24 Effective Strategies for Implementing AJAX
Twice a month we revisit some of our readers' favorite posts from Nettuts history.
Implementing AJAX technology can be an accidental thing. If it's done well, users will rave about the smoothness it provides to the general user experience, and if you mess up, you'll be subject to their wrath. Here are 24 tips to guide you through the process of implementing AJAX technology in your web applications.
1.Understand what it all means
First, you need to understand what AJAX is, what it stands for, and how it has revolutionized certain parts of the Internet. Before making an informed decision, you need to understand what its advantages are
The following is a list of must-read articles to help you get started quickly.
- Wikipedia
- AJAX-based MDC
- DevX
2.Check appropriate usage scenarios
AJAX sounds great, but there are only so many places you can implement it without sounding like another bullet point. Conduct proper research and testing to ensure you are implementing AJAX for the right reasons. Because it sounds good is not a valid reason.
The correct usage scenario is if you have a lot of data on the backend and want to update the UI when the user needs to access that data, or when you want to emulate a proper desktop application and handle everything asynchronously. An extremely bad situation is when you load every page of your static website via AJAX for no reason. Please use your judgment here.
3.Learn to use original code implementation
Before you dive into coding, understand the original code. Libraries are great for reducing the time needed to create browser-agnostic code, but when something goes wrong with your code, it's better to know how to do it without the help of a library.
I highly recommend Jeffrey's tutorials on making AJAX requests using raw JavaScript (here and here).
4.Use library
Once you have mastered raw JS handling AJAX implementation, it is best to move to JavaScript libraries that provide strong support for AJAX. Any major library like jQuery, Prototype or MooTools should do the trick.
The library not only provides an exhaustive feature set that you can use, but also ensures that your code is compatible with all browsers without requiring you to do any extra action.
Here are some of our favorite features that include proper AJAX functionality:
- jQuery
- Dojo
- MooTools
- prototype
- Yahoo User Interface Library
- Google Network Toolkit
5.Master the Library
Once you've mastered making AJAX requests using your library of choice, it's time to take it to the next level and master it. It may sound redundant, but there is a big difference between the two.
As each library gets bigger and each version contains more features, developers hide a lot of functionality from beginners. For example, did you know that there are multiple ways to make AJAX calls in jQuery? Or are many of the event firing methods only available for core AJAX calls? Many people don't know this and therefore fail to take advantage of the untapped potential of libraries.
Here are some curated resources for your perusal:
- jQuery 1.4 Reference Guide
- jQuery Enlightenment
- Learn the advanced parts of jQuery
- Comparison between jQuery and MooTools
6.Provide feedback
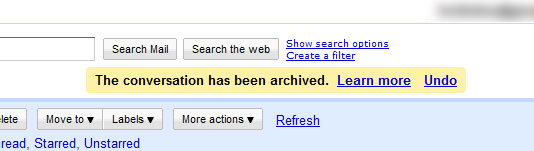
The main reason people used to object to AJAX was that they couldn't really tell when the application had updated the data it contained. This is also an integral part of the general user experience and is more relevant to AJAX.
So, even if it’s the smallest thing, remember to provide feedback to users to let them know that their actions have been registered. Did the user click the button? Let them know!
7.Utilize appropriate events and callback functions
Whether you use raw JS or a library to implement this functionality, you can access the status of the request, i.e. whether the request was successful; encountered an error, and finally completed.
Properly use these events and their respective callbacks to manipulate the UI for a better user experience. For example, if the request was unsuccessful, you need to update the UI to reflect that their changes were unsuccessful, and if they were successful, you need to tell them. Don't make users wait!
With jQuery, you can use success and error callbacks. You can also call other callbacks such as complete and beforeSend for appropriate use.
$.ajax({
//Other code
success: function(msg)
{
// Update the UI here to reflect that the request was successful.
doSomethingClever();
},
error: function(msg)
{
// Update the UI here to reflect that the request was unsuccessful
doSomethingMoreClever();
},
complete: function(msg)
{
// Update the UI here to reflect completion
doSomethingEvenMoreClever();
}
});
- Display quoted text -
8.Choose the correct format for the job
Just because XML appears in an abbreviation doesn't mean you can only use XML as the payload. You are free to choose any format you like. JSON? certainly. XML? nature. HTML? certainly. Raw string? certainly.
