 PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 Workerman
Workerman
 Use Webman to implement continuous integration and deployment of websites
Use Webman to implement continuous integration and deployment of websites
Use Webman to implement continuous integration and deployment of websites

Use Webman to achieve continuous integration and deployment of websites
With the rapid development of the Internet, the work of website development and maintenance has become more and more complex. In order to improve development efficiency and ensure website quality, continuous integration and deployment have become an important choice. In this article, I will introduce how to use the Webman tool to implement continuous integration and deployment of the website, and attach some code examples.
1. What is Webman
Webman is an open source continuous integration and deployment tool based on Java. It provides a set of simple and easy-to-use command line tools and APIs to manage the construction of projects. Test and deploy. It supports a variety of build tools and version control systems, including Maven, Gradle, Git, and SVN.
2. Install Webman
Before we begin, we first need to install Webman. Webman provides two installation methods: use Maven to build the Webman executable file, or directly download the precompiled executable file. Here, we choose to use Maven to build Webman.
- Install Java and Maven
First, make sure Java and Maven are installed on your machine. You can check by running the following command:
java -version mvn -version
If not installed, please install Java and Maven first.
- Clone Webman repository
Run the following command to clone the Webman repository:
git clone https://github.com/sheaffei/webman.git
- Build Webman
Enter the root directory of Webman and run the following command to build Webman:
cd webman mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
After the build is completed, you can find the generated executable file webman in the webman/target directory. jar.
3. Configuring Webman
The configuration file is an important part of using Webman. We need to create the webman.yaml file in the project root directory and configure it.
The following is a simple webman.yaml example:
project-name: my-website build: type: maven goals: clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true output-dir: target deploy: type: ftp host: ftp.example.com port: 21 username: your-username password: your-password target-dir: /var/www/html
In this example, we configure a named my-website project. The build phase uses Maven and sets the build target and output path. The FTP protocol is used in the deployment phase, and the host name, port number, user name, password and target path of the FTP server are set.
4. Use Webman
After the configuration is completed, we can start using Webman for continuous integration and deployment. Run the following command to execute Webman:
java -jar webman.jar build
This command will execute the build phase in the configuration file and output the build results to the path specified by output-dir. If the build is successful, you can run the following command to execute the deployment phase:
java -jar webman.jar deploy
This command will execute the deployment phase in the configuration file and upload the build results to the specified path of the FTP server.
5. Conclusion
Through the above simple examples, we have learned how to use Webman to achieve continuous integration and deployment of the website. Webman provides a set of simple and easy-to-use tools and APIs to help us improve development efficiency and ensure website quality. At the same time, Webman also supports a variety of build tools and version control systems, which can be flexibly configured according to actual needs. I hope this article can inspire you and help you better apply Webman to achieve continuous integration and deployment.
The above is the detailed content of Use Webman to implement continuous integration and deployment of websites. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
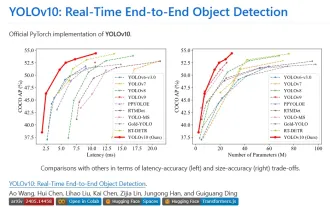 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 pm 12:07 PM
How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 pm 12:07 PM
How to solve the problem that Tomcat cannot successfully access the war package after deploying it requires specific code examples. As a widely used Java Web server, Tomcat allows developers to package their own developed Web applications into war files for deployment. However, sometimes we may encounter the problem of being unable to successfully access the war package after deploying it. This may be caused by incorrect configuration or other reasons. In this article, we'll provide some concrete code examples that address this dilemma. 1. Check Tomcat service
 Jenkins in PHP Continuous Integration: Master of Build and Deployment Automation
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Jenkins in PHP Continuous Integration: Master of Build and Deployment Automation
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
In modern software development, continuous integration (CI) has become an important practice to improve code quality and development efficiency. Among them, Jenkins is a mature and powerful open source CI tool, especially suitable for PHP applications. The following content will delve into how to use Jenkins to implement PHP continuous integration, and provide specific sample code and detailed steps. Jenkins installation and configuration First, Jenkins needs to be installed on the server. Just download and install the latest version from its official website. After the installation is complete, some basic configuration is required, including setting up an administrator account, plug-in installation, and job configuration. Create a new job On the Jenkins dashboard, click the "New Job" button. Select "Frees
 Gunicorn Deployment Guide for Flask Applications
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Gunicorn Deployment Guide for Flask Applications
Jan 17, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to deploy Flask application using Gunicorn? Flask is a lightweight Python Web framework that is widely used to develop various types of Web applications. Gunicorn (GreenUnicorn) is a Python-based HTTP server used to run WSGI (WebServerGatewayInterface) applications. This article will introduce how to use Gunicorn to deploy Flask applications, with
 Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Dec 29, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Best practices and common problem solutions for deploying web projects on Tomcat
Dec 29, 2023 am 08:21 AM
Best practices for deploying Web projects with Tomcat and solutions to common problems Introduction: Tomcat, as a lightweight Java application server, has been widely used in Web application development. This article will introduce the best practices and common problem solving methods for Tomcat deployment of web projects, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand and apply. 1. Project directory structure planning Before deploying a Web project, we need to plan the directory structure of the project. Generally speaking, we can organize it in the following way
 C# Development Advice: Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery Practices
Nov 22, 2023 pm 05:28 PM
C# Development Advice: Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery Practices
Nov 22, 2023 pm 05:28 PM
In the current software development process, continuous integration (ContinuousIntegration) and continuous delivery (ContinuousDelivery) have become key practices for development teams to improve product quality and speed up delivery. Whether you're a large software enterprise or a small team, you can benefit from both areas. This article will provide C# developers with some suggestions on continuous integration and continuous delivery practices. Automated builds and tests Automated builds and tests are the foundation of continuous integration. make
 How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:43 AM
How to solve the problem of inaccessibility after Tomcat deploys war package
Jan 13, 2024 am 11:43 AM
The solution to the problem that Tomcat cannot be accessed after deploying the war package requires specific code examples. Introduction: In Web development, Tomcat is one of the most widely used Java Web servers. However, sometimes after we deploy the war package to Tomcat, there is an inaccessible problem. This article will introduce several situations that may lead to inaccessibility, and give corresponding solutions and code examples. 1. Ensure that the war package has been deployed correctly. The first step is to ensure that the war package has been correctly deployed to Tomcat’s webapp.
 PHP Jenkins 101: The only way to get started with CI/CD
Mar 09, 2024 am 10:28 AM
PHP Jenkins 101: The only way to get started with CI/CD
Mar 09, 2024 am 10:28 AM
Introduction Continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) are key practices in modern software development that help teams deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. Jenkins is a popular open source CI/CD tool that automates the build, test and deployment process. This article explains how to set up a CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins using PHP. Set up Jenkins Install Jenkins: Download and install Jenkins from the official Jenkins website. Create project: Create a new project from the Jenkins dashboard and name it to match your php project. Configure source control: Configure your PHP project's git repository as Jenkin



