 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Still annoyed by Matplotlib's cumbersome layer settings! ? Come and take a look at this Python drawing toolkit
Still annoyed by Matplotlib's cumbersome layer settings! ? Come and take a look at this Python drawing toolkit
Still annoyed by Matplotlib's cumbersome layer settings! ? Come and take a look at this Python drawing toolkit
- ProPlot library introduction
- ProPlot example demonstration
ProPlot library introduction
When using Python-matplotlib to draw charts, the default color and format themes can only help us become familiar with the drawing functions. If you want to design excellent visualization works (whether it is publication level or slightly artistic), you need to be familiar with a large number of drawing functions, such ascolors, scales, spines, fonts, etc. When it comes to drawingMultiple subplots, these operations will consume a lot of our energy, will inevitably lead to lengthy code writing, and are also error-prone. For details, you can check out my previous article Python-matplotlib Academic Scatter Chart EE Statistics and Drawing and Python-matplotlib horizontally stacked column chart drawing. In addition, if you need to use matplotlib for drawing every day and often need to beautify the charts, then the Proplot drawing package is perfect for you, and don’t worry about not getting used to it. People have highly praised matplotlib. Encapsulation, greatly simplifying the drawing function. Below we will briefly introduce its installation and main usage methods. If you want to know more about it, you can go to the official website.
Installation
We can install directly using pip or conda That’s it,
#for pip pip install proplot #for conda conda install -c conda-forge proplot
Of course, due to the continuous update of the version, you can also use the following code for update processing:
#for pip pip install --upgrade proplot #for conda conda upgrade proplot
format() simplified code
Proplot drawing charts does not require setting each drawing property like matplotlib does. The format() function provided provides the format of changing all settings at once. ization method. Let’s first give a simple example, as follows:
Use matplotlib to draw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
import matplotlib as mpl
with mpl.rc_context(rc={'axes.linewidth': 1, 'axes.color': 'gray'}):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharey=True)
axs[0].set_ylabel('bar', color='gray')
for ax in axs:
ax.set_xlim(0, 100)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mticker.MultipleLocator(10))
ax.tick_params(width=1, color='gray', labelcolor='gray')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', which='minor', bottom=True)
ax.set_xlabel('foo', color='gray')ProPlot drawing
import proplot as plot fig, axs = plot.subplots(ncols=2) axs.format(linewidth=1, color='gray') axs.format(xlim=(0, 100), xticks=10, xtickminor=True, xlabel='foo', ylabel='bar')
You can see the simplicity of Proplot from this simple example.
A-b-c Add multiple sub-picture serial numbers
In addition to the aboveformat() greatly reduce the code In terms of quantity, we have introduced a drawing method that I think is more convenient -The serial number of multiple subgraphs is automatically added. Specific examples are as follows:
# 样本数据
import numpy as np
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
data = 2 * (state.rand(100, 5) - 0.5).cumsum(axis=0)
import proplot as plot
fig, axs = plot.subplots(ncols=2)
axs[0].plot(data, lw=2)
axs[0].format(xticks=20, xtickminor=False)
axs.format(abc=True,abcstyle='(A)',abcsize=12,abcloc='ul',
suptitle='Abc label test', title='Title',
xlabel='x axis', ylabel='y axis'
)
plt.savefig(r'E:\Data_resourses\DataCharm 公众号\Python\学术图表绘制\ProPlot\abc_01.png',
dpi=900)The effect is as follows: 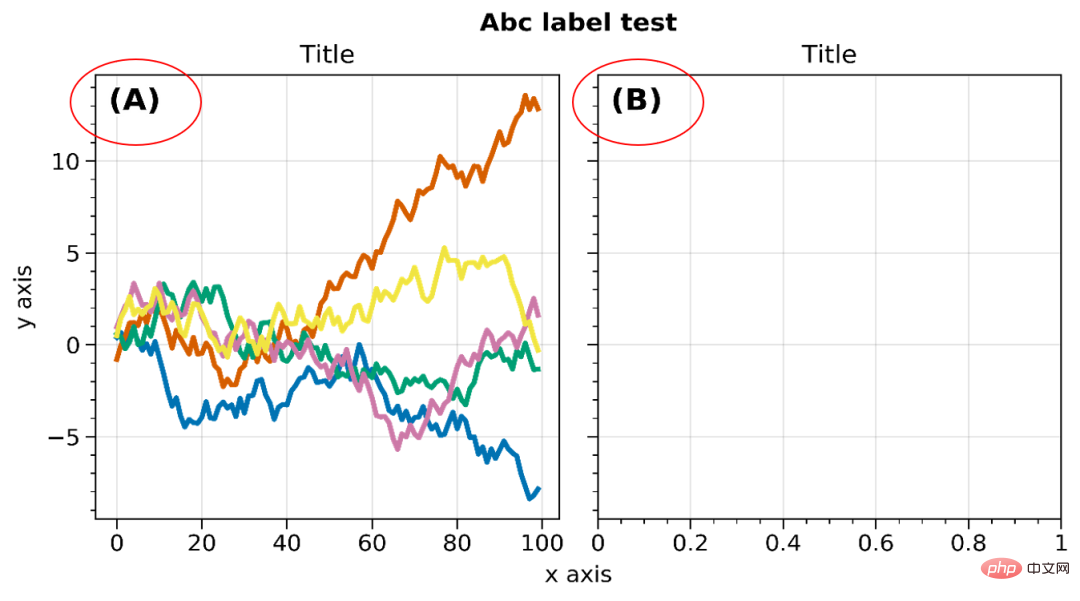
You can also perform style (abcstyle), position (abcloc), size ( abcsize) and other settings. For other detailed settings, please refer to the official website.