所以,本质上,无论什么事情都能让你的船漂浮。您不限于任何格式。您可以选择使您手头的工作更轻松并且对特定实例最有意义的格式。
9.广泛阅读
AJAX 虽然相对而言很古老,但仍然在不断变化。令人兴奋的新解决方案每天都会被创造出来,同时经常会发布涵盖该主题的极其详尽的书籍。无论是网络开发博客(就像这个!)还是书籍,请继续阅读以了解最新的发展。
以下是我最常访问和/或阅读最多的博客和书籍:
- CSS 技巧
- 斯努克.ca
- 詹姆斯·帕多尔西的博客
- 雷米·夏普的博客
10.不断实验
阅读一本书又一本书、一篇又一篇文章固然很棒,但要掌握该主题,您需要卷起袖子自己编写一些代码。相信我,与仅仅连续阅读而不编写任何代码来更好地理解您所学的内容相比,您会更快地学到更多知识,然后编写一些相关代码。
11.利用Firebug
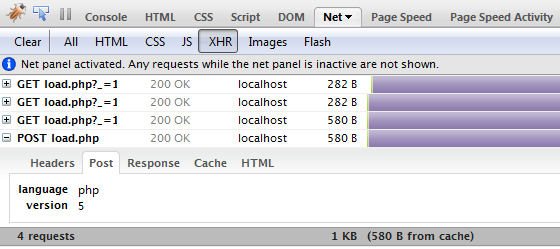
Firebug 可以说是每个 Web 开发人员手中最重要的工具。除了令人印象深刻的 JavaScript 调试和其他强大功能之外,它还可以让您查看每个 AJAX 请求的发出情况以及有关该请求的无数其他详细信息,包括它的来源、其有效负载是什么等等。您可以在这里下载。
这里还有一些推荐的资源:
- 您应该使用 Firebug 的 10 个理由
- Firebug 解释
- 如何将 Firebug 与 CSS 结合使用
- 使用 Firebug 轻松实现 CSS
12.牢记使用旧浏览器的用户
除非您的网络应用程序类似于 Google 地图,否则为用户提供后备方案始终是一个好主意,以便他们仍然可以使用您的应用程序。典型的例子是许多 Web 应用程序,如果它们有能力的话,它们会通过 AJAX 路由所有用户交互,否则会回退到正常的 HTML 版本。
13.可书签性
添加书签的倾向是普通网络用户的普遍习惯,您的应用程序必须尊重这一点。使用 AJAX,浏览器的地址栏不会更新,这意味着当用户想要为包含通过 AJAX 动态加载的内容的页面添加书签时,他/她将添加初始页面而不是更新的页面。这提出了一个巨大的问题。
幸运的是,有一些技术可以解决这个问题。以下是旨在帮助您解决此问题的精选文章列表:
- 内容与风格
- jQuery 历史记录插件
- 非常简单的历史
14.使用适当的动画
这是另一个用户体验问题,可能会损害原本出色的应用程序。通常,对于 AJAX 应用程序,用户可能甚至没有注意到用户界面的元素或其包含的数据发生了更改。鉴于此问题,开发人员必须使用不花哨、有品味的动画来吸引用户的注意,即用户界面已更新以反映用户的操作。
您可以在此处了解如何使用 jQuery 创建高雅的跨浏览器动画。
15.尊重后退按钮
后退按钮是另一个已成为普通网络用户习惯的操作。确保您的应用程序遵循这一受人尊敬的范例,以避免激怒用户。相信我,如果后退按钮突然无法按预期工作,他们会的。
这里是一个文章列表,应该可以帮助您解决这个问题。
- 内容与风格
- jQuery 历史记录插件
- 非常简单的历史
16.智能地改变DOM
想象一下:您的请求已成功并返回了您希望用来更新用户界面的数据块。如果该数据块几乎没有单独的块,您可以照常继续。相反,如果有 15 个连续元素需要更新,最好只创建这些元素,在内存中修改它们的数据,然后一次性替换 DOM 中的数据,而不是每次都单独访问每个元素并更新 DOM .
