C++ program to get the size of a given number

The magnitude of a given number means the difference between that particular number and zero. It can also represent the size of a mathematical object relative to other objects within the mathematical object Same species. We're going to follow the first definition here, and the size or absolute value Numbers are represented as |x|, where x is a real number. We explore ways to show The absolute value or magnitude of a given real number.
Simple method
We can write a program ourselves to find the size of a given real number. this Examples are explained below.
grammar
int value;
if (value < 0) {
value = (-1) * value;
}
algorithm
- Get input in a numeric variable (integer/double).
- If number < 0, then< 0,则
- Number := number * (-1)
- otherwise,
- Return the number as is.
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// finds the magnitude value of a given number
int solve(int value){
// if smaller than zero, then multiply by -1; otherwise return the number itself
if (value < 0) {
value = (-1) * value;
}
// return the magnitude value
return value;
}
int main(){
int n = -19;
//display the number and its magnitude
cout << "The number is: " << n << endl;
cout << "The magnitude value of the number is: " << solve(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
The number is: -19 The magnitude value of the number is: 19
Use abs() function
abs() function returns the absolute value or magnitude of a given number. it All numeric types are supported and can be used in the C STL.
grammar
double value; double absValue = abs(value);
algorithm
Get the numeric input in a variable named value. (name can be anything)
Use the abs() function to convert to the absolute/magnitude value of a given variable.
Display/use magnitude values.
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// finds the magnitude value of a given number
double solve(double value){
// return the magnitude value using the abs function
return abs(value);
}
int main(){
double n = -197.325;
//display the number and its magnitude
cout << "The number is: " << n << endl;
cout << "The magnitude value of the number is: " << solve(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
The number is: -197.325 The magnitude value of the number is: 197.325
in conclusion
Various mathematical operations are required to determine the magnitude value. because Among them, we have to design methods to find the magnitude value and learn Outputs the same various built-in functions. In the given article we have discussed Both methods are suitable for C programming language.
The above is the detailed content of C++ program to get the size of a given number. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Translate the following into Chinese: C program to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
Translate the following into Chinese: C program to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
Given below is a C language algorithm to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers: Algorithm Step 1 - Start Step 2 - Read Roman numerals at runtime Step 3 - Length: = strlen(roman) Step 4 - For i=0 to Length-1 Step 4.1-switch(roman[i]) Step 4.1.1-case'm': &nbs
 C++ program to compare the lexicographic order of two strings
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
C++ program to compare the lexicographic order of two strings
Sep 04, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
Lexicographic string comparison means that strings are compared in dictionary order. For example, if there are two strings 'apple' and 'appeal', the first string will come last because the first three characters of 'app' are the same. Then for the first string the character is 'l' and in the second string the fourth character is 'e'. Since 'e' is shorter than 'l', it will come first if we sort lexicographically. Strings are compared lexicographically before being arranged. In this article, we will see different techniques for lexicographically comparing two strings using C++. Using the compare() function in C++ strings The C++string object has a compare()
![How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/171064142025068.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]
Mar 17, 2024 am 10:10 AM
How to increase disk size in VirtualBox [Guide]
Mar 17, 2024 am 10:10 AM
We often encounter situations where the predefined disk size has no room for more data? If you need more virtual machine hard disk space at a later stage, you must expand the virtual hard disk and partitions. In this post, we will see how to increase disk size in VirtualBox. Increasing the disk size in VirtualBox It is important to note that you may want to back up your virtual hard disk files before performing these operations, as there is always the possibility of something going wrong. It is always a good practice to have backups. However, the process usually works fine, just make sure to shut down your machine before continuing. There are two ways to increase disk size in VirtualBox. Expand VirtualBox disk size using GUI using CL
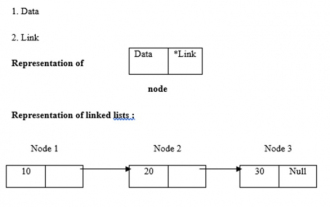 C program to find length of linked list
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
C program to find length of linked list
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
Linked lists use dynamic memory allocation, i.e. they grow and shrink accordingly. They are defined as collections of nodes. Here, a node has two parts, data and links. The representation of data, links and linked lists is as follows - Types of linked lists There are four types of linked lists, as follows: - Single linked list/Singly linked list Double/Doubly linked list Circular single linked list Circular double linked list We use the recursive method to find the length of the linked list The logic is -intlength(node *temp){ if(temp==NULL) returnl; else{&n
 C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Hyperbolic functions are defined using hyperbolas instead of circles and are equivalent to ordinary trigonometric functions. It returns the ratio parameter in the hyperbolic sine function from the supplied angle in radians. But do the opposite, or in other words. If we want to calculate an angle from a hyperbolic sine, we need an inverse hyperbolic trigonometric operation like the hyperbolic inverse sine operation. This course will demonstrate how to use the hyperbolic inverse sine (asinh) function in C++ to calculate angles using the hyperbolic sine value in radians. The hyperbolic arcsine operation follows the following formula -$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\:+\:\sqrt{x^2\:+\:1})}, Where\:In\:is\:natural logarithm\:(log_e\:k)
 C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
The rename function changes a file or directory from its old name to its new name. This operation is similar to the move operation. So we can also use this rename function to move files. This function exists in the stdio.h library header file. The syntax of the rename function is as follows: intrename(constchar*oldname,constchar*newname); The function of the rename() function accepts two parameters. One is oldname and the other is newname. Both parameters are pointers to constant characters that define the old and new names of the file. Returns zero if the file was renamed successfully; otherwise, returns a nonzero integer. During a rename operation
 C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
A map is a special type of container in C++ in which each element is a pair of two values, namely a key value and a map value. The key value is used to index each item, and the mapped value is the value associated with the key. Regardless of whether the mapped value is unique, the key is always unique. To print map elements in C++ we have to use iterator. An element in a set of items is indicated by an iterator object. Iterators are primarily used with arrays and other types of containers (such as vectors), and they have a specific set of operations that can be used to identify specific elements within a specific range. Iterators can be incremented or decremented to reference different elements present in a range or container. The iterator points to the memory location of a specific element in the range. Printing a map in C++ using iterators First, let's look at how to define
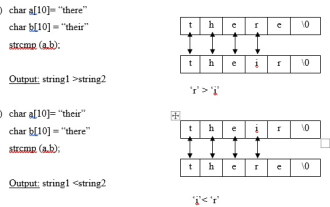 Write a C program that uses the strncmp library function to compare two strings
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
Write a C program that uses the strncmp library function to compare two strings
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
Strncmp is a predefined library function, present in the string.h file, which is used to compare two strings and display which string is larger. strcmp function (string comparison) This function compares two strings. It returns the ASCII difference of the first non-matching character in the two strings. Syntax intstrcmp(string1,string2); If the difference is equal to zero, then string1=string2. If the difference is positive, string1>string2. If the difference is negative, string1<string2. Example strncmp function This function is used to compare the first n characters of two strings. syntax strn




