JavaScript implementation of binary search algorithm
In this article, I will compare linear search and binary search algorithms. You'll learn pseudocode for linear and binary algorithms, view examples demonstrating both approaches, understand time complexity, and get a step-by-step guide on how to implement the algorithms.
Introduction
As a programmer, you want to find the best solution to a problem so that your code is not only correct but also efficient. Choosing a suboptimal algorithm can mean longer completion times, increased code complexity, or worse, program crashes.
You may have used search algorithms to locate items in a data collection. The JavaScript language has several methods (such as find) to find items in an array. However, these methods use linear search. The linear search algorithm starts at the beginning of the list and compares each element to the search value until it is found.
This is good when the number of elements is small. However, when you search large lists containing thousands or millions of elements, you need a better way to locate items. This is when you use binary search.
In this tutorial, I will explain how binary search works and how to implement the algorithm in JavaScript. First, let's review the linear search algorithm.
Linear search
We will first explain how to implement linear search in JavaScript. We will create a function called linearSearch that accepts integers or strings and arrays as parameters. The function will search for the value in each element in the array and, if found, return the value's position in the array. If the value is not in the array, -1 is returned.
Pseudocode for linear search
Set found to false
Set position to −1
Set index to 0
while found is false and index < number of elements
if list[index] is equal to search value
Set found to true
Set position to index
else Add 1 to index
return position
Step-by-step instructions for linear search
Suppose the input of our linear search is [1,9,13,16,3,4,0,12]. If the value we are searching for is 16, the above logic will return 3. And, if we search for 11, the above logic will return -1. Let's break it down.
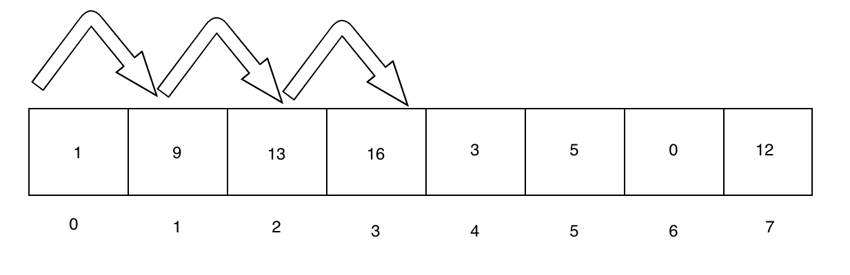
We do this by setting found to false, position to -1, and index Set to 0 to initialize the algorithm. Then we iterate:
| step | index |
List[index] |
Location |
