 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C++
C++
 Given a graph, C program to implement depth-first search (DFS) traversal using adjacency matrix
Given a graph, C program to implement depth-first search (DFS) traversal using adjacency matrix
Given a graph, C program to implement depth-first search (DFS) traversal using adjacency matrix

Introduction
Graph theory allows us to study and visualize relationships between objects or entities. In current computer science technology, graph traversal plays a crucial role in exploring and analyzing different types of data structures. One of the key operations performed on a graph is traversal - following a specific path to visit all vertices or nodes. DFS traversal based on a depth-first approach allows us to explore the depth of the graph before backtracking and exploring other branches. In this article, we will implement DFS traversal using the adjacency matrix representation in C.
Use adjacency matrix for DFS traversal
A graph consists of two main components, namely vertices or nodes that represent entities or elements, and edges that connect these vertices, describing the relationships between them.
The only way to represent the relationship between vertices in a weighted or unweighted graph is through an adjacency matrix. It usually takes the form of a square matrix, where rows represent source vertices and columns represent target vertices, and each cell contains information about the existence or weight of an edge between corresponding pairs.
Example
The input is given through a specific set of elements using the four vertices of the graph. The input is:
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1
Suppose the starting vertex of the graph is 2. The graph will be traversed starting from vertex "2". The adjacent vertices of vertex "2" are obviously 1 and 3. Since the starting vertex is 2, it cannot be accessed again during the traversal. Vertex 3 is visited after vertex 2, then we need to check the adjacent vertices 1 and 2 of vertex 3. Vertex 1 and vertex 2 have been visited and the traversal stops.
Method 1: C program involving DFS traversal using adjacency matrix as input in given graph
The input is defined with some numbers and using a for loop it will iterate the adjacency matrix and return the DFS traversal.
algorithm
Step 1: The program first defines a constant "MAX" to represent the maximum number of nodes in the given graph, and initializes an array named "visited" to track whether a specific node exists during the traversal has been visited.
Step 2: The "dfs()" function takes a square adjacency matrix as a parameter, "adjMatrix" represents our graph, the total number of vertices is "vCount", and the starting vertex is `start`. This function performs a recursive depth-first search traversal of the given graph.
Step 3: In the "dfs()" function, we mark each currently processed vertex as "visited" using the index in the boolean-based "visited[]" array , and print its value accordingly.
Step 4: The loop inside "dfs()" recursively iterates all unvisited neighbors of the current node until it is impossible to obtain a vertex connected to it.
Step 5: In main(), we use a nested loop to read the user's input, such as the number of vertices of "vCount" and their corresponding connections into the adjacency matrix.
Step 6: We then prompt the user for the desired starting vertex and then initialize each element of the "visited[]" array to zero (since no nodes have been visited yet).
Step 7: Finally, the program calls the "dfs()" function with the appropriate parameters to start the depth-first search traversal and prints out the DFS traversal path.
Example
//Including the required header files
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 100
int visited[MAX];
//dfs function is defined with three arguments
void dfs(int adjMatrix[][MAX], int vCount, int start) {
visited[start] = 1;
printf("%d ", start);
for(int i=0; i<vCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[start][i] && !visited[i]) {
dfs(adjMatrix,vCount,i);
}
}
}
//main function is used to implement the above functions
int main() {
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
int vCount;
// Assigning the variable with value of 4
vCount = 4;
// Assigning the adjacency matrix directly same the example given above
adjMatrix[0][0] = 1;
adjMatrix[0][1] = 0;
adjMatrix[0][2] = 0;
adjMatrix[0][3] = 1;
adjMatrix[1][0] = 0;
adjMatrix[1][1] = 1;
adjMatrix[1][2] = 1;
adjMatrix[1][3] = 0;
adjMatrix[2][0] = 0;
adjMatrix[2][1] = 1;
adjMatrix[2][2] = 1;
adjMatrix[2][3] = 0;
adjMatrix[3][0] = 1;
adjMatrix[3][1] = 0;
adjMatrix[3][2] = 0;
adjMatrix[3][3] = 1;
//Declaring the start variable as integer data type and later assigned with a value of 2
int start;
// Assigning the starting vertex directly
start = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX; ++i) {
visited[i] = 0;
}
printf("\nDFS Traversal: ");
dfs(adjMatrix, vCount, start);
return 0;
}
Output
DFS Traversal: 2 1
in conclusion
By using the adjacency matrix as the representation of the graph, we can perform DFS efficiently on large or complex data sets. In this paper, we explain this in detail and propose a C program that implements a depth-first search traversal using an adjacency matrix-based representation. Depth-first search is a powerful algorithm for exploring and analyzing graph structures.
