Display snowflakes falling using arcade library in Python
arcade library is a Python library for creating 2D arcade style video games and simulations. If you want to use the arcade library to create a snowing effect, you can first create a new arcade window and set a dark blue background color to represent the night sky.
Using the arcade library in Python
The arcade library is a Python library used for developing 2D games and applications. It provides a simple interface to create interactive graphics and animations. In this article, we'll use the arcade library to create a simple snowfall animation.
To get started, we need to install the arcade library. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal or command prompt −
pip install arcade
Once the installation is completed, we can start writing our code. Here's a simple program that displays snowfall −
import arcade
import random
SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
SNOWFLAKE_SIZE = 64
class Snowflake:
def __init__(self):
self.x = random.randrange(SCREEN_WIDTH)
self.y = SCREEN_HEIGHT + SNOWFLAKE_SIZE
self.speed = random.randrange(5, 20)
self.angle = random.uniform(0, 2 * 3.1415)
def update(self):
self.x += self.speed * math.sin(self.angle)
self.y -= self.speed * math.cos(self.angle)
if self.y < -SNOWFLAKE_SIZE:
self.y = SCREEN_HEIGHT + SNOWFLAKE_SIZE
self.x = random.randrange(SCREEN_WIDTH)
def draw(self):
arcade.draw_circle_filled(self.x, self.y, SNOWFLAKE_SIZE, arcade.color.WHITE)
class Snowfall(arcade.Window):
def __init__(self, width, height):
super().__init__(width, height, "Snowfall")
arcade.set_background_color(arcade.color.BLUE_GRAY)
self.snowflakes = []
for i in range(100):
self.snowflakes.append(Snowflake())
def on_draw(self):
arcade.start_render()
for snowflake in self.snowflakes:
snowflake.draw()
def on_update(self, delta_time):
for snowflake in self.snowflakes:
snowflake.update()
if __name__ == "__main__":
window = Snowfall(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT)
arcade.run()
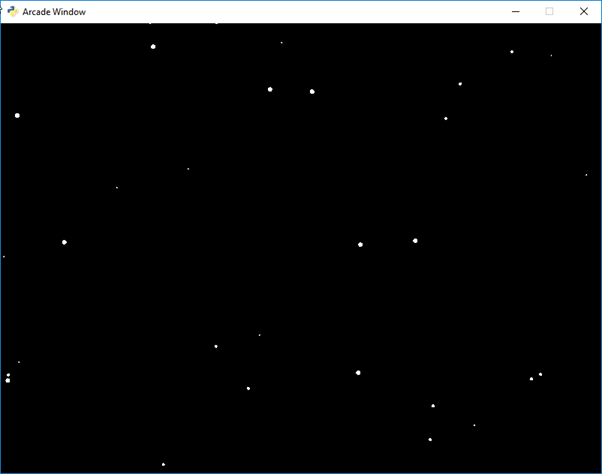
Output
Next, you can create a list of snowflakes, where each snowflake is represented as a tuple of (x, y, size) values. The x and y values represent the snowflake's position on the screen, and the size value represents the snowflake's size.
On each frame of the game loop, you update the position of each snowflake by adding a small random amount to its y-value. You can also check if the snowflake has fallen from the bottom of the screen, and if so, reset its position to a random x value at the top of the screen.
Finally, you can draw each snowflake on the screen using the arcade.draw_circle_filled() function, which accepts (x, y) position and size values as parameters.
Let's go over the code step-by-step.
First, we import the arcade library and the random module, which we'll use to generate random values for the snowflakes. We also define some constants: SCREEN_WIDTH and SCREEN_HEIGHT, which define the size of our window, and SNOWFLAKE_SIZE, which defines the size of our snowflakes.
Next, we define a Snowflake class. This class represents a single snowflake. In the constructor, we generate random values for the snowflake's position, speed, and angle. The update() method updates the snowflake's position based on its speed and angle. If the snowflake falls off the bottom of the screen, we reset its position to the top of the screen. The draw() method draws the snowflake on the screen using the arcade.draw_circle_filled() function.
After that, we define a Snowfall class. This class represents our main application window. In the constructor, we set the background color to blue-gray and create a list of 100 snowflakes. In the on_draw() method, we iterate over the list of snowflakes and call each snowflake's draw() method. In the on_update() method, we iterate over the list of snowflakes and call each snowflake's update() method.
Finally, we create an instance of the Snowfall class and call arcade.run() to start the application.
This code creates a Snowflake class to represent each snowflake, and a SnowfallGame class to manage the game loop and draw the snowflakes on the screen. The on_draw() method is called each frame to draw the snowflakes, and the on_update() method is called each frame to update the position of the snowflakes. The arcade.run() function starts the game loop and keeps the window open until the user closes it.
That's it! When you run the program, you should see a window with snowflakes falling on the screen.
In addition, Python provides a turtle drawing function, and we can use turtle drawing to achieve the snowflake effect shown below.
The above is the detailed content of Display snowflakes falling using arcade library in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.




