Explain the concept of classes in C#
Class is one of the basic types in C#. We can think of a class as a blueprint for objects related to the problem domain. It is a template for the objects we create, defining the structure and behavior that will be shared by sets of objects created from this class. Simply put, the class is a cookie-cutter, and the object is the cookie itself.
Classes also support encapsulation, which is an important concept in object-oriented programming. This means combining data and operations that process the data in one place and providing a simple API to users of that object. Classes allow us to encapsulate data and hide irrelevant details from other classes.
We can create a class using the class keyword followed by the name of the class.
// User.cs
public class User{
private string name;
private int salary;
public void Promote(){
salary += 1000;
}
}In the above example, User is a class that represents the user. This class encapsulates two pieces of data - name and salary. These are called class fields and contain the user's name and salary. It also has a method called Promote() which is used to increase the user's salary.
Each class has an associated access modifier that controls whether the class will be visible to other classes. Below are the five possible values we can provide for the access modifier.
| Access Modifier | Description |
|---|---|
| Public | Unrestricted access |
| Protected | Limited access to derived classes |
| Internal | to program Limited access to assembly |
| Protected internal | Restricted access to assembly or derived class |
| Private | No external access |
To create an instance of a class, we can use the new keyword. The new operator calculates the number of bytes required for an object's data and allocates memory for the object. It then returns a pointer (also called a reference) to the newly created object.
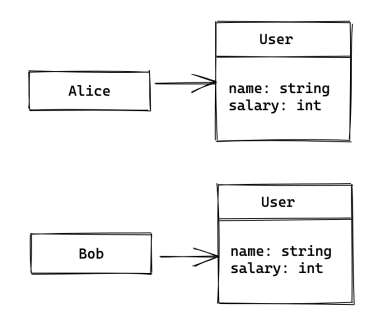
var alice = new User(); var bob = new User();
Then, store this reference in the variable to the left of the equal sign. In the above example, Alice and Bob save a reference or pointer to the newly created object.
In C#, the naming convention of classes follows PascalCase, that is, the first letter of each word in a compound word is capitalized, such as StringBuilder, UserController, etc. There is no need to create a class matching the class name in the file. However, most C# projects use this convention.
Constructor
In the above example, when we created instances of User class (i.e. alice and bob), we did not provide their initial name and salary. Typically, a newly created object requires some information to do its job, and the constructor is used to initialize the class's data.
We can add a constructor to specify the name and salary for the user like this:
public class User{
private string name;
private int salary;
public User(string name, int salary){
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public void Promote(){
salary += 1000;
}
}Having the constructor enables us to pass the user's name and salary when creating a new instance.
var alice = new User("Alice", 50000);
var bob = new User("Bob", 45000);There can be multiple constructors in a class. Having multiple constructors allows us to initialize the class in different ways. For example, we could add another constructor that just takes a username and assigns a default salary.
public User(string name){
this.name = name;
this.salary = 50000;
}Example
Example demonstration
using System;
class Program{
static void Main(){
var alice = new User();
alice.Print();
var bob = new User();
bob.Print();
var chris = new User("Chris", 50000);
chris.Print();
var debs = new User("Debs", 45000);
debs.Print();
var scott = new User("Scott");
scott.Print();
}
}
public class User{
private string name;
private int salary;
public User(){
}
public User(string name){
this.name = name;
this.salary = 50000;
}
public User(string name, int salary){
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public void Promote(){
salary += 1000;
}
public void Print(){
Console.WriteLine($"{name}: {salary}");
}
}Output
: 0 : 0 Chris: 50000 Debs: 45000 Scott: 50000
The above is the detailed content of Explain the concept of classes in C#. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().
 How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
The usage methods of symbols in C language cover arithmetic, assignment, conditions, logic, bit operators, etc. Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, assignment operators are used for assignment and addition, subtraction, multiplication and division assignment, condition operators are used for different operations according to conditions, logical operators are used for logical operations, bit operators are used for bit-level operations, and special constants are used to represent null pointers, end-of-file markers, and non-numeric values.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 .NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
.NET Deep Dive: Mastering Asynchronous Programming, LINQ, and EF Core
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:07 PM
The core concepts of .NET asynchronous programming, LINQ and EFCore are: 1. Asynchronous programming improves application responsiveness through async and await; 2. LINQ simplifies data query through unified syntax; 3. EFCore simplifies database operations through ORM.
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 Avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
A strategy to avoid errors caused by default in C switch statements: use enums instead of constants, limiting the value of the case statement to a valid member of the enum. Use fallthrough in the last case statement to let the program continue to execute the following code. For switch statements without fallthrough, always add a default statement for error handling or provide default behavior.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.






