Case explanation JVM memory space (recommended collection)
Today, let’s talk with you about the topic of JVM memory space. This is also a question that is often asked in interviews at first-tier Internet companies. It is recommended that friends collect it and take it out often. Read, focus on understanding. Okay, no more talk, let’s get to the main topic today.
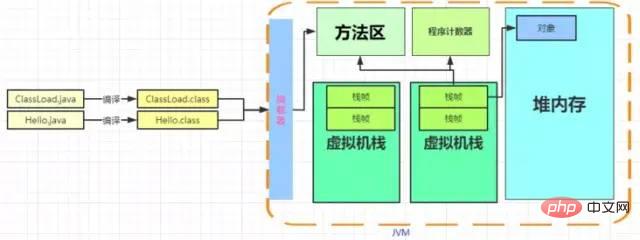
The JVM will divide the memory into different data areas, so where are the loaded classes allocated?
The following figure shows various areas of memory, including: method area, heap, virtual machine stack, local method stack, and program counter.
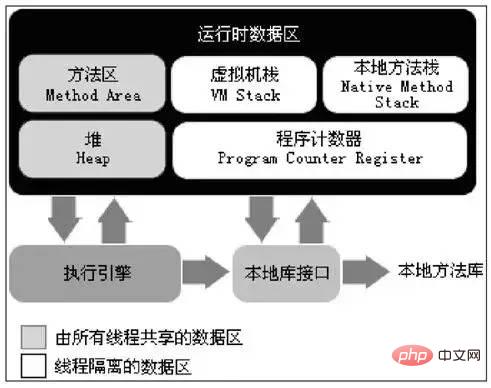
Method area
The method area is used to store the data that has been used by the virtual machine Loaded class information, constants, static variables, code compiled by the just-in-time compiler and other data. The five stages of class loading are mentioned in Class Loading. In the loading phase, the static storage structure represented by the byte stream will be converted into the runtime data structure of the method area. In the preparation phase, all the memory used by the variables will be allocated in the method area.
Program Counter
Come on a simple code, calculate (1 2)*3 and return
public int cal() {
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
return (a + b) * c;
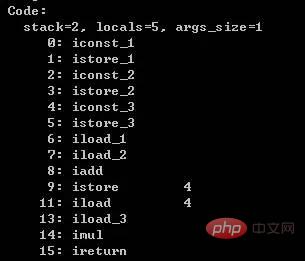
}When this code is loaded into the virtual machine, it becomes the following bytecode. When the virtual machine executes it, it will be executed line by line.