随着要进行的编辑数量的增加,单独修改 DOM 会导致性能变差。
因此,对于像这样的 HTML 块:
<div id="container"> <span id="elem1"></span> <span id="elem2"></span> </div>
而不是这样做:
$("#elem1").html("Value 1");
$("#elem2").html("Value 2");
这样做:
var updatedText = "<span id=\"elem1\">Value1</span>
<span id=\"elem2\">Value2</span>";
$("#container").html(updatedText);
仅两个元素可能看起来需要大量工作,但一旦您将其推断为更多元素,仅性能就值得了。它会更快,因为无论更新后的 HTML 中有多少元素,您都只需更新 DOM 一次。但使用通常的方法时,DOM 所需的编辑次数与元素数量成线性比例,这反过来又降低了性能。
17.评论您的代码
这是显而易见的,但请正确注释您的代码。很有可能,您的代码至少会被数百人查看,希望向您学习,并且发表评论肯定会为您赢得额外的代表积分和典范饼干。
您不一定需要注释代码的每一点;仅评论重要的部分就足够了。
这太过分了!
$.ajax({
// Switch off caching
cache: false,
//Set the type of request
type: "GET",
// Set the timeout
timeout: 5000,
// Specify the proper handler
url: "handler.php",
success: function(msg)
{
// Update the UI here to reflect that the request was successful.
doSomethingClever();
},
error: function(msg)
{
// Update the UI here to reflect that the request was unsuccessful
doSomethingMoreClever();
}
});
这是一种更好的添加评论的方式,因为其中很多内容都是不言自明的。
// Make an AJAX call to handler.php and update the UI
$.ajax({
cache: false,
type: "GET",
timeout: 5000,
url: "handler.php",
success: function(msg)
{
doSomethingClever();
},
error: function(msg)
{
doSomethingMoreClever();
}
});
18.对请求类型做出明智的决定
这严格来说是一个通用的 Web 应用程序提示,而不是专门的 AJAX 提示,但请特别注意您发出的请求类型:GET 或 POST。 XMLHttpRequest 对象能够发出两种类型的请求,但由您决定发出哪种类型的请求。
顾名思义,GET 请求用于从源获取数据,而 POST 请求用于提交要处理的数据。对于 AJAX GET 请求,与普通 GET 请求一样,您必须手动将查询数据作为 URL 本身的一部分传递,而不是自动发送数据的 POST 请求。另请注意,GET 请求会自动缓存,而 POST 请求则不会。
19.使用合适的IDE
当谈到 JavaScript 时,请不要成为精英主义者并限制自己使用普通的老式记事本。使用合适的 IDE,特别是支持您选择的 JavaScript 库的 IDE,您的工作效率将会大幅提升。
对于 PC 忠实用户
- InType
- 电子文本编辑器
- Notepad++
- Aptana
- DreamWeaver CS4
献给我的果味弟兄们
- Coda
- 浓缩咖啡
- TextMate
- Aptana
- DreamWeaver CS4
20.参与社区
像这样成为出色的 Web 开发社区的一部分,不仅会让您接触到更广泛的想法,还会引导您走上编写更好代码的道路。通过撰写和评论类似的文章,您不仅可以向那些在该主题上知识水平不如您的人传授知识,还可以从对您的代码进行评论的更有经验的人那里学到更多东西。
正如杰夫所说,只有当你把某件事教给别人时,你才能真正理解它。
21.调整您的响应时间
我所说的响应时间仅指一件事:用户触发 AJAX 请求之前的时间。考虑一下,您正在使用 AJAX 从服务器检索搜索建议的输入框中键入内容。响应时间是按键和发出 AJAX 调用之间的持续时间。太快了,您将不得不对搜索短语的每个字母执行多个请求。太慢,您会让用户绞尽脑汁想知道他是如何破坏应用程序的。
这不仅限于上述情况。这适用于每个非确定(点击)用户操作。与您的用户一起进行严格测试,以找到最佳延迟。
22.使用状态指示器
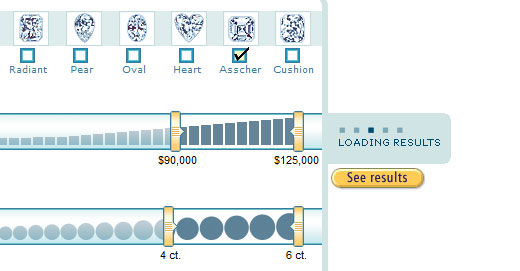
这是上述观点的延伸,但同样重要。来自桌面应用程序或一般 Web 应用程序范例的用户在使用支持 AJAX 的 Web 应用程序时会感到困惑。虽然在进行更改时通知用户是件好事,但您还需要确保首先让他们知道请求已启动。
这就是状态指示器的作用。这些是您在应用程序中看到的旋转或弹跳的小 GIF。在功能上,它们类似于桌面操作系统中使用的沙漏光标。
这是一个很棒的小工具,可以让您创建您选择的指标。
23.欣赏 JSON-P 的强大功能
通常,作为您创建的跨站点混搭的一部分,您需要通过 AJAX 请求访问其他站点的数据。这直接违背了大多数浏览器强制执行的跨域限制。在这种情况下,您可以只使用 JSON-P,而不是采用屏蔽和代理等奇特解决方案。
JSON-P,即带填充的 JSON,本质上可以让我们规避此限制,并让我们从第三方域获取数据。以下是帮助您入门的文章列表:
- 维基百科链接
- 雷米·夏普的博客
- 詹姆斯·帕多尔西的博客
24.自由提问
不要羞于提问。我们每个人都是从新手开始的,都是从提问开始的。有很多地方可以澄清您的疑虑,包括 Nettuts+ 的评论部分。永远、永远不要害怕提问。尽量表现得有礼貌一点!它总是有帮助的。
This is everyone
We're done. Twenty-four points to remember when implementing AJAX in your site or web application. Hope this is useful to you and you find it interesting. I'll keep an eye on the comments section and if you have any counterarguments or different opinions on the matter, please leave a comment.
Have questions? Have something nice to say? criticize? Hit the comments section and leave me a message. Happy coding!
Writing Plus Tutorial
Did you know you can earn up to $600 writing PLUS tutorials and/or screencasts for us? We are looking for in-depth and well-written tutorials on HTML, CSS, PHP and JavaScript. If you are able, please contact Jeffrey at nettuts@tutsplus.com.
Please note that actual compensation will depend on the quality of the final tutorial and screencasts.

- Follow us on Twitter or subscribe to the Nettuts RSS Feed for the best web development tutorials on the web.
