 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Highly recommended 15 high-level Python libraries that get twice the result with half the effort
Highly recommended 15 high-level Python libraries that get twice the result with half the effort
Highly recommended 15 high-level Python libraries that get twice the result with half the effort
Why do I like Python? For beginners, this is a simple and easy-to-learn programming language;Another reason:The large number of third-party libraries available out of the box is exactly what 230,000 user-contributed packages make Python truly powerful and popular.
1. Dash
Dash is a relatively new software package, it is built in pure Python Ideal for data visualization apps and therefore especially suitable for anyone working with data. Dash is a hybrid of Flask, Plotly.js and React.js.
##2. Pygame
Pygame is a Python decorator for the SDL multimedia library. SDL (Simple DirectMedia Layer) is a cross-platform development library designed to provide a low-level interface to the following:Audio
- ##Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joystick
Graphics hardware based on OpenGL and Direct3D
Pygame is highly portable and can be used on almost all platforms and operating systems run on. Although it has a complete game engine, you can also use this library to play MP3 files directly from Python scripts.
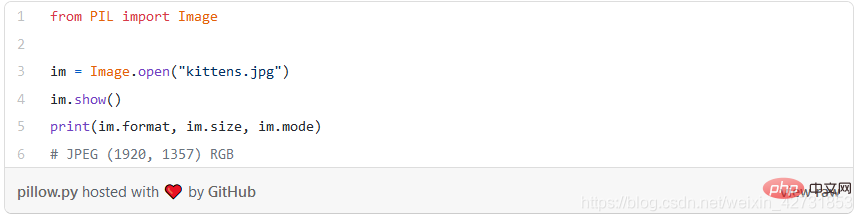
3. Pillow
Pillow is specially designed for processing images. You can use this library to create miniatures. Thumbnail, convert between file formats, rotate, apply filters, display images and more. This is ideal if you need to perform batch operations on many images.
To understand it quickly, look at the following code example (loaded and rendered):
##4. Colorama
Colorama allows you to work with colors in the terminal, perfect for Python scripts, the documentation is short and sweet, and can be found on the Colorama PyPI page .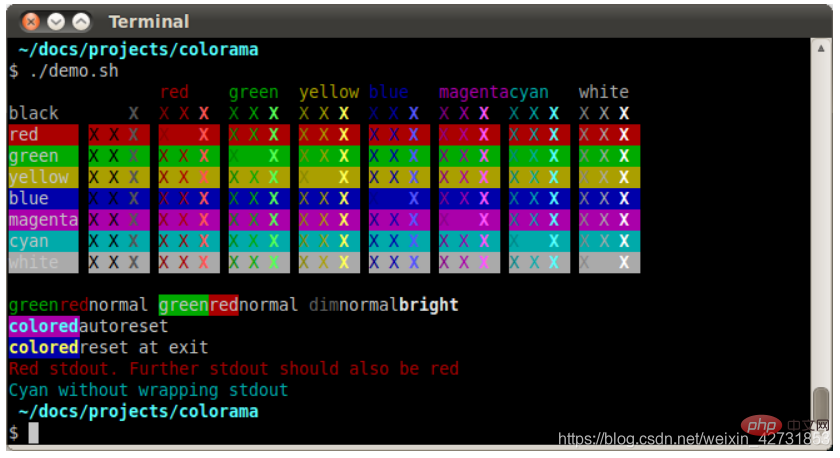
Using JSON in Python is very easy because JSON maps very well to Python dictionaries. Additionally, Python comes with its own excellent json library for parsing and creating JSON. To me, this is one of its best features. If I need to work with JSON, I might consider using Python.