Colorbars and legends
- ##axis Colorbars and Legend
import proplot as plot
import numpy as np
fig, axs = plot.subplots(nrows=2, share=0, axwidth='55mm', panelpad='1em')
axs.format(suptitle='Stacked colorbars demo')
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
N = 10
# Repeat for both axes
for j, ax in enumerate(axs):
ax.format(
xlabel='data', xlocator=np.linspace(0, 0.8, 5),
title=f'Subplot #{j+1}'
)
for i, (x0, y0, x1, y1, cmap, scale) in enumerate((
(0, 0.5, 1, 1, 'grays', 0.5),
(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5, 'reds', 1),
(0.5, 0, 1, 0.5, 'blues', 2)
)):
if j == 1 and i == 0:
continue
data = state.rand(N, N) * scale
x, y = np.linspace(x0, x1, N + 1), np.linspace(y0, y1, N + 1)
m = ax.pcolormesh(
x, y, data, cmap=cmap,
levels=np.linspace(0, scale, 11)
)
ax.colorbar(m, loc='l', label=f'dataset #{i+1}')
plt.savefig(r'E:\Data_resourses\DataCharm 公众号\Python\学术图表绘制\ProPlot\colorbar_legend_02.png',
dpi=900)The effect is as follows: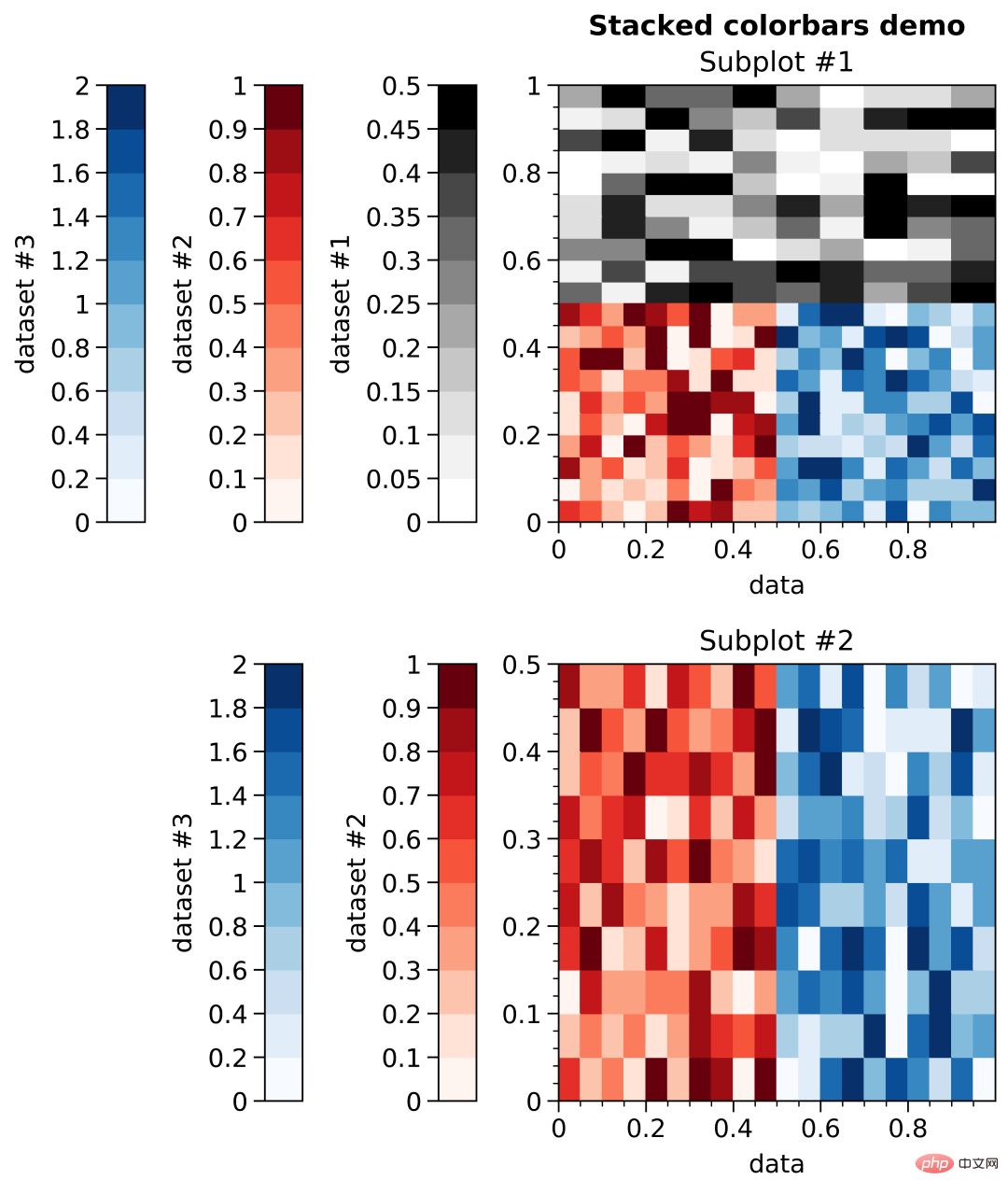
Figure 颜色条和图例
import proplot as plot
import numpy as np
fig, axs = plot.subplots(ncols=3, nrows=3, axwidth=1.4)
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
m = axs.pcolormesh(
state.rand(20, 20), cmap='grays',
levels=np.linspace(0, 1, 11), extend='both'
)[0]
axs.format(
suptitle='Figure colorbars and legends demo', abc=True,
abcloc='l', abcstyle='(a)', xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel'
)
fig.colorbar(m, label='column 1', ticks=0.5, loc='b', col=1)
fig.colorbar(m, label='columns 2-3', ticks=0.2, loc='b', cols=(2, 3))
fig.colorbar(m, label='stacked colorbar', ticks=0.1, loc='b', minorticks=0.05)
fig.colorbar(m, label='colorbar with length <1', ticks=0.1, loc='r', length=0.7)效果如下:
时间刻度(Datetime ticks)
Datetime ticks
import proplot as plot
