI-driven IoT devices. This involves understanding the user's needs, preferences and the ability to override or intervene when necessary.
Job Shifting and Workforce Adaptation
The integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things may raise concerns about job losses and changes in the workforce landscape. While AI can automate routine tasks, it can also create new opportunities and augment human capabilities. However, organizations must proactively address the potential impact on the workforce. This involves retraining and upskilling employees for new roles that leverage the AI capabilities of IoT, facilitating a harmonious transition between human workers and AI-driven systems.
Addressing these challenges and limitations requires a holistic approach that includes strong security measures, scalable infrastructure, ethical considerations and effective human-machine interaction. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things and ensure its responsible and beneficial integration into our lives.
Next, we will explore the key technologies and techniques that promote the integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. Understanding these advances will provide insights into the foundations of artificial intelligence in IoT systems and its transformative potential.
Key Technologies and Skills of Internet of Things Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence plays a vital role in realizing the functions of the Internet of Things. Let’s explore the key technologies and techniques that will drive the convergence of AI and IoT, empowering intelligent and autonomous systems.
Machine Learning Algorithms Using Artificial Intelligence to Analyze IoT Data
Machine learning forms the basis of artificial intelligence for IoT, enabling devices to learn patterns, make predictions, and adapt to changing environments.
Here are some important machine learning techniques used in IoT:
Supervised learning
Supervised learning involves training a machine learning model using a labeled dataset. In IoT applications, this technology can be used for tasks such as anomaly detection, predictive maintenance, or classification based on sensor data. Supervised learning algorithms, such as decision trees, support vector machines, or neural networks, enable IoT devices to learn from historical data and make accurate predictions.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning involves training a machine learning model using unlabeled data sets. In the Internet of Things, unsupervised learning algorithms are valuable for tasks such as clustering similar devices, identifying patterns in data, or detecting anomalies without prior knowledge of expected outcomes. Techniques such as k-means clustering or hierarchical clustering are often used to reveal hidden structures and relationships in IoT data.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning enables IoT devices to learn through interaction with the environment. In this approach, the device receives feedback in the form of rewards or punishments depending on its behavior. Over time, through trial and error, the device learns to make decisions that maximize returns. Reinforcement learning is particularly useful in autonomous IoT systems, such as robotics or smart grid optimization.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence-Driven IoT Applications
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on training multi-layer neural networks to learn complex patterns and representations . Deep learning combined with the Internet of Things unlocks a variety of possibilities. Here are the key aspects:
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
CNN is good at processing and analyzing image and video data. In IoT applications, CNNs can be used for tasks such as object recognition, facial recognition, or video surveillance. These networks learn hierarchical representations of visual data, enabling IoT devices to extract valuable information from images or videos captured by sensors or cameras.
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
RNN is suitable for processing sequential data, such as time series sensor data. In IoT, RNNs can be used for tasks such as predicting future sensor readings, detecting anomalies in time series data, or natural language processing for IoT devices. By capturing dependencies and temporal relationships in data, RNN enables IoT devices to understand sequential information and make predictions.
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
GAN consists of two neural networks: a generator network and a discriminator network. GANs can be used in IoT to generate synthetic data or augment existing data sets. For example, GANs can create real sensor data to expand training datasets or simulate various scenarios for testing IoT systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) provides artificial intelligence support for IoT devices
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables IoT devices to understand and process human language, enabling seamless interaction and communication . Here are the key NLP technologies used in AI-driven IoT applications:
Speech Recognition
NLP-based speech recognition enables IoT devices to convert spoken words into text. This technology allows users to interact with IoT devices using voice commands, facilitating hands-free and intuitive control of connected systems.
Natural Language Understanding
NLP technology enables IoT devices to understand and interpret the meaning behind human language. By extracting relevant information, entities, and intent from textual data, IoT devices can more accurately understand user queries, commands, or requests. Natural language understanding (NLU) technologies, such as named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, or language parsing, enable IoT devices to extract valuable insights from text data.
Language Generation
Language generation technology allows IoT devices to generate human-like responses or output. This feature enables devices to provide informative contextual responses to user queries or engage in natural conversations. By leveraging technologies such as text generation models or language models, IoT devices can enhance user experience and create more engaging interactions.
Edge Computing and Artificial Intelligence at the Edge of IoT
Edge computing brings AI capabilities closer to the data source, reducing latency, improving responsiveness and enhancing privacy. The following are the key aspects of edge AI:
Local Data Processing
By performing AI calculations locally on IoT devices or edge computing nodes, data processing and analysis can be performed in real time without the need for serious Rely on cloud infrastructure. This reduces the need for continuous data transfer, lowers latency, and enables faster decision-making in time-sensitive applications.