JMESPath makes processing JSON in Python easier by allowing you to explicitly specify how to extract elements from a JSON document. Here are some basic examples to give you an idea of its capabilities:
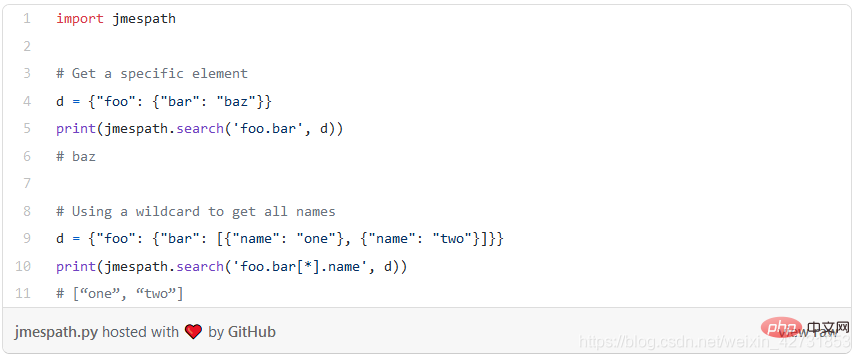
##6. Requests
Requests is built on the world's most downloaded Python library, urllib3, which makes web requests incredibly simple, powerful, and versatile. The following code example illustrates how simple it is to use requests.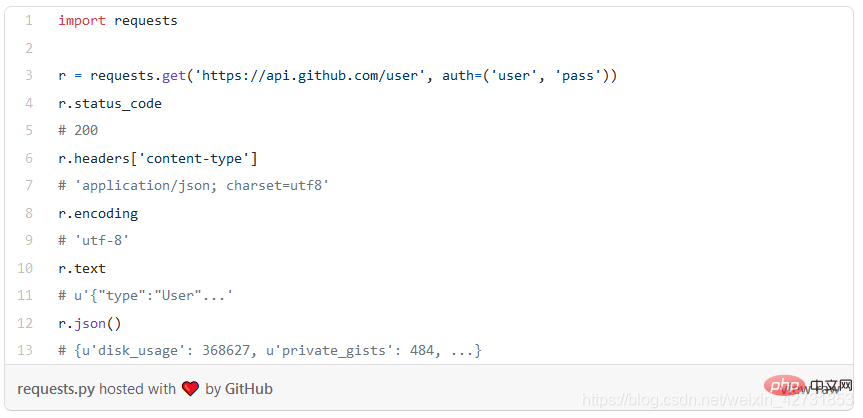
Authentication
Use cookies
Perform POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.
Use a custom certificate
Use Session
Using a proxy
7. Simplejson
What's wrong with the local json module in Python? No! Actually, Python's json is simplejson. Meaning, Python took a version of simplejson and incorporated it into every distribution. But using simplejson has some advantages:It works on more Python versions.
#It is updated more frequently than the version that comes with Python.
#It has the (optional) part written in C, so it's very fast.

I would just use the default json unless you specifically need it:
Speed
Things not in the standard library
Simplejson is much faster than json because it implements some key parts in C. Unless you are processing millions of JSON files, you won't be interested in this kind of speed.
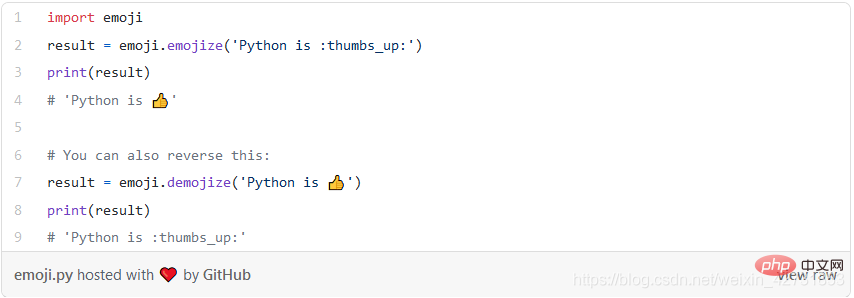
8. Emoji
The Emoji library is very interesting, but not everyone likes emoticons. Emoji packages are very useful when analyzing perspective media data.

The following is a simple code example:
##9. Chardet
You can use the chardet module to detect the character set of a file or data stream. This is useful when analyzing large amounts of random text, for example. However, it can also be used when working with remotely downloaded data when you don't know what the character set is.10. Python-dateutil
The python-dateutil module provides a powerful addition to the standard datetime module Extension. My experience is that where regular Python datetime functionality ends, python-dateutil comes in. You can do a lot of cool things with this library. I'm limiting these examples to ones I've found particularly useful: fuzzing dates in log files, for example: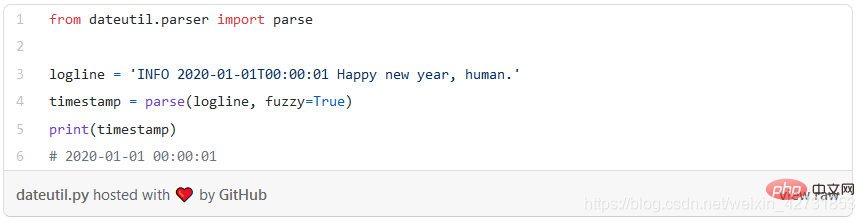
See full documentation for more functions, for example:
Calculate relative increment (next month, next year, next Monday, last week of the month, etc.) and the relative delta between two given date objects.