turn up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
1 |
-1 |
false |
| 2 | 1 |
9 |
-1 |
false |
| 3 | 2 |
13 |
-1 |
false |
| 4 | 3 |
16 |
3 |
true |
如果我们对数组中不存在的元素遵循上述逻辑,您将看到代码返回 -1,因为 found = false,并且 position = -1 直到最后。
线性搜索的Javascript实现
这是线性搜索算法的 JavaScript 实现:
function linearSearch(value, list) {
let found = false;
let position = -1;
let index = 0;
while(!found && index < list.length) {
if(list[index] == value) {
found = true;
position = index;
} else {
index += 1;
}
}
return position;
}
线性搜索的属性
需要注意的是,线性搜索算法不需要使用排序列表。此外,该算法可以定制以用于不同的场景,例如通过键搜索对象数组。如果您有一个包含名字和姓氏键的客户数据数组,您可以测试该数组是否包含具有指定名字的客户。在这种情况下,您不需要检查 list[index] 是否等于我们的搜索值,而是检查 list[index].first。
线性搜索的时间复杂度
如果搜索的元素是列表中的第一个元素,则可以实现最佳情况的时间复杂度。现在,搜索只需一次比较即可完成。因此,最好情况的时间复杂度为O(1)。
如果搜索的元素是最后一个元素或者不存在于列表中,则会出现最坏情况的时间复杂度。在这种情况下,搜索必须比较数组中的所有元素。我们说输入数据的长度为 n,这意味着由于进行了 n 次比较,总体时间复杂度为 O(n)。
在上面的示例中,我在包含八个元素的数组上使用了 linearSearch 函数。在最坏的情况下,当搜索值不在列表中或位于列表末尾时,该函数将必须进行八次比较。因为我们的数组很小,所以不需要使用不同的算法进行优化。然而,超过某一点,使用线性搜索算法就不再有效,这时使用二分搜索算法会更好。
线性搜索的平均时间复杂度也是O(n)。
线性搜索的空间复杂度
该算法的整体空间复杂度相当于数组的大小。因此,O(n)。您不需要保留任何额外的空间来完成此算法。
二分查找
假设您正在玩一个猜数字游戏。系统会要求您猜测 1 到 100 之间的一个数字。如果您的数字过高或过低,您将会得到提示。
您的策略是什么?你会随机选择数字吗?您会从 1 开始,然后是 2,依此类推,直到您猜对为止?即使您有无限的猜测,您也希望在尽可能少的尝试中做出正确的猜测。因此,您可以从猜测 50 开始。如果数字较大,您可以猜测 75。如果数字较小,则意味着数字在 50 到 75 之间,您会选择中间的数字。你会继续这样,直到得到正确的数字。这类似于二分搜索的工作原理。
有两种实现二分查找的方法:
- 迭代法
- 递归方法
迭代二分搜索的伪代码
下面是一些使用迭代方法表达二分搜索的伪代码:
do until the low and high pointers have not met or crossed
mid = (low + high)/2
if (x == arr[mid])
return mid
else if (x > arr[mid])
low = mid + 1
else
high = mid - 1
递归二分搜索的伪代码
这是使用递归方法实现二分查找的伪代码。
binarySearch(arr, x, low, high)
if low > high
return False
else
mid = (low + high) / 2
if x == arr[mid]
return mid
else if x > arr[mid]
return binarySearch(arr, x, mid + 1, high)
else
return binarySearch(arr, x, low, mid - 1)
无论使用何种技术,二分搜索算法始终使用分而治之的方法。
分步说明
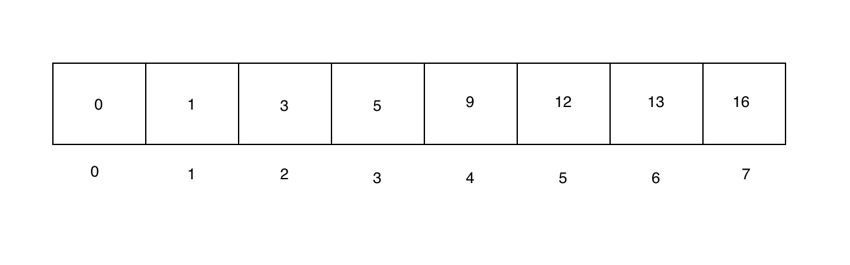
让我们考虑一个数组 [1,9,13,16,3,5,0,12],其中 searchValue 是 13。
我们从执行二分搜索所需的排序数组开始。请注意,对数组进行排序的成本很高,但一旦完成,就可以多次有效地搜索该数组。
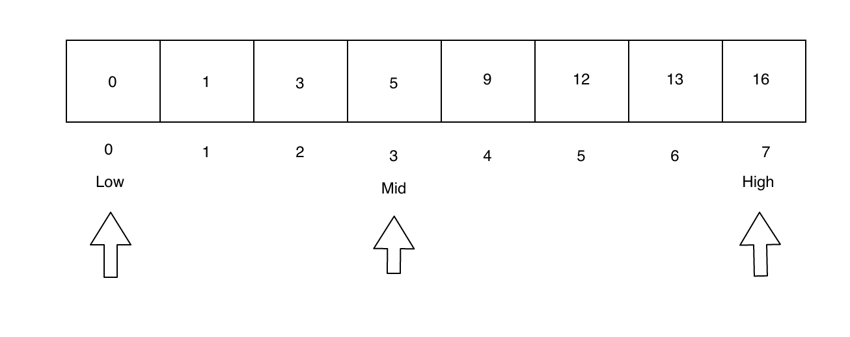
现在,高指针和低指针将分别设置为第一个和最后一个元素。中间指针设置为 (low - high) / 2 给出的索引。
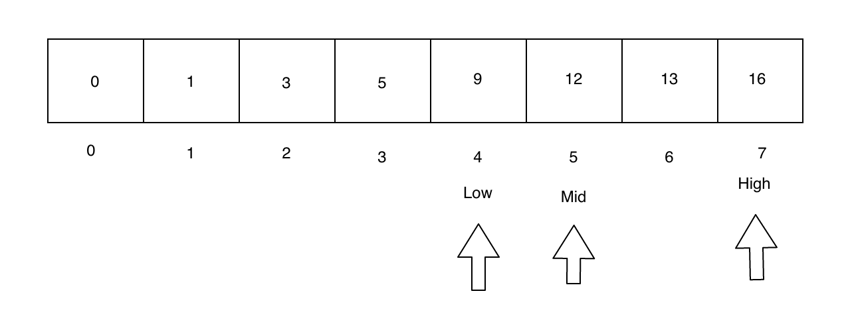
由于 searchValue > mid,我们需要搜索数组的右侧。因此,我们将 low 指针设置为紧接在 mid 之后,并将 mid 重置为位于 low 和 high 指针之间。
同样,目标值位于数组的右侧。我们再次调整低指针和高指针。现在低和中指针是相同的。
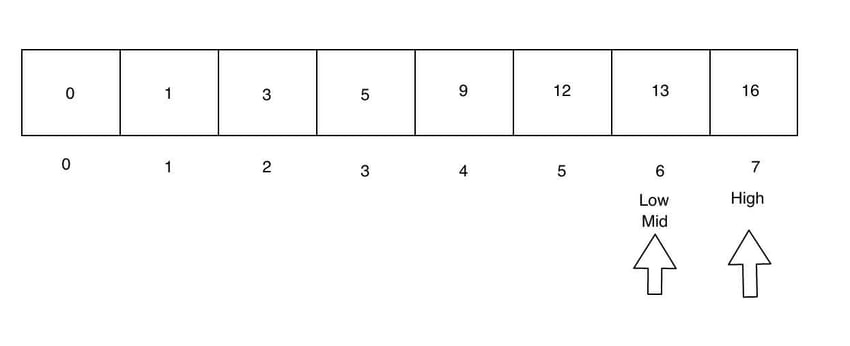
现在,在 mid 处找到了 searchValue,这意味着我们已经到达搜索的末尾!
