The handwritten RPC framework is really not just for pretending to be 13!
During the interview, it is easy to be asked by the interviewer:
How to design an RPC framework?
You may not have been asked, maybe you are lucky, or maybe you are not at this level yet. Usually the monthly salary is more than 20k, and they will basically ask some design questions.
From the interviewer’s perspective: Asking this type of question is better than an eight-part essay, which involves many technical points. For example: knowledge about design patterns, communication protocols, dynamic agents, virtualization, thread pools, etc.
Okay, let’s not go too far, let’s start talking about today’s topic.
RPC is a Remote procedure call. Many people may not particularly understand these words. To put it simply:
It’s like calling a local The method is the same as calling the remote service.
For example, the following case: a user operates a service:
public interface UserService{
String findUserNameById(Integer userId);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
String findUserNameById(Integer userId){
//查数据或查缓存获取到用户名
return "田哥"
}
}Now a controller wants to call the findUserNameById method of UserServiceImpl to obtain the user name.
@RestController
public class UserController{
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return userService.findUserNameById(1);
}
}Assuming that the three classes UserController, UserServiceImpl, and UserService are all in the same project, it is very simple for the controller to call the findUserNameById method.
However, if the controller is another project and wants to be called as above (subtle difference, the feeling is still the same), then we can use the RPC framework.
1. The interface UserService needs to be placed in a separate project, which we usually call an api project.
2. UserServiceImpl needs to be placed in a separate project, which we usually call the provider project.
3. Controller, through a web or other (consumer) project
4. Type the API into a jar package, and then reference it in both the consumer project and the provider project.
The RPC frameworks on the market, such as: Dubbo (Alibaba), Thrift (FaceBook), gRpc (Google), brpc (Baidu), etc., all focus on different aspects to solve the original purpose. Some want extreme perfection, some pursue extreme performance, and some prefer extreme simplicity.
RPC Principle
Back to what we said earlierCalling remote services like calling local services, what technical support is needed?
Dynamic proxy, because our consumer project only has the interface UserServicedefined and no implementation class. Do you want to call a method of the interface? Then you can only create a proxy object.Encoding, that is, the consumer needs to pass the request parameters to the provider. The network transmission process first encodes our parameters and then passes them to the provider. The provider then decodes the passed parameters. Network communication, cross-process will definitely involve network communication. Network transmission protocol, consumer and provider must have a standard for the parameter information going back and forth. How do you pass it to me? Otherwise I How do you know