The above is the detailed content of 24 Effective Strategies for Implementing AJAX. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Detailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 Custom Google Search API Setup Tutorial
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:06 AM
Custom Google Search API Setup Tutorial
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:06 AM
This tutorial shows you how to integrate a custom Google Search API into your blog or website, offering a more refined search experience than standard WordPress theme search functions. It's surprisingly easy! You'll be able to restrict searches to y
 Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
So here you are, ready to learn all about this thing called AJAX. But, what exactly is it? The term AJAX refers to a loose grouping of technologies that are used to create dynamic, interactive web content. The term AJAX, originally coined by Jesse J
 Example Colors JSON File
Mar 03, 2025 am 12:35 AM
Example Colors JSON File
Mar 03, 2025 am 12:35 AM
This article series was rewritten in mid 2017 with up-to-date information and fresh examples. In this JSON example, we will look at how we can store simple values in a file using JSON format. Using the key-value pair notation, we can store any kind
 8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout Plugins
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout Plugins
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
Leverage jQuery for Effortless Web Page Layouts: 8 Essential Plugins jQuery simplifies web page layout significantly. This article highlights eight powerful jQuery plugins that streamline the process, particularly useful for manual website creation
 What is 'this' in JavaScript?
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:15 AM
What is 'this' in JavaScript?
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:15 AM
Core points This in JavaScript usually refers to an object that "owns" the method, but it depends on how the function is called. When there is no current object, this refers to the global object. In a web browser, it is represented by window. When calling a function, this maintains the global object; but when calling an object constructor or any of its methods, this refers to an instance of the object. You can change the context of this using methods such as call(), apply(), and bind(). These methods call the function using the given this value and parameters. JavaScript is an excellent programming language. A few years ago, this sentence was
 Improve Your jQuery Knowledge with the Source Viewer
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
Improve Your jQuery Knowledge with the Source Viewer
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
jQuery is a great JavaScript framework. However, as with any library, sometimes it’s necessary to get under the hood to discover what’s going on. Perhaps it’s because you’re tracing a bug or are just curious about how jQuery achieves a particular UI
 10 Mobile Cheat Sheets for Mobile Development
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
10 Mobile Cheat Sheets for Mobile Development
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
This post compiles helpful cheat sheets, reference guides, quick recipes, and code snippets for Android, Blackberry, and iPhone app development. No developer should be without them! Touch Gesture Reference Guide (PDF) A valuable resource for desig






