 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Summary:
Go language is a fast and efficient programming language suitable for building high-performance network applications. However, when we develop a website in Go language, we may encounter some access speed bottlenecks. This article will introduce several local optimization techniques to solve such problems, with code examples.
- Using connection pool
In the Go language, each request to the database or third-party service requires a new connection. In order to reduce the overhead caused by connection creation and destruction, we can use a connection pool to manage connection reuse. The following is a sample code implemented using the built-in connection pool in the Go language:
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"fmt"
"log"
"sync"
_ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql"
)
var (
dbConnPool *sync.Pool
)
func initDBConnPool() {
dbConnPool = &sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
db, err := sql.Open("mysql", "username:password@tcp(localhost:3306)/dbname")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return db
},
}
}
func getDBConn() *sql.DB {
conn := dbConnPool.Get().(*sql.DB)
return conn
}
func releaseDBConn(conn *sql.DB) {
dbConnPool.Put(conn)
}
func main() {
initDBConnPool()
dbConn := getDBConn()
defer releaseDBConn(dbConn)
// 使用数据库连接进行数据操作
}By using the connection pool, we can reduce the number of connection creation and destruction times and increase the speed of database access.
- Using caching
In website development in Go language, it is often necessary to read some data that does not change frequently, such as configuration files, static files, etc. To reduce the number of disk reads, we can cache this data in memory. The following is a sample code implemented using the built-in cache library of the Go language:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/patrickmn/go-cache"
)
var (
dataCache *cache.Cache
)
func initCache() {
dataCache = cache.New(5*time.Minute, 10*time.Minute)
}
func getDataFromCache(key string) ([]byte, error) {
if data, found := dataCache.Get(key); found {
return data.([]byte), nil
}
// 从磁盘或数据库中读取数据
data, err := getDataFromDiskOrDB(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
dataCache.Set(key, data, cache.DefaultExpiration)
return data, nil
}
func getDataFromDiskOrDB(key string) ([]byte, error) {
// 从磁盘或数据库中读取数据的实现
}
func main() {
initCache()
data, err := getDataFromCache("example")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(string(data))
}By using cache, we can reduce the number of reads from the disk or database and increase the speed of data reading.
- Using concurrency
The Go language inherently supports concurrency. By using goroutine and channels, we can implement concurrent execution of tasks and improve the processing capabilities of the program. The following is a sample code that uses concurrent processing of requests:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"sync"
)
func fetchURL(url string, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer wg.Done()
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error fetching URL %s: %s
", url, err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 处理响应
}
func main() {
urls := []string{
"https://example.com",
"https://google.com",
"https://facebook.com",
}
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(len(urls))
for _, url := range urls {
go fetchURL(url, &wg)
}
wg.Wait()
}By using concurrent processing of requests, we can execute multiple requests at the same time, improving the processing capacity of the program and the response speed of the service.
Summary:
By using local optimization techniques such as connection pooling, caching and concurrency, we can better solve the bottleneck problem of Go language website access speed. These tips can be applied to other web application development as well. Through reasonable optimization, we can improve the access speed of the website and enhance the user experience.
The above is the detailed content of Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 PHP8.1 released: Introducing curl for concurrent processing of multiple requests
Jul 08, 2023 pm 09:13 PM
PHP8.1 released: Introducing curl for concurrent processing of multiple requests
Jul 08, 2023 pm 09:13 PM
PHP8.1 released: Introducing curl for concurrent processing of multiple requests. Recently, PHP officially released the latest version of PHP8.1, which introduced an important feature: curl for concurrent processing of multiple requests. This new feature provides developers with a more efficient and flexible way to handle multiple HTTP requests, greatly improving performance and user experience. In previous versions, handling multiple requests often required creating multiple curl resources and using loops to send and receive data respectively. Although this method can achieve the purpose
 Solve the problem of slow download speed of edge browser
Dec 21, 2023 pm 10:22 PM
Solve the problem of slow download speed of edge browser
Dec 21, 2023 pm 10:22 PM
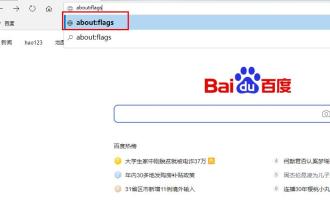
Many friends need a browser to download, but many friends who use edge report that the download speed is too slow, so how to improve the download speed? Let’s take a look at how to improve it. The download speed of the edge browser is slow: 1. Open the edge browser and enter the URL "about:flags". 2. After completion, enter "Developer Settings". 3. Pull down and check "Allow background tabs to be in low power mode" and "Allow limits on the rendering pipeline to improve battery life. This flag is locked to false by forcevsyncpaintbeat." 4. Continue to scroll down to "Network" and set "Enable TCP Quick Open" to "Always Enable".