what you want to express. Serialization and deserialization Data compression, during data network transmission, if the data is too large , we have to consider whether the data can be compressed. Registration Center, if the provider performs cluster deployment (the same service is deployed on multiple machines), then we need to perform manual maintenance on the consumer. If the volume is large Get up, the workload can be imagined. Dynamic awareness of service online and offline, if the provider is down or a new node is deployed, then the consumer needs to know which services are offline and which services On the line. Dynamic routing, if the provider is deployed in a cluster (the same service is deployed on multiple machines), we cannot have all consumers fall on the same node, so Resources cannot be fully utilized, and the ancient emperor's rain and dew are all stained . Dynamic routing involves a variety of algorithms, such as randomization, polling, weighting, etc.
Why is a registration center needed? I have shared it before:
Meituan Interview: How to design a registration center?
造轮子
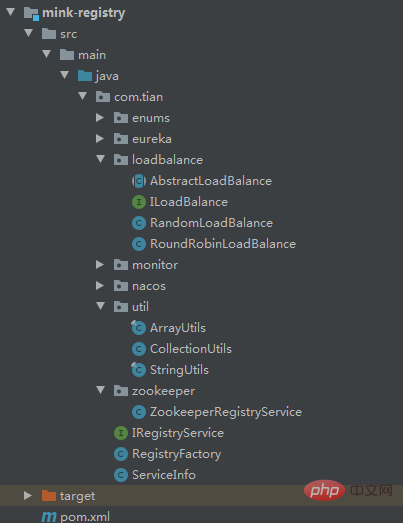
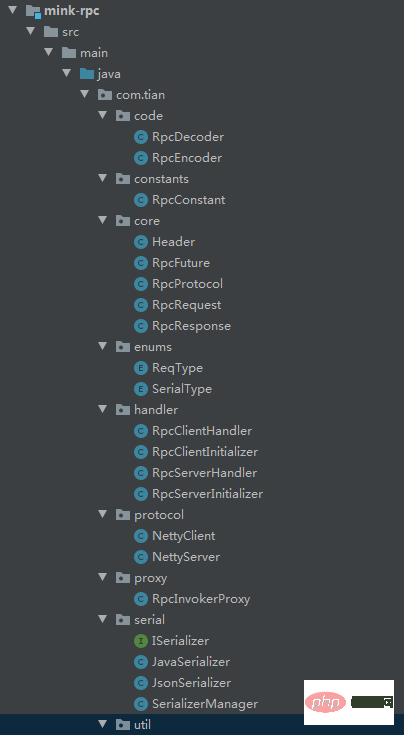
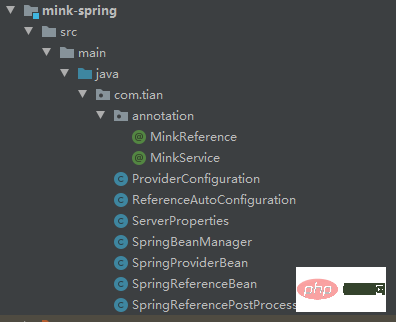
根据上面的这些原理,田哥也搞了一个RPC框架,命名为mink(一个动物的名称)。
--mink ----mink-rpc rpc基本功能 ----mink-registry 服务注册与发现 ----mink-spring 集成SpringBoot
然后,我们把mink-spring打成jar包,服务发布和服务引用都把这个jar给依赖进去。
框架使用
上面,我们创造了轮子,下面,我们就来看如何使用。
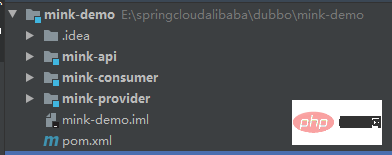
mink-demo就是一个Spring Boot项目,有三个module。
我们把mink-api打成jar包,共consumer和provider使用。
也就是我们在consumer和provider都引入:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.tian</groupId>
<artifactId>mink-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>下面,我们来看看provider端的代码:
<dependency> <groupId>com.tian</groupId> <artifactId>mink-spring</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.tian</groupId> <artifactId>mink-api</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.5.4</version> </dependency>
我们的mink框架,只需要引入mink-spring依赖即可。
接着就是properties的配置:
mink.rpc.servicePort=20880 mink.rpc.registryType=0 mink.rpc.registryAddress=127.0.0.1:2181
再来看看具体服务实现类:
package com.tian.service;
import com.tian.annotation.MinkService;
/**
* @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 用户服务
* @createTime 2022年08月23日 18:16
*/
@MinkService
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public String findUserNameByiD(Integer id) {
System.out.println("服务调用");
return "tian";
}
}这一步,我们只需要在实现类上加上注解@MinkService即可。
最后就是项目启动类:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.tian.service","com.tian"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}我们启动项目(注册中心用的是zookeeper):
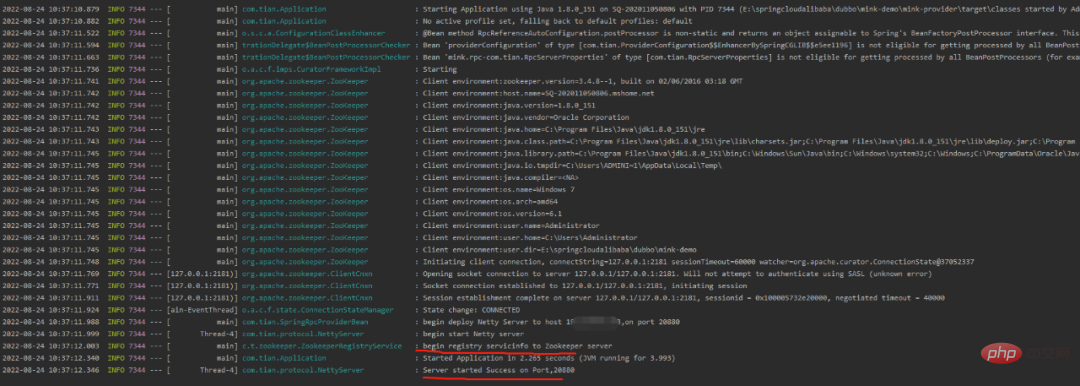
从日志中可以看出,我们的服务已经成功注册到注册中心了。
下面,我们来看看consumer端代码。
首先来看看依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.tian</groupId> <artifactId>mink-spring</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.tian</groupId> <artifactId>mink-api</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.5.4</version> </dependency>org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web 2.5.4
这依赖也很简单,没什么好说的。
再来看看properties配置项:
mink.rpc.registryType=0 mink.rpc.registryAddress=127.0.0.1:2181 server.port=8090
是不是也很简单?