import numpy as np
plot.rc.update(
linewidth=1.2, fontsize=10, ticklenratio=0.7,
figurefacecolor='w', facecolor='pastel blue',
titleloc='upper center', titleborder=False,
)
fig, axs = plot.subplots(nrows=5, axwidth=6, aspect=(8, 1), share=0)
axs[:4].format(xrotation=0) # no rotation for these examples
# Default date locator
# This is enabled if you plot datetime data or set datetime limits
axs[0].format(
xlim=(np.datetime64('2000-01-01'), np.datetime64('2001-01-02')),
title='Auto date locator and formatter'
)
# Concise date formatter introduced in matplotlib 3.1
axs[1].format(
xlim=(np.datetime64('2000-01-01'), np.datetime64('2001-01-01')),
xformatter='concise', title='Concise date formatter',
)
# Minor ticks every year, major every 10 years
axs[2].format(
xlim=(np.datetime64('2000-01-01'), np.datetime64('2050-01-01')),
xlocator=('year', 10), xformatter='\'%y', title='Ticks every N units',
)
# Minor ticks every 10 minutes, major every 2 minutes
axs[3].format(
xlim=(np.datetime64('2000-01-01T00:00:00'), np.datetime64('2000-01-01T12:00:00')),
xlocator=('hour', range(0, 24, 2)), xminorlocator=('minute', range(0, 60, 10)),
xformatter='T%H:%M:%S', title='Ticks at specific intervals',
)
# Month and year labels, with default tick label rotation
axs[4].format(
xlim=(np.datetime64('2000-01-01'), np.datetime64('2008-01-01')),
xlocator='year', xminorlocator='month', # minor ticks every month
xformatter='%b %Y', title='Ticks with default rotation',
)
axs.format(
ylocator='null', suptitle='Datetime locators and formatters demo'
)
plot.rc.reset()
plt.savefig(r'E:\Data_resourses\DataCharm 公众号\Python\学术图表绘制\ProPlot\datetick.png',
dpi=900)效果如下:
以上是我认为ProPlot 比较优秀的几点,当然,大家也可以自行探索,发现自己喜欢的技巧。
ProPlot 实例演示
我们使用之前的推文数据进行实例操作,详细代码如下:
#开始绘图
labels = ['L1', 'L2', 'L3', 'L4', 'L5']