The above is the detailed content of Given a graph, C program to implement depth-first search (DFS) traversal using adjacency matrix. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use Prim's algorithm in C++
Sep 20, 2023 pm 12:31 PM
How to use Prim's algorithm in C++
Sep 20, 2023 pm 12:31 PM
Title: Use of Prim algorithm and code examples in C++ Introduction: Prim algorithm is a commonly used minimum spanning tree algorithm, mainly used to solve the minimum spanning tree problem in graph theory. In C++, Prim's algorithm can be used effectively through reasonable data structures and algorithm implementation. This article will introduce how to use Prim's algorithm in C++ and provide specific code examples. 1. Introduction to Prim algorithm Prim algorithm is a greedy algorithm. It starts from a vertex and gradually expands the vertex set of the minimum spanning tree until it contains
 How to implement graph topological sorting algorithm using java
Sep 19, 2023 pm 03:19 PM
How to implement graph topological sorting algorithm using java
Sep 19, 2023 pm 03:19 PM
How to use Java to implement a topological sorting algorithm for graphs Introduction: Graph is a very common data structure and has a wide range of applications in the field of computer science. The topological sorting algorithm is a classic algorithm in graph theory that can sort a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to determine the dependencies between nodes in the graph. This article will introduce how to use the Java programming language to implement the topological sorting algorithm of the graph, and come with specific Java code examples. 1. Define the data structure of the graph. Before implementing the topological sorting algorithm, we first need to define
 How to use java to implement the Hamiltonian cycle algorithm of graphs
Sep 21, 2023 am 09:03 AM
How to use java to implement the Hamiltonian cycle algorithm of graphs
Sep 21, 2023 am 09:03 AM
How to use Java to implement the Hamiltonian cycle algorithm for graphs. A Hamiltonian cycle is a computational problem in graph theory, which is to find a closed path containing all vertices in a given graph. In this article, we will introduce in detail how to implement the Hamiltonian cycle algorithm using the Java programming language and provide corresponding code examples. Graph Representation First, we need to represent the graph using an appropriate data structure. In Java, we can represent graphs using adjacency matrices or adjacency linked lists. Here we choose to use an adjacency matrix to represent the graph. Define a file called
 In-depth exploration of the application and implementation methods of non-linear data structures of trees and graphs in Java
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:22 AM
In-depth exploration of the application and implementation methods of non-linear data structures of trees and graphs in Java
Dec 26, 2023 am 10:22 AM
Understanding Trees and Graphs in Java: Exploring Applications and Implementations of Nonlinear Data Structures Introduction In computer science, data structures are the way data is stored, organized, and managed in computers. Data structures can be divided into linear data structures and non-linear data structures. Trees and graphs are the two most commonly used types of nonlinear data structures. This article will focus on the concepts, applications and implementation of trees and graphs in Java, and give specific code examples. The Concept and Application of Tree A tree is an abstract data type, a collection of nodes and edges. Each node of the tree contains a number
 How to set up two pictures to animate at the same time in PPT
Mar 26, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
How to set up two pictures to animate at the same time in PPT
Mar 26, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
1. Double-click to open the test document. 2. After clicking the job to create the first ppt document, click Insert--Picture--From File in the menu. 3. Select the file we inserted and click Insert. 4. Insert another one in the same way, and drag and adjust the two pictures to the appropriate position. 5. Select two pictures at the same time, right-click - Group - Group, so that the two pictures become one. 6. Select the merged graphic, right-click - Customize animation. 7. Click Add Effect, select an effect, and click OK. When you look at the PPT, you will find that the two pictures are moving together.
 How to use java to implement the Euler cycle algorithm of graphs
Sep 19, 2023 am 09:01 AM
How to use java to implement the Euler cycle algorithm of graphs
Sep 19, 2023 am 09:01 AM
How to use Java to implement the Euler cycle algorithm for graphs? Euler circuit is a classic graph theory problem. Its essence is to find a path that can pass through each edge in the graph once and only once, and finally return to the starting node. This article will introduce how to use Java language to implement the Euler cycle algorithm of graphs, and provide specific code examples. 1. Graph representation method Before implementing the Euler loop algorithm, you first need to choose a suitable graph representation method. Common representations include adjacency matrices and adjacency lists. In this article, we will use adjacency lists to
 Find the number of sink nodes in a graph using C++
Sep 01, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
Find the number of sink nodes in a graph using C++
Sep 01, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
In this article, we describe important information for solving the number of sink nodes in a graph. In this problem, we have a directed acyclic graph with N nodes (1 to N) and M edges. The goal is to find out how many sink nodes there are in a given graph. A sink node is a node that does not generate any outgoing edges. Here is a simple example - Input:n=4,m=2Edges[]={{2,3},{4,3}}Output:2 Simple way to find the solution In this method we will iterate The edges of the graph, push the different elements from the set pointed to by the edge into it, and then subtract the size of the set from the total number of nodes that exist. Example#include<bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespa
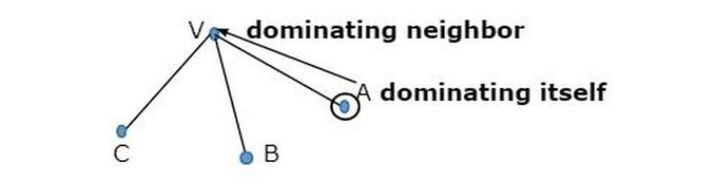 Prove that the dominant set of a graph is NP-complete
Sep 19, 2023 pm 02:09 PM
Prove that the dominant set of a graph is NP-complete
Sep 19, 2023 pm 02:09 PM
A dominant set of a graph is an NP-complete problem, which is a subset of vertices such that every vertex or adjacent vertex in the subset is in the subset. The full form of NP is "non-deterministic polynomial" which will check the problem in polynomial time, meaning we can check in polynomial time whether the solution is correct. Polynomial time has the best complexity for codes like linear search time complexity – n, binary search – logn, merge sort – n(log)n etc. NP-complete graphs provide a good solution in reasonable time. This application is used in areas such as network control, topology creation in computer laboratories, social networks and distributed computing. Let us understand and check whether a node has the dominant set of an NP-complete graph. according to