Privacy and Security
Edge computing allows sensitive data to remain local, minimizing the risks associated with transferring data to the cloud. Artificial intelligence algorithms deployed at the edge can process and analyze data on-site, reducing privacy concerns and enhancing data security. This is especially important in scenarios where data confidentiality is critical.
Bandwidth Optimization
Edge AI helps alleviate bandwidth constraints by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred to the cloud. By performing local data processing and transmitting only relevant insights or summaries, edge computing can optimize network bandwidth usage and reduce associated costs.
The fusion of these technologies and processes promotes the integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, enabling intelligent decision-making, real-time insights, and seamless human-computer interaction.
Future Trends in Artificial Intelligence for the Internet of Things
The convergence of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things continues to evolve, paving the way for exciting future trends and opportunities. Let’s explore some of the key areas that hold huge potential in the field of AI for IoT.
Edge Artificial Intelligence and Decentralized IoT Architecture
Edge Artificial Intelligence brings artificial intelligence capabilities to the edge of the network and is expected to play a vital role in the future of the Internet of Things. By processing data locally on edge devices, AI algorithms can provide real-time insights and intelligent decisions without relying heavily on cloud infrastructure. This enables faster response times, reduced latency, and enhanced privacy. Decentralized IoT architecture powered by edge AI will promote greater autonomy and intelligence at the edge of the network, enabling more efficient and smarter IoT systems.
Integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain in IoT systems
The integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology brings huge potential to IoT applications. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature can solve key challenges in IoT such as data security, privacy and trust. The combination of artificial intelligence and blockchain can achieve secure and trustworthy data exchange, promote autonomous decision-making in distributed IoT networks, and ensure data integrity and transparency. This convergence opens up new avenues for decentralized AI-driven IoT systems, especially in areas such as supply chain management, smart contracts, and secure data sharing.
AI-driven autonomous IoT systems
The future of artificial intelligence in IoT lies in developing autonomous systems that can make intelligent decisions and operate independently. AI-powered autonomous IoT systems can leverage advanced machine learning algorithms, reinforcement learning techniques, and sensor fusion to sense their environment, learn from interactions, and make informed decisions in real time. This paves the way for self-optimizing and adaptive IoT networks, where devices can dynamically adjust their behavior, optimize resource allocation, and collaborate intelligently without human intervention. Autonomous IoT systems have transformative potential in areas such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
The potential impact of 5G on the artificial intelligence-driven Internet of Things
The emergence of 5G technology will completely change the landscape of artificial intelligence-driven Internet of Things systems. With ultra-low latency, high-speed connections and massive device capacity, 5G networks will bring new opportunities for artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency will enable real-time data processing, facilitate seamless communication between devices, and support the proliferation of artificial intelligence-driven applications. This will drive advances in areas such as augmented reality, smart infrastructure, telemedicine and connected autonomous vehicles, changing the way we interact with IoT devices and opening the door to new use cases.
The future of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things is promising. By leveraging edge AI, integrating blockchain, developing autonomous systems, and leveraging the power of 5G, we can unlock new frontiers of intelligence, connectivity, and innovation. As we embrace these future trends, it is critical to continue to address the challenges of ensuring ethical AI practices and maintaining a focus on human-centered design to realize the full potential of AI in the IoT.
Summary
Artificial intelligence has become a powerful force changing the landscape of the Internet of Things. By integrating AI capabilities into IoT systems, we unlock endless possibilities, enabling devices to analyze data, make intelligent decisions, and deliver personalized experiences.
Artificial intelligence can improve data analysis and decision-making, enhance automation and efficiency, predictive maintenance, and personalized user experience. It has the potential to revolutionize various industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to transportation and smart cities. However, like any transformative technology, AI in IoT comes with challenges and limitations. Security and privacy concerns, data management, scalability issues, and ethical considerations must be carefully addressed. By implementing strong security measures, scalable infrastructure, and transparent AI practices, we can ensure the responsible and beneficial integration of AI in IoT systems.
Looking to the future, the future of artificial intelligence in the Internet of Things is promising. Edge artificial intelligence and decentralized IoT architecture will drive greater autonomy and intelligence at the network edge. The convergence of artificial intelligence and blockchain will enhance data security, trust and decentralized decision-making. The emergence of AI-driven autonomous IoT systems and 5G networks will pave the way for self-optimizing, real-time smart IoT networks, enabling breakthrough applications and use cases.
As we move into this future, it is critical to continue advancing AI technology, fostering collaboration among industry stakeholders, and fostering ethical AI practices. By doing so, we can harness the full potential of AI in the Internet of Things to transform our lives, industries and the world as we know it.
The above is the detailed content of Explore the dynamic convergence of AI and IoT. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
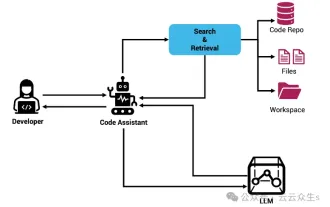 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year