data_a = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
data_b = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
data_c = [12, 20, 24, 17, 16]
x = np.arange(len(labels))
width = .25
fig, axs = plot.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=1, sharey=1, width=10,height=4)
#for mark, data in zip()
axs[0].plot(x,y1, marker='s',c='k',lw=.5,label='D1',markersize=8)
axs[0].plot(x,y2, marker='s',c='k',ls='--',lw=.5,markersize=8,markerfacecolor='white',markeredgewidth=.4,label='D2')
axs[0].plot(x,y3,marker='^',c='k',lw=.5,markersize=8,markerfacecolor='dimgray',markeredgecolor='dimgray',
label='D3')
axs[0].plot(x,y4,marker='^',c='k',lw=.5,markersize=8,label='D4')
axs[1].bar(x-width/2, data_a,width,label='category_A',color='#130074',ec='black',lw=.5)
axs[1].bar(x+width/2, data_b, width,label='category_B',color='#CB181B',ec='black',lw=.5)
axs[1].bar(x+width*3/2, data_c,width,label='category_C',color='#008B45',ec='black',lw=.5)
#先对整体进行设置
axs.format(ylim=(0,40),
xlabel='', ylabel='Values',
abc=True, abcloc='ur', abcstyle='(A)',abcsize=13,
suptitle='ProPlot Exercise'
)
#再对每个子图进行设置
axs[0].format(ylim=(10,40),title='Multi-category scatter plot')
axs[1].format(title='Multi-category bar plot',xticklabels=['L1', 'L2', 'L3', 'L4', 'L5'])
plt.savefig(r'E:\Data_resourses\DataCharm 公众号\Python\学术图表绘制\ProPlot\test_01.png',
dpi=900)
plt.show()效果如下: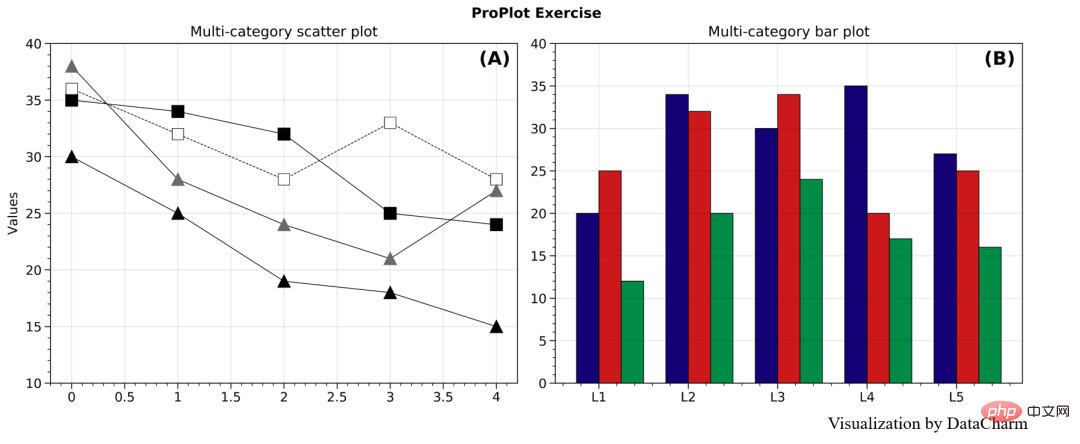
只是简单的绘制,其他的设置也需要熟悉绘图函数,这里就给大家做个简单的演示。
总结
本期推文我们介绍了matplotlib非常优秀的科学图表绘图库PrpPlot, 在一定程度上极大了缩减了定制化绘制时间,感兴趣的同学可以持续关注这个库,当然,还是最好在熟悉matplotlib基本绘图函数及图层属性设置函数的基础上啊。
The above is the detailed content of Still annoyed by Matplotlib's cumbersome layer settings! ? Come and take a look at this Python drawing toolkit. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.