 Solve the problem of limited download speed in win11
Dec 31, 2023 pm 08:17 PM
Solve the problem of limited download speed in win11
Dec 31, 2023 pm 08:17 PM
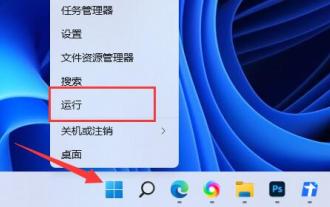
Some friends always feel that the Internet speed is very slow, and they find that their win11 download speed is limited. They don't know how to solve it. In fact, we only need to modify the Internet speed limit policy in the Group Policy Editor. The download speed of win11 is limited: The first step is to right-click the start menu and open "Run". The second step is to enter "gpedit.msc" and click "OK" to open the group policy. Step 3: Expand "Administrative Templates" under "Computer Configuration" Step 4: Click "Network" on the left, double-click "QoS Packet Scheduler" on the right Step 5: Check "Enabled" and set the bandwidth limit below Change it to "0" and finally click "OK" to save. In addition to the system speed limit, in fact some download software also has speed limit, so it is not necessarily the system speed limit.
 Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Aug 07, 2023 am 10:07 AM
Local optimization techniques to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed
Aug 07, 2023 am 10:07 AM
Local optimization tips to solve the bottleneck of Go language website access speed Summary: Go language is a fast and efficient programming language suitable for building high-performance network applications. However, when we develop a website in Go language, we may encounter some access speed bottlenecks. This article will introduce several local optimization techniques to solve such problems, with code examples. Using connection pooling In the Go language, each request to the database or third-party service requires a new connection. In order to reduce the overhead caused by connection creation and destruction, we can
 How to deal with distributed caching and caching strategies in C# development
Oct 08, 2023 pm 11:36 PM
How to deal with distributed caching and caching strategies in C# development
Oct 08, 2023 pm 11:36 PM
How to deal with distributed caching and caching strategies in C# development Introduction: In today's highly interconnected information age, application performance and response speed are crucial to user experience. Caching is one of the important ways to improve application performance. In distributed systems, dealing with caching and developing caching strategies becomes even more important because the complexity of distributed systems often creates additional challenges. This article will explore how to deal with distributed caching and caching strategies in C# development, and demonstrate the implementation through specific code examples. 1. Introduction using distributed cache
 How does the golang framework handle concurrency and asynchronous programming?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:49 PM
How does the golang framework handle concurrency and asynchronous programming?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:49 PM
The Go framework uses Go's concurrency and asynchronous features to provide a mechanism for efficiently handling concurrent and asynchronous tasks: 1. Concurrency is achieved through Goroutine, allowing multiple tasks to be executed at the same time; 2. Asynchronous programming is implemented through channels, which can be executed without blocking the main thread. Task; 3. Suitable for practical scenarios, such as concurrent processing of HTTP requests, asynchronous acquisition of database data, etc.
 Caching Strategies in Laravel: Improving Application Performance and Scalability
Aug 12, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Caching Strategies in Laravel: Improving Application Performance and Scalability
Aug 12, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Caching Strategies in Laravel: Improving Application Performance and Scalability Introduction Performance and scalability are crucial factors when developing web applications. As applications grow in size, so does the amount of data and computation, which can lead to slower application response times and impact the user experience. To improve application performance and scalability, we can use caching strategies to speed up data access and processing. What is cache? Caching is a technology that stores calculation results or data in memory. when data
 Coroutines implement PHP multi-thread programming and efficient concurrent processing
Jun 30, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
Coroutines implement PHP multi-thread programming and efficient concurrent processing
Jun 30, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
PHP multi-threaded programming practice: using coroutines to implement concurrent task processing. With the development of Internet applications, the requirements for server performance and concurrent processing capabilities are becoming higher and higher. Traditional multi-threaded programming is not easy to implement in PHP, so in order to improve PHP's concurrent processing capabilities, you can try to use coroutines to implement multi-threaded programming. Coroutine is a lightweight concurrency processing model that can implement concurrent execution of multiple tasks in a single thread. Compared with traditional multi-threading, coroutine switching costs are lower



