Memoization (1D, 2D and 3D) Dynamic Programming in Java
Memoization is a technique based on dynamic programming used to improve the performance of recursive algorithms by ensuring that a method does not run multiple times on the same set of inputs, by recording the results (stored in an array) of the provided inputs. Memoization can be achieved through a top-down approach that implements recursive methods.
Let’s understand this situation through a basic Fibonacci sequence example.
1-D memoization
We will consider a recursive algorithm with only one non-constant parameter (only one parameter's value changes), so this method is called 1-D memoization . The following code is for finding the Nth (all terms up to N) in the Fibonacci sequence.
Example
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
System.out.println("Calculating fibonacci number for: " + n);
return (fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2));
}Output
If we run the above code with n=5, the following output will be generated.
Calculating fibonacci number for: 5 Calculating fibonacci number for: 4 Calculating fibonacci number for: 3 Calculating fibonacci number for: 2 Calculating fibonacci number for: 2 Calculating fibonacci number for: 3 Calculating fibonacci number for: 2
The Fibonacci value for n=5 is: 5
Note that the Fibonacci numbers for 2 and 3 are calculated multiple times. Let us understand better by drawing the above recursion tree for the condition n=5.
The two child nodes of the node will represent the recursive calls it makes. You can see that F(3) and F(2) are calculated multiple times, which can be avoided by caching the results after each step.
We will use an instance variable memoize Set to cache the results. First check if n already exists in the memoize Set, if so, return the value; if not, calculate the value and add it to the set.
Example
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TutorialPoint {
private Map<Integer, Integer> memoizeSet = new HashMap<>(); // O(1)
public int fibMemoize(int input) {
if (input == 0)
return 0;
if (input == 1)
return 1;
if (this.memoizeSet.containsKey(input)) {
System.out.println("Getting value from computed result for " + input);
return this.memoizeSet.get(input);
}
int result = fibMemoize(input - 1) + fibMemoize(input - 2);
System.out.println("Putting result in cache for " + input);
this.memoizeSet.put(input, result);
return result;
}
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1)
return 1;
System.out.println("Calculating fibonacci number for: " + n);
return (fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TutorialPoint tutorialPoint = new TutorialPoint();
System.out.println("Fibonacci value for n=5: " + tutorialPoint.fibMemoize(5));
}
}Output
If we run the above code, the following output will be generated
Adding result in memoizeSet for 2 Adding result in memoizeSet for 3 Getting value from computed result for 2 Adding result in memoizeSet for 4 Getting value from computed result for 3 Adding result in memoizeSet for 5
The Fibonacci value when n=5 is :5
As can be seen from the above, the Fibonacci numbers of 2 and 3 will not be calculated again. Here, we introduce a HashMap memorizes to store the calculated values. Before each Fibonacci calculation, check whether the value of the input has been calculated in the collection. If not, add the value of the specific input to the collection. middle.
2-D Memorization
In the above program, we have only one non-constant parameter. In the following program, we will take an example of a recursive program that has two parameters that change their value after each recursive call, and we will implement memoization on the two non-constant parameters for optimization. This is called 2-D memoization.
For example: We will implement the standard longest common subsequence (LCS). If a set of sequences is given, the longest common subsequence problem is to find the subsequence common to all sequences that has the largest length. There will be 2^n possible combinations.
Example
class TP {
static int computeMax(int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
static int longestComSs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) {
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1))
return 1 + longestComSs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1);
else
return computeMax(longestComSs(X, Y, m, n - 1), longestComSs(X, Y, m - 1, n));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String word_1 = "AGGTAB";
String word_2 = "GXTXAYB";
System.out.print("Length of LCS is " + longestComSs(word_1, word_2, word_1.length(),word_2.length()));
}
}Output
If we run the above code, the following output will be generated
Length of LCS is 4
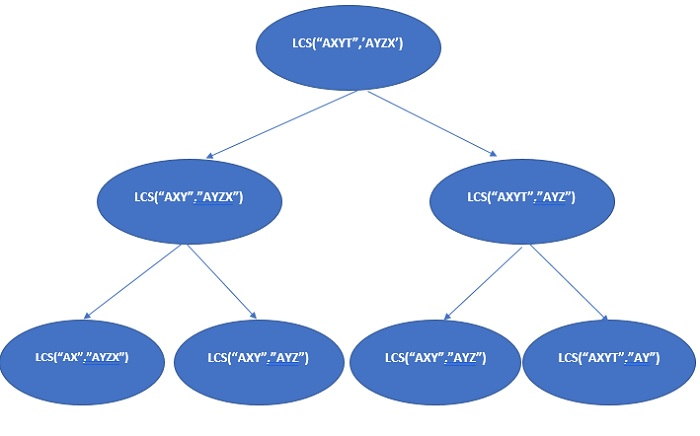
In the above In the recursion tree, lcs("AXY", "AYZ") is solved multiple times.
