How many non-access modifiers are there in Java?

Java provides some other modifiers to provide functionality beyond visibility. These modifiers are called non-access modifiers
- static Members declared as static are common to all instances of the class. Static members are class-level members that are stored in class memory.
- Final This modifier is used to restrict further modifications to a variable, method, or class. The value of a variable declared final cannot be modified once it obtains its value. Final methods cannot be overridden in subclasses, nor can you create subclasses of the Final class.
- AbstractThis modifier can be used with a class or method. You cannot apply this modifier to variables and constructors. Methods declared abstract must be modified in subclasses. You cannot instantiate a class declared abstract.
- SynchronizationThis modifier is used to control access to a specific method or block by multiple threads. Only one thread can enter a method or block declared as synchronized.
- Transient This modifier is used in the serialization process. Variables declared as transient are not serialized during object serialization.
- Volatile The volatile modifier is used in multi-threaded programming. If you declare a field as volatile, it signals to threads that its value must be read from main memory rather than from their own stack. Because volatile fields are common to all threads and will be updated frequently by multiple threads.
- Strictfp This modifier is used for floating point calculations. This keyword ensures that you get the same floating point representation on every platform. This modifier makes floating point variables more consistent across multiple platforms.
The above is the detailed content of How many non-access modifiers are there in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The difference between final, finally, and finalize in Java
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:16 PM
The difference between final, finally, and finalize in Java
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:16 PM
The difference between final, finally, and finalize in Java requires specific code examples. In Java programming, you often encounter the three keywords final, finally, and finalize. Although they are spelled similarly, they have different meanings and usages. This article will explain the differences between these three keywords in detail and give code examples to help readers better understand. 1. Final keyword The final keyword can be used for classes, methods and variables. Its function is to make the modified class
 In Java, is it possible to define a constant using only the final keyword?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
In Java, is it possible to define a constant using only the final keyword?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
A constant variable is a variable whose value is fixed and only one copy exists in the program. Once you declare a constant variable and assign a value to it, you cannot change its value again throughout the program. Unlike other languages, Java does not directly support constants. However, you can still create a constant by declaring a variable static and final. Static - Once you declare a static variable, they will be loaded into memory at compile time, i.e. only one copy will be available. Final - Once you declare a final variable, its value cannot be modified. Therefore, you can create a constant in Java by declaring the instance variable as static and final. Example Demonstration classData{&am
 What is the function of java final keyword
Nov 25, 2022 pm 04:26 PM
What is the function of java final keyword
Nov 25, 2022 pm 04:26 PM
In Java, final can be used to modify classes, methods and variables. The final modified class means that the class cannot be inherited by any other class, which means that this class is a leaf class in an inheritance tree, and the design of this class has been considered perfect and does not need to be modified or extended. The method in the final modified class means that the class cannot be inherited by any other class and cannot be overridden; that is, the method is locked to prevent the inherited class from changing it. final modifies a variable in a class, indicating that the variable cannot be changed once it is initialized.
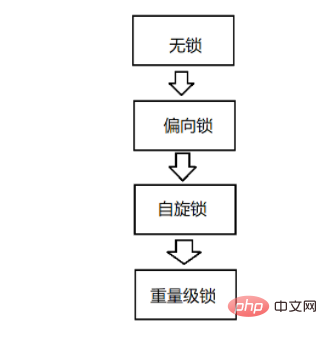 The principles and usage scenarios of Synchronized in Java and the usage and difference analysis of the Callable interface
Apr 21, 2023 am 08:04 AM
The principles and usage scenarios of Synchronized in Java and the usage and difference analysis of the Callable interface
Apr 21, 2023 am 08:04 AM
1. Basic features 1. It starts with an optimistic lock, and if lock conflicts are frequent, it is converted to a pessimistic lock. 2. It starts with a lightweight lock implementation, and if the lock is held for a long time, it is converted to a heavyweight lock. 3. The spin lock strategy that is most likely used when implementing lightweight locks 4. It is an unfair lock 5. It is a reentrant lock 6. It is not a read-write lock 2. The JVM will synchronize the locking process Locks are divided into no lock, biased lock, lightweight lock, and heavyweight lock states. It will be upgraded sequentially according to the situation. Biased lock assumes that the male protagonist is a lock and the female protagonist is a thread. If only this thread uses this lock, then the male protagonist and the female protagonist can live happily forever even if they do not get a marriage certificate (avoiding high-cost operations). But the female supporting role appears
 How are final objects created in Java?
Apr 11, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
How are final objects created in Java?
Apr 11, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
There are two ways to create final objects in Java: declaring a final variable or declaring a class using the final modifier. When a final variable is declared, the object is created through an initializer; when a final class is declared, the class instance is immutable. Importantly, references to final objects can still change, but the objects they point to are immutable.
 What is the function and usage of static in C language
Jan 31, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
What is the function and usage of static in C language
Jan 31, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
The role and usage of static in C language: 1. Variable scope; 2. Life cycle; 3. Internal function; 4. Modify global variables; 5. Modify function; 6. Other uses; Detailed introduction: 1. Variable scope, when If there is the static keyword before a variable, then the scope of the variable is limited to the file in which it is declared. In other words, the variable is a "file-level scope", which is very useful for preventing the "duplicate definition" problem of variables; 2. Life cycle, static variables are initialized once when the program starts executing, and destroyed when the program ends, etc.
 How to use static, this, super, and final in Java
Apr 18, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use static, this, super, and final in Java
Apr 18, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
1. static Please look at the following program first: publicclassHello{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//(1)System.out.println("Hello, world!");//(2)}} Have seen this Segment programs are familiar to most people who have studied Java. Even if you have not learned Java but have learned other high-level languages, such as C, you should be able to understand the meaning of this code. It simply outputs "Hello, world" and has no other use. However, it shows the main purpose of the static keyword.
 final variable in java
Sep 24, 2023 pm 08:49 PM
final variable in java
Sep 24, 2023 pm 08:49 PM
Final variables can only be explicitly initialized once. A reference variable declared as Final can never be reassigned to refer to a different object. However, the data within the object can be changed. Therefore, the state of the object can change, but the reference cannot. For variables, the final modifier is usually used with static to make the constant a class variable. Example publicclassTest{ finalintvalue=10; //Thefollowingareexamplesofdeclaringconstants: &a




