Python program to draw histogram using turtle
Graphical representations of data provide an enhanced understanding of the complex substructure of the data, helping us to easily interpret hidden patterns and trends. Imagine how convenient it would be if we could draw similar relationships programmatically? Python provides a rich module specifically designed to perform such operations, it is called "turtle".
The "turtle" module is a built-in library in Python that allows us to draw graphics on the "turtle graphics screen". In this article, we will create a bar chart using the turtle module.
Understanding the Turtle module
The turtle module uses a virtual turtle object to create graphics. There are different functions associated with this module that empowers this turtle object to move around the screen and draw over it. Let's talk about the different functions we require to create a bar chart.
Turtle function for creating bar charts
Turtle() − This function creates a new turtle object.
fillcolor() − This function sets the color of the turtle to the color of the fill bar.
begin_fill() − This function starts the filling process and remembers the starting point.
left() − This function causes the turtle to turn 90 degrees to the left.
right() − This function causes the turtle to turn 90 degrees to the right.
forward() − This function causes the turtle to move forward by the specified unit.
write() − This function will write a string (height value) on the histogram.
end_fill() − This function closes the graphic and stops the filling process.
All these functions together create a bar chart, but we must prepare a proper program to make these functions work as a whole. Now that we understand the mechanics, let's draw a bar chart.
Draw a bar chart
The Turtle module is inspired by the LOGO programming language, which allows users to create shapes on a virtual screen. To draw the bar chart, we need to set the turtle to the lower left corner of the screen. By default, the turtle is located at the center point (0,0), but we can change these coordinates using the "setworldcoordinates()" method.
This method allows the user to rescale the window and make it fit for the data. It takes four coordinates −
The coordinates are the X and Y axes of the lower left corner and the lower right corner.
The X and Y axis coordinates of the upper left and upper right corners.
This method serves as a reset tool to adjust coordinates according to the size of the data. We set these coordinates using the maximum histogram height value and total space value.
The Chinese translation ofExample
is:Example
The following is an implementation of the concepts discussed above.
We will create a function that accepts a "turtle object", "bar height" and "bar color" as parameters. We will then write functions to plot bars with different heights and colors.
The different height and color values will be passed in the form of a list, and we will iterate through calling the function for each value.
Finally, we will use the turtle object to make a brush and start the drawing process. Once the drawing is complete, we will close the turtle instance. The turtle graphics screen is created through the "Screen()" method.
Example
is:Example
import turtle
def BarGraph(turtleOBJ, Bar_height, Bar_color):
turtleOBJ.fillcolor(Bar_color)
turtleOBJ.begin_fill()
turtleOBJ.left(90)
turtleOBJ.forward(Bar_height)
turtleOBJ.write(str(Bar_height))
turtleOBJ.right(90)
turtleOBJ.forward(80)
turtleOBJ.right(90)
turtleOBJ.forward(Bar_height)
turtleOBJ.left(90)
turtleOBJ.end_fill()
Bar_heights = [23, 94, 42, 150, 200, 56, 240,40]
Bar_color = ["orange", "purple", "green", "red", "black", "grey", "white", "violet"]
maxBarVal = max(Bar_heights)
Graph_Range = len(Bar_heights)
Space = 20
screen = turtle.Screen()
screen.setworldcoordinates(0 - Space, 0 - Space, 50 * Space, maxBarVal + Space)
screen.bgcolor("Brown")
turtleOBJ = turtle.Turtle()
turtleOBJ.pensize(3)
for bar in range(len(Bar_heights)):
BarGraph(turtleOBJ, Bar_heights[bar], Bar_color[bar])
screen.exitonclick()
Output
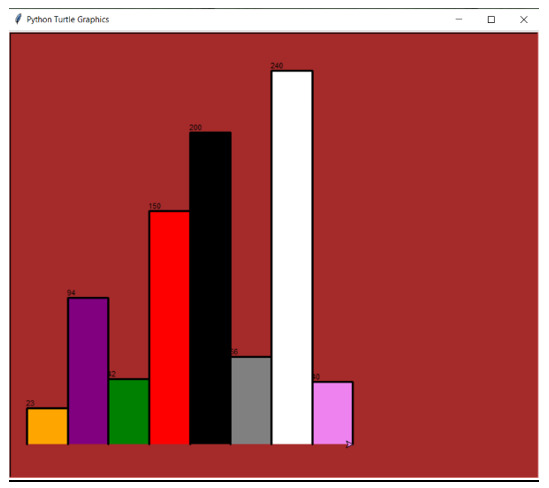
Other insights
We can add a frame to this bar chart and design the scale of the X-axis and Y-axis. The turtle module is strictly for creating graphs based on the data we have. We cannot use it to make statistical estimates. Although it can be used with other powerful Python libraries such as "NumPy" and "Pandas", providing them with statistical and visualization capabilities. For more in-depth and precise estimation, we use the "matplotlib" library.
in conclusion
This article explains the mechanics of the turtle module and how to use it to create a histogram. We discussed various functions and parameters that can be used to programmatically generate histograms on the turtle graphics screen. The values used in the program are based on the data we want to visualize and cannot be further statistically interpreted.