#Java is multi-threaded. After the thread switches back, it needs to know where the original execution position is. The program counter is used to record this execution position. In order to ensure that the counters between threads do not affect each other, this memory area is private to the thread.
虚拟机栈
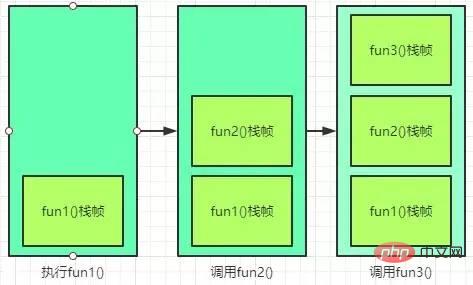
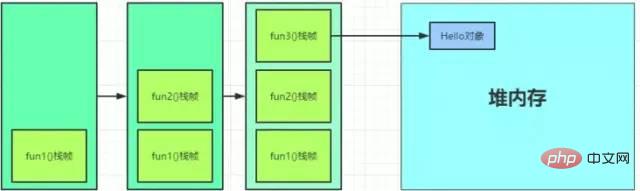
虚拟机栈也是线程私有的,生命周期与线程相同。每个线程都有自己的虚拟机栈,如果这个线程执行了一个方法,就会创建一个栈帧,方法从调用直至执行完成的过程,就对应着一个栈帧在虚拟机栈中入栈到出栈的过程。比如下面的例子,fun1调用fun2,fun2调用fun3,fun3创建Hello对象。
public void fun1() {
fun2();
}
public void fun2() {
fun3();
}
public void fun3() {
Hello hello = new Hello();
}调用的时候,流程图如下:
执行完成的时候,流程图如下:
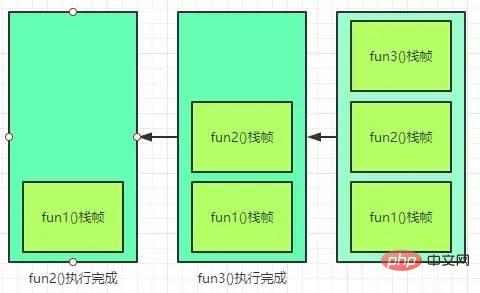
每一个栈帧都包括了局部变量表、操作数栈、动态连接、方法返回地址和一些额外的附加信息。局部变量主要是存放方法参数以及方法内部定义的局部变量,操作数栈是一个后入先出栈,当方法刚刚开始执行的时候,这个方法的操作数栈是空的,在方法的执行过程中,会有各种字节码指令往操作数栈中写入和提取内容,也就是出栈/入栈操作。
我们通过上面(1+2)*3的例子,把方法区、程序计数器、虚拟机栈的协同工作理一下。首先通过javap查看它的字节码,经过类加载器加载后,此时这个字节码存在方法区中。stack表示栈深度是2,locals是本地变量的slot个数,args_size是入参的个数,默认是this。栈的深度、本地变量个数,入参个数,都是在编译器决定的。

如下图,指令的位置是方法区,局部变量和操作数栈的位置是虚拟机栈,程序计数器就在程序计数器(这个下面的图就不再重复)。当执行偏地址为0的指令的时候,程序计数器为0,局部变量第一个值是this,当前的指令就是方法区0:iconst_1,指令iconst_1就是把int常量值1进栈,这个1就到了虚拟机栈的操作数栈中。
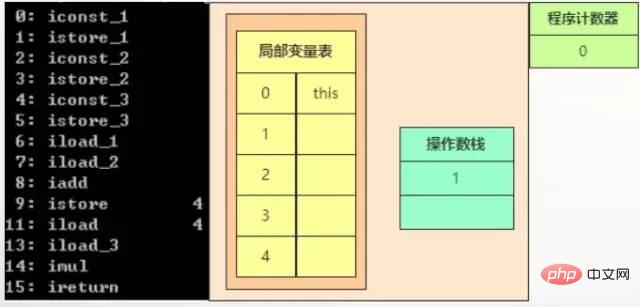
当执行偏地址为1的指令的时候,程序计数器为1,把操作数栈的值赋值到局部变量,此时操作数栈清空了,局部变量多了一个1,这条指令执行完,就是对应上面int a=1的语句。
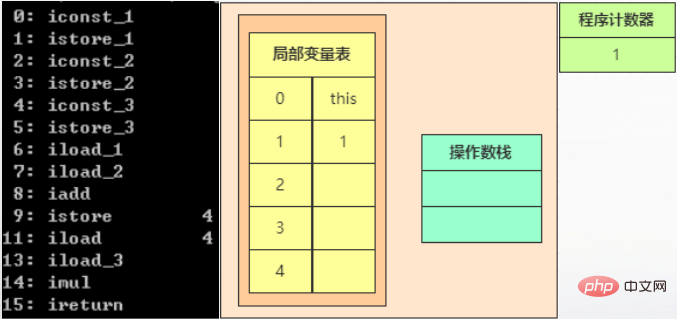
In addition, the assignments of the two statements b and c correspond to instructions 2, 3, 4, and 5, which will not be repeated here. After executing 5, as shown in the following figure:
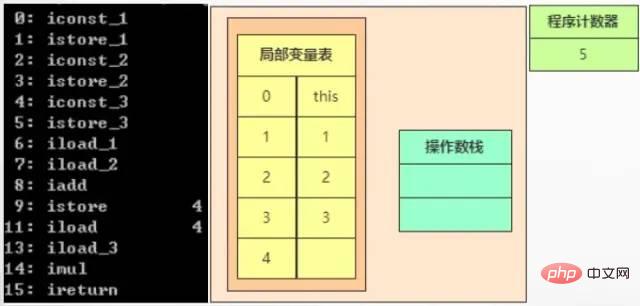
When executing 6, iload_1 is executed, which is to push the second int-type local variable onto the top of the stack. Here The variable is 1.