| 步骤 | low |
mid |
high |
列表[mid] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
3 |
7 |
5 |
| 2 | 4 |
5 |
7 |
9 |
| 3 | 6 |
6 |
7 |
13 |
二分查找的Javascript实现
现在让我们用 JavaScript 编写二分搜索算法!
我们将创建一个函数 binarySearch,它接受一个值和一个数组作为参数。如果找到该值,它将返回列表中出现该值的索引。如果没有找到该值,则返回-1。这是我们用 JavaScript 编写的实现:
//note that list must be sorted for this function to work
function binarySearch(value, list) {
let low = 0; //left endpoint
let high = list.length - 1; //right endpoint
let position = -1;
let found = false;
let mid;
while (found === false && low <= high) {
mid = Math.floor((low + high)/2);
if (list[mid] == value) {
found = true;
position = mid;
} else if (list[mid] > value) { //if in lower half
high = mid - 1;
} else { //in in upper half
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return position;
}
时间复杂度
我们使用二分搜索来查找数组中的元素的主要原因之一是它的时间复杂度。在最佳情况下,二分查找的时间复杂度为O(1)。当数组中间的元素与搜索元素匹配时,就会发生这种情况。
在最坏的情况下,使用二分搜索搜索元素的时间复杂度为 O(log n) — 对于较大的 n 值,远低于 O(n)。要了解 log(n) 的增长速度比 n 慢多少,这里有一个 log(n) 典型值表.
| n | 日志(n) |
| 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 3 |
| 1024 | 10 |
| 1,000,000 | 19.9 |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 59.8 |
因此,正如您所看到的,n 越大,二分搜索相对于线性搜索的改进就越大。
对于使用二分搜索来搜索项目,平均情况时间复杂度也是O(log n)。
空间复杂度
实现二分查找的空间复杂度还是O(n)。
二分查找的属性
与线性搜索不同,二分搜索使用排序列表。这让我们可以使用“分而治之”的算法来解决问题。
结论
在本教程中,我们了解了如何实现线性搜索和二分搜索算法。线性搜索算法更简单,并且不需要排序数组。然而,使用较大的数组效率很低。在最坏的情况下,算法必须搜索所有元素进行 n 次比较(其中 n 是元素数量)。
二分查找算法则需要先对数组进行排序,并且实现起来比较复杂。然而,即使考虑到排序成本,它的效率也更高。例如,具有 10 个元素的数组对于二分搜索最多进行 4 次比较,而对于线性搜索则最多进行 10 次比较,这并不是一个很大的改进。然而,对于具有 1,000,000 个元素的数组,二分查找的最坏情况也只有 20 次比较。这相对于线性搜索来说是一个巨大的改进!
了解如何使用二分搜索不仅仅是面试问题的练习。这是一项实用技能,可以让您的代码更高效地工作。
这篇文章已根据 Divya Dev 的贡献进行了更新。 Divya 是一位拥有五年以上经验的前端开发人员。她是安娜大学的毕业生和金牌获得者。
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript implementation of binary search algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Discussion on the realization of parallax scrolling and element animation effects in this article will explore how to achieve similar to Shiseido official website (https://www.shiseido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/)...
 The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
In-depth discussion of the root causes of the difference in console.log output. This article will analyze the differences in the output results of console.log function in a piece of code and explain the reasons behind it. �...
 Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Learning JavaScript is not difficult, but it is challenging. 1) Understand basic concepts such as variables, data types, functions, etc. 2) Master asynchronous programming and implement it through event loops. 3) Use DOM operations and Promise to handle asynchronous requests. 4) Avoid common mistakes and use debugging techniques. 5) Optimize performance and follow best practices.
 Can PowerPoint run JavaScript?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
Can PowerPoint run JavaScript?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
JavaScript can be run in PowerPoint, and can be implemented by calling external JavaScript files or embedding HTML files through VBA. 1. To use VBA to call JavaScript files, you need to enable macros and have VBA programming knowledge. 2. Embed HTML files containing JavaScript, which are simple and easy to use but are subject to security restrictions. Advantages include extended functions and flexibility, while disadvantages involve security, compatibility and complexity. In practice, attention should be paid to security, compatibility, performance and user experience.