Uses a superset of the iCalendar specification to calculate dates based on repetition rules.
Time zone (tzinfo) implementation for tzfiles (/etc/localtime, /usr/share/zoneinfo, etc.), TZ environment strings (all known formats ), iCalendar format file, given range (with the help of relative increments), local computer time zone, fixed offset time zone, UTC time zone and Windows registry based time zone.
# Internal latest world time zone information based on the Olson database.
Calculate the Easter Sunday date for any year using the Western, Orthodox or Julian algorithm.
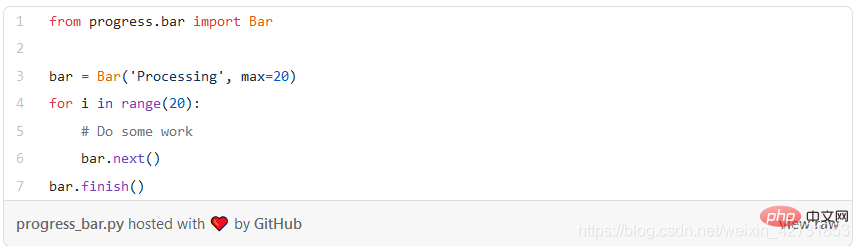
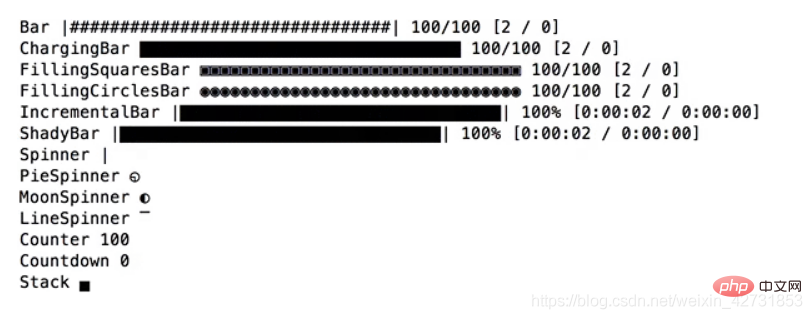
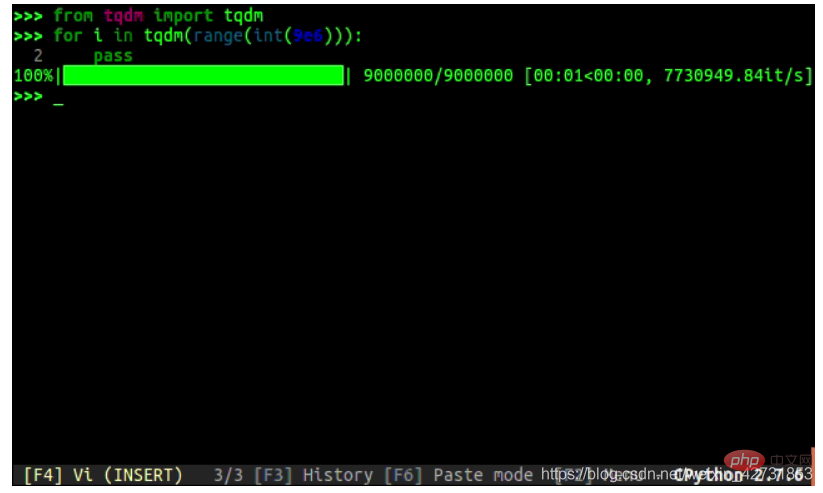
11. Progress bar: progress and tqdm
A little cheating here, because these are two package, but it would be unfair to ignore one of them.
You can create your own progress bar, which might be fun, but using the progress or tqdm packages is faster and less error-prone.
progress
With the help of this package you can easily create progress bars:
##12. IPython
Comprehensive object introspection.
#Input history persists across sessions.
#Cache output results during a session with automatically generated references.
Tab completion, supports completion of python variables and keywords, file names and function keywords by default.
# "Magic" command used to control the environment and perform many IPython or operating system related tasks.
# Session recording and reloading.
#Integrated access to the pdb debugger and Python profiler.
A little-known feature of IPython: its architecture also allows for parallel and distributed computing.
