A matrix probability problem?

Here we will see a matrix probability problem. We have a rectangular matrix. We can move in four directions from the current cell with equal probability. The four directions are left, right, up, and down. We want to calculate the probability after N moves starting from position M[i,j].
Here we have to do some things related to DFS. We will recursively traverse the four possible rooms starting from the current room. Then we calculate the probability of taking one less step. Since the four directions have equal probabilities, each direction will contribute 0.25 of the total probability. We will return 0 if a matrix boundary is crossed and 1 when N moves are completed. Let's look at the algorithm to get this idea.
Algorithm
matProb(m, n, x, y, N)
Begin if x,y is not in matrix boundary m, n, then return 0 if N is 0 , then return 1 prob := 0 prob := prob + matProb(m, n, x-1, y, N-1) * 0.25 prob := prob + matProb(m, n, x+1, y, N-1) * 0.25 prob := prob + matProb(m, n, x, y+1, N-1) * 0.25 prob := prob + matProb(m, n, x, y-1, N-1) * 0.25 return prob End
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
bool isSafe(int x, int y, int m, int n) { //function to check whether (x,y)
is in matrix or not
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n){
return true;
}
return false;
}
double matProb(int m, int n, int x, int y, int N) {
if (!isSafe(x, y, m, n)) //if coundary is crossed
return 0.0;
if (N == 0) //when N is 0, or N is completed, return 1
return 1.0;
double probability = 0.0;
probability += matProb(m, n, x - 1, y, N - 1) * 0.25; //move left
probability += matProb(m, n, x, y + 1, N - 1) * 0.25; //move up
probability += matProb(m, n, x + 1, y, N - 1) * 0.25; //move right
probability += matProb(m, n, x, y - 1, N - 1) * 0.25; //move down
return probability;
}
int main() {
int m = 7, n = 8;
int x = 1, y = 1;
int N = 4;
cout << "Matrix Probability is " << matProb(m, n, x, y, N);
}Output
Matrix Probability is 0.664062
The above is the detailed content of A matrix probability problem?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
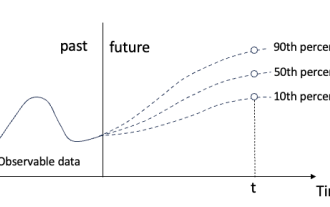 Quantile regression for time series probabilistic forecasting
May 07, 2024 pm 05:04 PM
Quantile regression for time series probabilistic forecasting
May 07, 2024 pm 05:04 PM
Do not change the meaning of the original content, fine-tune the content, rewrite the content, and do not continue. "Quantile regression meets this need, providing prediction intervals with quantified chances. It is a statistical technique used to model the relationship between a predictor variable and a response variable, especially when the conditional distribution of the response variable is of interest When. Unlike traditional regression methods, quantile regression focuses on estimating the conditional magnitude of the response variable rather than the conditional mean. "Figure (A): Quantile regression Quantile regression is an estimate. A modeling method for the linear relationship between a set of regressors X and the quantiles of the explained variables Y. The existing regression model is actually a method to study the relationship between the explained variable and the explanatory variable. They focus on the relationship between explanatory variables and explained variables
 Exploring the History and Matrix of Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence Tutorial (2)
Nov 20, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Exploring the History and Matrix of Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence Tutorial (2)
Nov 20, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
In the first article of this series, we discussed the connections and differences between artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, data science, and more. We also made some hard choices about the programming languages, tools, and more that the entire series would use. Finally, we also introduced a little bit of matrix knowledge. In this article, we will discuss in depth the matrix, the core of artificial intelligence. But before that, let’s first understand the history of artificial intelligence. Why do we need to understand the history of artificial intelligence? There have been many AI booms in history, but in many cases the huge expectations for AI's potential failed to materialize. Understanding the history of artificial intelligence can help us see whether this wave of artificial intelligence will create miracles or is just another bubble about to burst. us
 How to solve the problem that jQuery cannot obtain the form element value
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
How to solve the problem that jQuery cannot obtain the form element value
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:01 PM
To solve the problem that jQuery.val() cannot be used, specific code examples are required. For front-end developers, using jQuery is one of the common operations. Among them, using the .val() method to get or set the value of a form element is a very common operation. However, in some specific cases, the problem of not being able to use the .val() method may arise. This article will introduce some common situations and solutions, and provide specific code examples. Problem Description When using jQuery to develop front-end pages, sometimes you will encounter
 Clustering effect evaluation problem in clustering algorithm
Oct 10, 2023 pm 01:12 PM
Clustering effect evaluation problem in clustering algorithm
Oct 10, 2023 pm 01:12 PM
The clustering effect evaluation problem in the clustering algorithm requires specific code examples. Clustering is an unsupervised learning method that groups similar samples into one category by clustering data. In clustering algorithms, how to evaluate the effect of clustering is an important issue. This article will introduce several commonly used clustering effect evaluation indicators and give corresponding code examples. 1. Clustering effect evaluation index Silhouette Coefficient Silhouette coefficient evaluates the clustering effect by calculating the closeness of the sample and the degree of separation from other clusters.