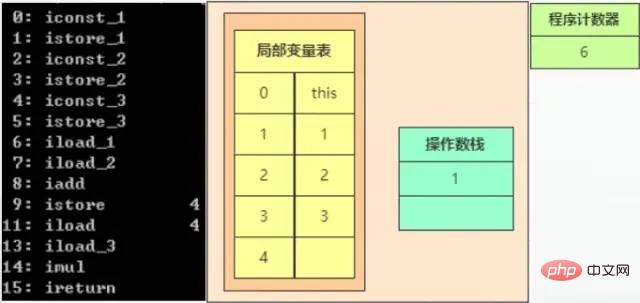
When executing 7, iload_2 is executed, which means pushing the third int-type local variable onto the top of the stack. The variable here is 2.
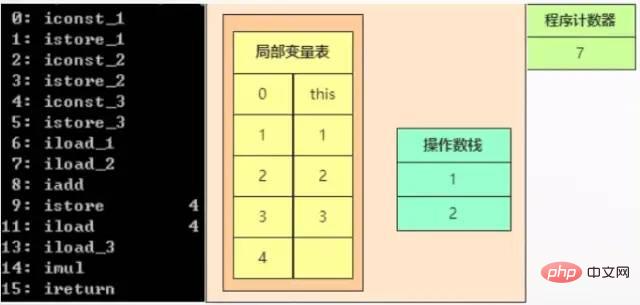
When executing 8, it is the iadd statement, which means that the two int-type elements on the top of the stack are popped out of the stack, and then pushed onto the top of the stack after the result is obtained.
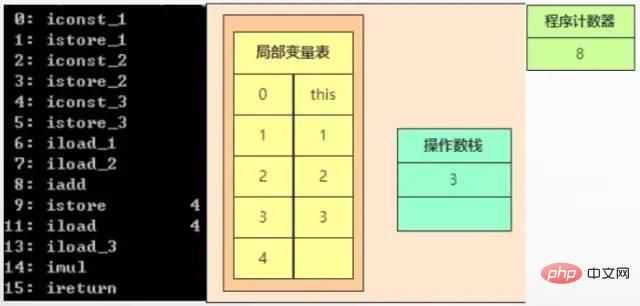
When executing 9, assign the element 3 on the top of the stack to the fifth local variable.
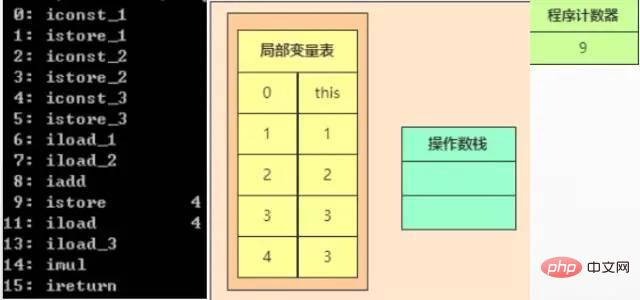
When execution reaches 11, the fifth local variable value is pushed onto the top of the stack. When execution reaches 13, the fourth local variable value is pushed onto the top of the stack. , when executing 14, the two int-type elements on the top of the stack are popped off the stack, and the multiplied result is pushed onto the stack. When executing 15, the current int-type element on the top of the stack is returned from the current method. These are almost the same as the above, so I won’t go into details.
Heap
The only purpose of the heap memory area is to store object instances, almost all object instances are here Allocate memory. For example, fun1 above calls fun2, fun2 calls fun3, and fun3 creates a Hello object. When the object is created in the fun3 method, it is created in the heap, and the address is assigned to the local variable of fun3. The Java heap can also be subdivided into: new generation and old generation; the new generation is also subdivided into Eden space, From Survivor space, and To Survivor space.
Summary
The overall process is as follows, first compile the java file into a class file, Loaded into the method area through the class loader. When a thread calls a method, it will create a stack frame, read the bytecode in the method area and execute the instruction. When the instruction is executed, the execution position will be recorded in the program counter. If an object is created, it will be created in the heap memory. After the method is executed, the stack frame will be popped.
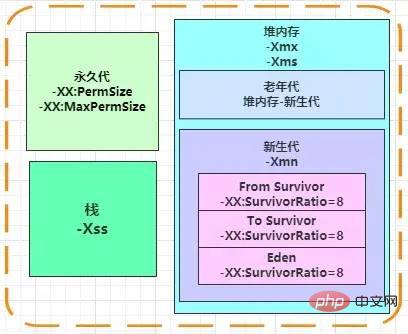
Related parameters
-XX:PermSize: Permanent generation memory capacity .
-XX:MaxPermSize: The maximum memory capacity of the permanent generation.