13. Homeassistant
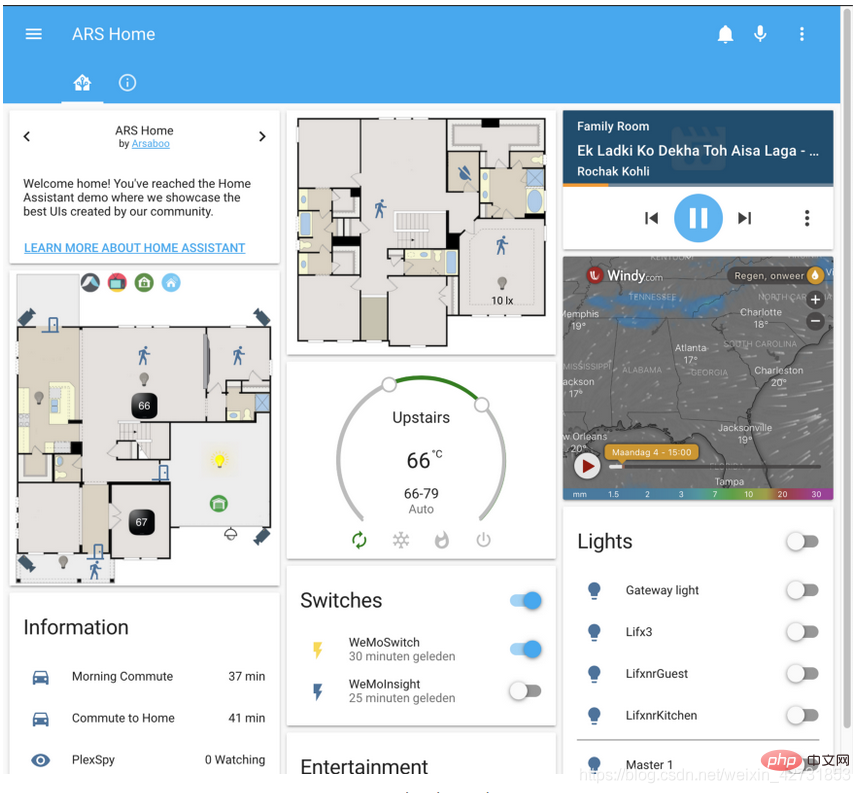
I love home automation. It was a bit of a hobby for me, but one I still feel deeply sorry for as it now controls a large portion of our house. I use Home Assistant to tie together all the systems in the house. Although it is indeed a complete application, you can also install it as a Python PyPI package.
Most of our light fixtures are automated, as are our blinds.
#I monitor our natural gas usage, electric usage and production (solar panels).
#I can track the location of most phones and initiate actions when they enter an area, such as turning on the garage lights when I get home.
# It can also control all our entertainment systems, such as Samsung TVs and Sonos speakers.
#It can automatically discover most devices on the network, so it is very easy to get started.
I've been using Home Assistant daily for 3 years now, it's still in beta, but it's the best platform out of all the platforms I've tried. It is able to integrate and control a variety of devices and protocols, and is all free and open source.
If you are interested in automating your home, make sure you get the chance! If you want to know more, please visit their official website. If you can, install it on your Raspberry Pi. This is by far the easiest and safest way to get started. I installed it on a more powerful server inside a Docker container.
14. Flask
Flask is my entry-level library for creating fast web services Or a simple website. This is a microframework, which means that Flask aims to keep the core simple but extensible. There are over 700 official and community extensions.
If you know you will be developing a large web application, you may want to look into a more complete framework. The most popular in this category is Django.
15. BeautifulSoup
If you extracted some HTML from your website, you need to parse it to get the actual content you want. Beautiful Soup is a Python library for extracting data from HTML and XML files. It provides simple methods to navigate, search and modify parse trees. It's very powerful and, even if broken, is capable of handling all kinds of HTML. Trust me, HTML is often broken, so this is a very powerful feature.
Some of its main features:
Beautiful Soup automatically converts incoming documents to Unicode and outgoing documents to UTF-8. You don't need to think about coding.
Beautiful Soup sits on top of popular Python parsers such as lxml and html5lib, allowing you to try different parsing strategies or increase flexibility.
BeautifulSoup parses whatever you provide and does the work of walking the tree for you. You can tell it "Find all links," or "Find the table title with bold font and give me that text."
The above is the detailed content of Highly recommended 15 high-level Python libraries that get twice the result with half the effort. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.