再来看看我们的controller代码:
package com.tian.controller;
import com.tian.annotation.MinkReference;
import com.tian.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 消费端
* @createTime 2022年08月23日 23:08
*/
@RestController
public class UserController {
@MinkReference
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return userService.findUserNameByiD(1);
}
}需要用到对应服务,只需要添加注解@MinkReference即可。
最后就是项目启动类,简单的不行。
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}启动日志:
访问:http://localhost:8090/test
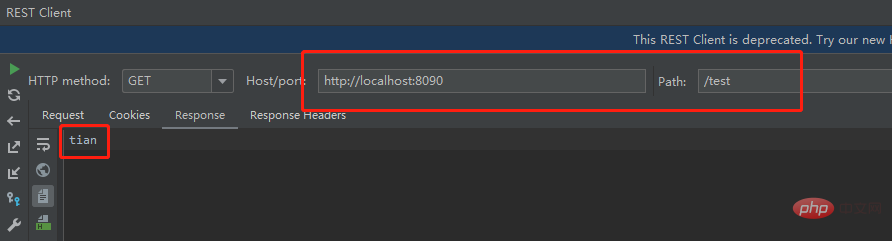
成功!整个过程,非常轻松地集成mink框架并在业务代码中使用。
总结起来,其实就三步:
1、pom中添加依赖
2、properties文件中配置注册中心信息
3、使用的时候加上注解@MinkReference或 @MinkService即可
The above is the detailed content of The handwritten RPC framework is really not just for pretending to be 13!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 The handwritten RPC framework is really not just for pretending to be 13!
Aug 16, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
The handwritten RPC framework is really not just for pretending to be 13!
Aug 16, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
You may not have been asked, maybe you're lucky, or maybe you're not at this level yet. Usually the monthly salary is more than 20k, and they will basically ask some design questions. From the interviewer's perspective: Asking this type of question is better than writing an eight-part essay, which involves many technical points. For example: knowledge about design patterns, communication protocols, dynamic agents, virtualization, thread pools, etc.
 Alibaba interviewer: Please handwrite an RPC framework for me.
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:24 PM
Alibaba interviewer: Please handwrite an RPC framework for me.
Aug 17, 2023 pm 04:24 PM
RPC is a computer communication protocol. This protocol allows a program running on one computer to call a subroutine on another computer without the developer having to additionally program this interaction.
 Principles and applications of RPC framework in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
Principles and applications of RPC framework in Go language
Jun 01, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
1. The concept of RPC framework In distributed systems, data often needs to be transferred between different servers and clients. The RPC (RemoteProcedureCall) framework is a commonly used technical means. The RPC framework allows applications to call functions or methods of another execution environment through remote messaging, thereby enabling the program to run on different computers. There are currently many RPC frameworks on the market, such as Google's gRPC, Thrift, Hessian, etc. This article mainly introduces
 How to develop RPC framework in PHP?
May 13, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
How to develop RPC framework in PHP?
May 13, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
RPC (RemoteProcedureCall) is an inter-process communication protocol that allows different processes to communicate and collaborate over the network on different physical machines. The RPC framework is attracting more and more attention because it can help developers easily implement the development of distributed systems. In this article, we will introduce step by step how to use PHP to develop RPC framework. 1. What is the RPC framework? The RPC framework is a framework used to implement remote procedure calls. In RPC-based
 What rpc frameworks are there?
Aug 03, 2023 am 10:17 AM
What rpc frameworks are there?
Aug 03, 2023 am 10:17 AM
The rpc frameworks include: 1. gRPC, a high-performance, open-source RPC framework developed by Google; 2. Apache Thrift, a cross-language RPC framework developed and open-sourced by Facebook; 3. Apache Dubbo, a high-performance, lightweight RPC framework, suitable for large-scale distributed systems; 4. Apache Axis2, an RPC framework based on Web service standards; 5. Spring Cloud, an open source framework for building distributed systems.
 Go language RPC framework evaluation: performance, ease of use, community support comparison
Feb 27, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
Go language RPC framework evaluation: performance, ease of use, community support comparison
Feb 27, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
As an important modern programming language, Go language is increasingly used in distributed system development. When building a distributed system, the choice of RPC (remote procedure call) framework is often crucial. This article will conduct a horizontal evaluation of the current mainstream Go language RPC frameworks, compare their advantages and disadvantages in terms of performance, ease of use, and community support, and attach specific code examples. 1. Performance comparison In distributed systems, performance is often one of the primary indicators that developers pay attention to. The following are some main
 How to implement a high-concurrency RPC framework in go language
Aug 05, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
How to implement a high-concurrency RPC framework in go language
Aug 05, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
Introduction to how to implement high-concurrency RPC framework in Go language: With the rapid development of the Internet, high-concurrency applications have attracted more and more attention. Using the RPC (RemoteProcedureCall) framework is a common solution. This article will introduce how to implement a high-concurrency RPC framework in the Go language, and will come with code examples. Introduction to the RPC framework: RPC is a communication protocol that allows a computer program to call a subroutine in another address space (usually located on the remote computer) without
 What are the RPC frameworks in PHP7.0?
May 29, 2023 am 11:10 AM
What are the RPC frameworks in PHP7.0?
May 29, 2023 am 11:10 AM
With the continuous development of computer technology, distributed systems have become mainstream, and remote procedure call (RPC) is an important means to implement distributed systems. As a popular Web programming language, PHP also has its own RPC framework, among which some new RPC frameworks were introduced in PHP7.0 version. This article will introduce the common RPC frameworks and their characteristics in PHP7.0. PHPRemoteProcedureCall(phpRPC)phpRPC is a lightweight RP