-XX:MetaspaceSize: The size of the initial value of the metaspace
-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize: The maximum size of the metaspace
-XX:CompressedClassSpaceSize: Store Klass classes in the metaspace The space size of the metadata part
-Xss: stack memory capacity.
-Xms: Heap memory capacity.
-Xmx: The maximum memory capacity of the heap, usually the same as the -Xms setting, to prevent the impact of runtime expansion.
-Xmn: New generation memory capacity, the old generation is the heap memory capacity - New generation memory capacity
-XX: SurvivorRatio=8: The new generation is also subdivided into Eden space and From Survivor space , To Survivor space, set to 8 to represent Eden space: From Survivor space: To Survivor space = 8:1:1. For example, the new generation has 10M, then the Eden space occupies 8M, and the From Survivor space and To Survivor space each occupy 1M.
The above is the detailed content of Case explanation JVM memory space (recommended collection). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
This project is designed to facilitate developers to monitor multiple remote host JVMs faster. If your project is Spring boot, it is very easy to integrate. Just introduce the jar package. If it is not Spring boot, don’t be discouraged. You can quickly initialize a Spring boot program and introduce it yourself. Jar package is enough
 Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
JVM command line parameters allow you to adjust JVM behavior at a fine-grained level. The common parameters include: Set the Java heap size (-Xms, -Xmx) Set the new generation size (-Xmn) Enable the parallel garbage collector (-XX:+UseParallelGC) Reduce the memory usage of the Survivor area (-XX:-ReduceSurvivorSetInMemory) Eliminate redundancy Eliminate garbage collection (-XX:-EliminateRedundantGCs) Print garbage collection information (-XX:+PrintGC) Use the G1 garbage collector (-XX:-UseG1GC) Set the maximum garbage collection pause time (-XX:MaxGCPau
 JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
Key points and precautions for mastering JVM memory usage JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) is the environment in which Java applications run, and the most important one is the memory management of the JVM. Properly managing JVM memory can not only improve application performance, but also avoid problems such as memory leaks and memory overflows. This article will introduce the key points and considerations of JVM memory usage and provide some specific code examples. JVM memory partitions JVM memory is mainly divided into the following areas: Heap (He
 Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
An introduction to the analysis of the functions and principles of the JVM virtual machine: The JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) virtual machine is one of the core components of the Java programming language, and it is one of the biggest selling points of Java. The role of the JVM is to compile Java source code into bytecodes and be responsible for executing these bytecodes. This article will introduce the role of JVM and how it works, and provide some code examples to help readers understand better. Function: The main function of JVM is to solve the problem of portability of Java programs on different platforms.
 Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java is a popular programming language. During the development of Java applications, you may encounter JVM memory overflow errors. This error usually causes the application to crash, affecting the user experience. This article will explore the causes of JVM memory overflow errors and how to deal with and avoid such errors. What is JVM memory overflow error? The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is the running environment for Java applications. In the JVM, memory is divided into multiple areas, including heap, method area, stack, etc. The heap is used to store created objects
 How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
JVM memory parameter settings: How to reasonably adjust the heap memory size? In Java applications, the JVM is the key component responsible for managing memory. Among them, heap memory is used to store object instances. The size setting of heap memory has an important impact on the performance and stability of the application. This article will introduce how to reasonably adjust the heap memory size, with specific code examples. First, we need to understand some basic knowledge about JVM memory. The JVM's memory is divided into several areas, including heap memory, stack memory, method area, etc. in
 Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Before writing a java program to check whether the JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit, let us first discuss about the JVM. JVM is a java virtual machine, responsible for executing bytecode. It is part of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). We all know that java is platform independent, but JVM is platform dependent. We need separate JVM for each operating system. If we have the bytecode of any java source code, we can easily run it on any platform due to JVM. The entire process of java file execution is as follows - First, we save the java source code with .java extension and the compiler converts it into bytecode with .class extension. This happens at compile time. Now, at runtime, J
 Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM principles: In-depth exploration of the working principle of the Java virtual machine requires specific code examples 1. Introduction With the rapid development and widespread application of the Java programming language, the Java Virtual Machine (JavaVirtualMachine, referred to as JVM) has also become indispensable in software development. a part of. As the running environment for Java programs, JVM can provide cross-platform features, allowing Java programs to run on different operating systems. In this article, we will delve into how the JVM works