The above is the detailed content of Python program to draw histogram using turtle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to run python program in notepad++
Apr 08, 2024 am 03:24 AM
How to run python program in notepad++
Apr 08, 2024 am 03:24 AM
Using Notepad++ to run a Python program requires the following steps: 1. Install the Python plug-in; 2. Create a Python file; 3. Set the run options; 4. Run the program.
 PyCharm usage tutorial: guide you in detail to run the operation
Feb 26, 2024 pm 05:51 PM
PyCharm usage tutorial: guide you in detail to run the operation
Feb 26, 2024 pm 05:51 PM
PyCharm is a very popular Python integrated development environment (IDE). It provides a wealth of functions and tools to make Python development more efficient and convenient. This article will introduce you to the basic operation methods of PyCharm and provide specific code examples to help readers quickly get started and become proficient in operating the tool. 1. Download and install PyCharm First, we need to go to the PyCharm official website (https://www.jetbrains.com/pyc
 How to make a histogram in WPS documents
Mar 20, 2024 pm 10:11 PM
How to make a histogram in WPS documents
Mar 20, 2024 pm 10:11 PM
WPS is a software we often use in our daily work. When doing statistics, we will use some charts for comparison and reference, such as the application of histograms. So do you know how to make a WPS histogram? The editor below will introduce how to make a WPS histogram. After we open the WPS software we are using, the interface will differ depending on the WPS version, but it will not affect the operation. Next, find the "Insert" option in the main menu bar. After opening it, you will see the chart option. After the chart is opened, the first one is the so-called column chart. In fact, there are three types of column charts, namely clustered column chart, stacked column chart and percentage stacked column chart. Which one we need can be done by ourselves. Select, let me first introduce the use of this clustered column chart. The choice is made
 PyCharm Advanced Tutorial: Use PyInstaller to package code into EXE format
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PyCharm Advanced Tutorial: Use PyInstaller to package code into EXE format
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PyCharm is a powerful Python integrated development environment that provides a wealth of functions and tools to help developers improve efficiency. Among them, PyInstaller is a commonly used tool that can package Python code into an executable file (EXE format) to facilitate running on machines without a Python environment. In this article, we will introduce how to use PyInstaller in PyCharm to package Python code into EXE format, and provide specific
 Does PyCharm Community Edition support enough plugins?
Feb 20, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Does PyCharm Community Edition support enough plugins?
Feb 20, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Does PyCharm Community Edition support enough plugins? Need specific code examples As the Python language becomes more and more widely used in the field of software development, PyCharm, as a professional Python integrated development environment (IDE), is favored by developers. PyCharm is divided into two versions: professional version and community version. The community version is provided for free, but its plug-in support is limited compared to the professional version. So the question is, does PyCharm Community Edition support enough plug-ins? This article will use specific code examples to
 python program development process
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
python program development process
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
The Python program development process includes the following steps: Requirements analysis: clarify business needs and project goals. Design: Determine architecture and data structures, draw flowcharts or use design patterns. Writing code: Program in Python, following coding conventions and documentation comments. Testing: Writing unit and integration tests, conducting manual testing. Review and Refactor: Review code to find flaws and improve readability. Deploy: Deploy the code to the target environment. Maintenance: Fix bugs, improve functionality, and monitor updates.
 Flask installation and configuration tutorial: a tool to easily build Python web applications
Feb 20, 2024 pm 11:12 PM
Flask installation and configuration tutorial: a tool to easily build Python web applications
Feb 20, 2024 pm 11:12 PM
Flask installation and configuration tutorial: A tool to easily build Python Web applications, specific code examples are required. Introduction: With the increasing popularity of Python, Web development has become one of the necessary skills for Python programmers. To carry out web development in Python, we need to choose a suitable web framework. Among the many Python Web frameworks, Flask is a simple, easy-to-use and flexible framework that is favored by developers. This article will introduce the installation of Flask framework,
 Llama3 comes suddenly! The open source community is boiling again: the era of free access to GPT4-level models has arrived
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:43 PM
Llama3 comes suddenly! The open source community is boiling again: the era of free access to GPT4-level models has arrived
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:43 PM
Llama3 is here! Just now, Meta’s official website was updated and the official announced Llama 38 billion and 70 billion parameter versions. And it is an open source SOTA after its launch: Meta official data shows that the Llama38B and 70B versions surpass all opponents in their respective parameter scales. The 8B model outperforms Gemma7B and Mistral7BInstruct on many benchmarks such as MMLU, GPQA, and HumanEval. The 70B model has surpassed the popular closed-source fried chicken Claude3Sonnet, and has gone back and forth with Google's GeminiPro1.5. As soon as the Huggingface link came out, the open source community became excited again. The sharp-eyed blind students also discovered immediately