 Teach you how to diagnose common iPhone problems
Dec 03, 2023 am 08:15 AM
Teach you how to diagnose common iPhone problems
Dec 03, 2023 am 08:15 AM
Known for its powerful performance and versatile features, the iPhone is not immune to the occasional hiccup or technical difficulty, a common trait among complex electronic devices. Experiencing iPhone problems can be frustrating, but usually no alarm is needed. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to demystify some of the most commonly encountered challenges associated with iPhone usage. Our step-by-step approach is designed to help you resolve these common issues, providing practical solutions and troubleshooting tips to get your equipment back in peak working order. Whether you're facing a glitch or a more complex problem, this article can help you resolve them effectively. General Troubleshooting Tips Before delving into specific troubleshooting steps, here are some helpful
 Python program to multiply two matrices using multidimensional arrays
Sep 11, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
Python program to multiply two matrices using multidimensional arrays
Sep 11, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
A matrix is a set of numbers arranged in rows and columns. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an mXn matrix, and m and n are called its dimensions. A matrix is a two-dimensional array created in Python using lists or NumPy arrays. In general, matrix multiplication can be done by multiplying the rows of the first matrix by the columns of the second matrix. Here, the number of columns of the first matrix should be equal to the number of rows of the second matrix. Input and output scenario Suppose we have two matrices A and B. The dimensions of these two matrices are 2X3 and 3X2 respectively. The resulting matrix after multiplication will have 2 rows and 1 column. [b1,b2][a1,a2,a3]*[b3,b4]=[a1*b1+a2*b2+a3*a3][a4,a5,a6][b5,b6][a4*b2+a
 The problem of generalization ability of machine learning models
Oct 08, 2023 am 10:46 AM
The problem of generalization ability of machine learning models
Oct 08, 2023 am 10:46 AM
The generalization ability of machine learning models requires specific code examples. With the development and application of machine learning becoming more and more widespread, people are paying more and more attention to the generalization ability of machine learning models. Generalization ability refers to the prediction ability of a machine learning model on unlabeled data, and can also be understood as the adaptability of the model in the real world. A good machine learning model should have high generalization ability and be able to make accurate predictions on new data. However, in practical applications, we often encounter models that perform well on the training set, but fail on the test set or real
 Label acquisition problem in weakly supervised learning
Oct 08, 2023 am 09:18 AM
Label acquisition problem in weakly supervised learning
Oct 08, 2023 am 09:18 AM
The label acquisition problem in weakly supervised learning requires specific code examples. Introduction: Weakly supervised learning is a machine learning method that uses weak labels for training. Different from traditional supervised learning, weakly supervised learning only needs to use fewer labels to train the model, rather than each sample needs to have an accurate label. However, in weakly supervised learning, how to accurately obtain useful information from weak labels is a key issue. This article will introduce the label acquisition problem in weakly supervised learning and give specific code examples. Introduction to the label acquisition problem in weakly supervised learning:






