Messaging in Java
Introduction
Message passing is a method of transmitting communication between projects or threads and is a basic idea in distributed systems and parallel programming. Depending on the specific needs of the implementation, message transfer in Java can be accomplished through various methods and structures
Use the power source java.util.concurrent container, which provides a series of interfaces and class libraries for establishing and processing threads as active locks and synchronization mechanisms. It is a single method in Java to implement message delivery, such as instances. For example, the Executor interface can be used immediately to execute tasks, while the Blocking Queue connection can be used to pass statements between concurrent processes.
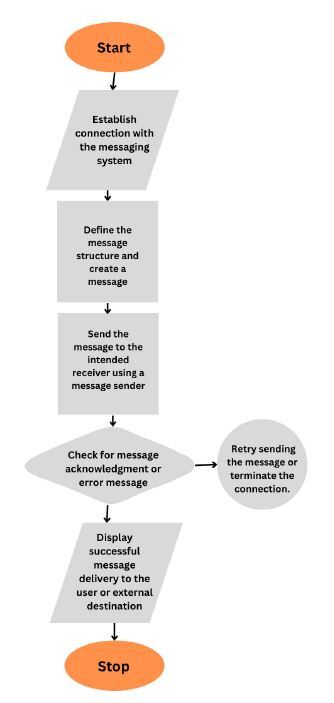
The above is a flow chart of the entire process of message passing in Java.
Interface Type
The Executor interface symbolizes a component that independently performs upload tasks. It allows you to disconnect assignment delivery from task execution, which is useful in situations where responsibilities may take a long time to complete or where multiple tasks must be performed simultaneously. The Executor interface establishes a single method and starts execution (Runnable command), which receives the properties of the Runnable object and schedules its operation.
The previous blocking queue interface represented an array of queues that would block when retrieving components through an empty list or inserting components into a completely full queue. This can be beneficial when chains need to interact with each other by communicating. The Blocking Queue interface includes techniques for adding and obtaining collection components, such as put(E e), take(), and poll().
Points
Another way to transport messages in Java is to leverage communication structures including Apache Kafka or Rabbit MQ. These platforms provide an interconnected communications fabric that enables communications to be exchanged simultaneously between various nodes in the network. Typically, a communication structure consists of multiple elements, including producers, consumers, agents, and topics. Producers are responsible for creating communications, and clients are responsible for consuming them. The agent acts as an intermediary between the business and the customer, and the questions are emblematic of the various types of reports that are created and used.
In addition, Java supports remote invocation (RMI) technology, which enables elements in a single JVM to call methods of components in different JVMs. RMI is a client-server architecture that allows things to pass factors while providing results to each other. RMI enables Java-generated objects to interact with each other over a network, enabling distributed softwareadvantage
Messaging has several advantages in Java programming, making it an effective tool for developing decentralized applications simultaneously. The main benefits of transporting messages in Java include -
Decoupling - The transport of messages enables elements or strings to share information with each other without knowing the underlying implementation details. Given that modifications to a single component of the framework rarely require modifications to the framework's individual components, the resulting decoupling makes programs more customizable and easier to operate.
Concurrency - The transmission of messages enables multiple threads or processes to run at the same time, thereby improving usage efficiency and scalability. Message transport allows applications to better utilize system resources by coordinating operations among individual threads or processes without requiring obvious security or synchronization techniques
Fault Tolerance - Message transport can help improve a system's fault tolerance by providing a way to identify and recover from errors. For example, if a communication fails to reach its intended recipient, the computer system can resend it or take additional steps to repair it.
Scalability - Messaging can improve usage adaptability by enabling it to be executed on multiple nodes in a distributed system. The software can handle more information or requests from customers while avoiding overloading each node by sharing the workload among them.
Interoperability - Messaging enables optimized utilization of interoperability by enabling it to interact with structures employing various coding languages or structures. The program can share information with different systems in an easy and open way by using standardized message and process formats.
shortcoming
Although transmitting messages has many advantages in Java programming, it also has some disadvantages that builders should be aware of before determining whether they should use this method. The main disadvantages of Java messaging are -Overhead - Messaging may add additional overhead to the IT infrastructure because communications must be developed, sent, obtained, and processed by relevant programs. This additional cost can be particularly expensive for programs that must trade large amounts of information or have minimal latency.
Complexity - Messaging complicates programs because it requires programmers to come up with and implement messaging protocols and deal with issues such as message routing, ordering, and error handling. The level of verbosity can make an application more difficult to understand and proceed with, especially for programmers unfamiliar with messaging.
Debugging - Messaging programs are more difficult to troubleshoot than other types of programs because tracing the progress of communication through the system makes it more difficult to locate the root cause of the error. This can make it more difficult to detect and remediate the insect in the process.
Security - Messaging tasks are susceptible to security vulnerabilities, including communication monitoring, modification, or spoofing. Developers must develop appropriate authentication, encryption, and authorization processes to keep the system secure, which adds additional complexity to the implementation.
Performance - While transmitting messages may enhance application performance and scalability in some cases, it may also adversely affect performance in other cases. For example, if a program must frequently transfer small amounts of data, the additional cost of sending messages may outweigh the benefits.
in conclusion
Finally, messaging is an influential approach to serialized and decentralized application development in Java. Decoupling, concurrency, fault tolerance, scalability and interoperability are just some of the benefits. However, it also has certain disadvantages, such as overhead, complexity, difficulty in debugging, security weaknesses, and possible efficiency issues.
Despite these obstacles, messaging remains an effective method for developing robust and marketable programs, especially where significant collaboration or distributed computing is required
The above is the detailed content of Messaging in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.