Due to the nature of this problem with overlapping substructures, repeated calculations of the same subproblems can be avoided by using memoization or tabulation.
The memoization method of recursive code is implemented as follows.
Example
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
class testClass {
final static int maxSize = 1000;
public static int arr[][] = new int[maxSize][maxSize];
public static int calculatelcs(String str_1, String str_2, int m, int n) {
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
if (arr[m - 1][n - 1] != -1)
return arr[m - 1][n - 1];
if (str_1.charAt(m - 1) == str_2.charAt(n - 1)) {
arr[m - 1][n - 1] = 1 + calculatelcs(str_1, str_2, m - 1, n - 1);
return arr[m - 1][n - 1];
}
else {
int a = calculatelcs(str_1, str_2, m, n - 1);
int b = calculatelcs(str_1, str_2, m - 1, n);
int max = (a > b) ? a : b;
arr[m - 1][n - 1] = max;
return arr[m - 1][n - 1];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
arr[i][j] = -1;
}
}
String str_1 = "AGGTAB";
String str_2 = "GXTXAYB";
System.out.println("Length of LCS is " + calculatelcs(str_1, str_2, str_1.length(),str_2.length()));
}
}Output
If we run the above code, the following output will be generated
Length of LCS is 4
Method
Observe that in the method There are 4 parameters in (calculatelcs), 2 of which are constants (do not affect memoization), and 2 non-constant parameters (m and n), which will change each time the method is recursively called. value. In order to achieve memoization, we introduce a two-dimensional array to store the calculated value of lcs(m,n), which is stored in arr[m-1][n-1]. When calling the function with the same parameters m and n again, we no longer perform a recursive call, but directly return arr[m-1][n-1], because the previously calculated lcs(m, n) has been stored in arr [m-1][n-1], thereby reducing the number of recursive calls.
Three-dimensional memoization
This is a memoization method for recursive programs with 3 non-constant parameters. Here, we take calculating the LCS length of three strings as an example.
The method here is to generate all possible subsequences of a given string (there are 3ⁿ possible subsequences in total) and match the longest common subsequence among them.
We will introduce a three-dimensional table to store the calculated values. Consider subsequences.
A1[1...i] i < N
A2[1...j] j < M
A3[1...k] k < K
If we find a common character (X[i]==Y[j ]==Z[k]), we need to recursively process the remaining characters. Otherwise, we will calculate the maximum value of
Keep X[i] for recursive processing of other characters
Keep Y[j] for recursive processing Other characters
Keep Z[k] Recursively handle other characters
So if we convert the above idea into a recursive function,
f(N,M,K)={1 f(N-1,M-1,K-1)if (X[N]==Y[M]==Z[K]maximum(f (N-1,M,K),f(N,M-1,K),f(N,M,K-1))}
f(N-1 ,M,K) = Reserve X[i] to recursively process other characters
f(N,M-1,K) = Reserve Y[j] to recursively process other characters
f(N,M,K-1) = Reserve Z[k] to recursively process other characters
Example
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.*;
class testClass {
public static int[][][] arr = new int[100][100][100];
static int calculatelcs(String str_1, String str_2, String str_3, int m, int n, int o) {
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
arr[i][j][0] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= o; j++) {
arr[0][i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= o; j++) {
arr[i][0][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= o; k++) {
if (str_1.charAt(i - 1) == str_2.charAt(j-1) && str_2.charAt(j1) == str_3.charAt(k-1)) {
arr[i][j][k] = 1 + arr[i - 1][j - 1][k - 1];
}
else {
arr[i][j][k] = calculateMax(arr[i - 1][j][k], arr[i][j - 1][k], arr[i][j][k - 1]);
}
}
}
}
return arr[m][n][o];
}
static int calculateMax(int a, int b, int c) {
if (a > b && a > c)
return a;
if (b > c)
return b;
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str_1 = "clued";
String str_2 = "clueless";
String str_3 = "xcxclueing";
int m = str_1.length();
int n = str_2.length();
int o = str_3.length();
System.out.print("Length of LCS is " + calculatelcs(str_1, str_2, str_3, m, n, o));
}
}Output
If we run the above code, the following output will be generated
Length of LCS is 4
The above is the detailed content of Memoization (1D, 2D and 3D) Dynamic Programming in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




