Merge sort technique explained in C
Sort is the process of arranging elements in ascending (or) descending order.
Types of sorting
C language provides five sorting techniques, as follows-
- Bubble sort (or) exchange sort
- Select Sorting
- Insertion sort (or) linear sort
- Quick sort (or) partition exchange sort
- Merge sort (or) external sort
Merge sort
Merge sort is a divide and conquer method. It splits the array in half, conquers and merges (combines) it recursively.
Let us consider an example given below -
Take an unsorted array and apply merge sort technique to sort the array.
38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10
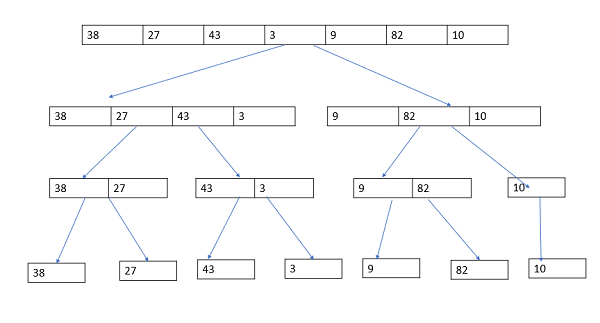
Now, combine the arrays by sorting as shown below-

Example
The following is a C program to sort elements using merge sort technique -
Real-time demonstration
#include <stdio.h>
#define max 10
int a[11] = { 10, 14, 19, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 42, 44, 0 };
int b[10];
void merging(int low, int mid, int high) {
int l1, l2, i;
for(l1 = low, l2 = mid + 1, i = low; l1 <= mid && l2 <= high; i++) {
if(a[l1] <= a[l2])
b[i] = a[l1++];
else
b[i] = a[l2++];
}
while(l1 <= mid)
b[i++] = a[l1++];
while(l2 <= high)
b[i++] = a[l2++];
for(i = low; i <= high; i++)
a[i] = b[i];
}
void sort(int low, int high) {
int mid;
if(low < high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
sort(low, mid);
sort(mid+1, high);
merging(low, mid, high);
} else {
return;
}
}
int main() {
int i;
printf("List before sorting</p><p>");
for(i = 0; i <= max; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
sort(0, max);
printf("</p><p>List after sorting</p><p>");
for(i = 0; i <= max; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}Output
When executing the above program, the following output will be produced-
List before sorting 10 14 19 26 27 31 33 35 42 44 0 List after sorting 0 10 14 19 26 27 31 33 35 42 44
The above is the detailed content of Merge sort technique explained in C. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does swap mean in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
What does swap mean in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
In C language, the swap instruction is used to exchange the values of two variables: swap(x, y): swap(x, y): swap the values of x and y can be achieved by using temporary variables or bit operations.
 What does C language of mean
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
What does C language of mean
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
The of operator points to a member of a structure or union, and is used as expr.member, which is used to access or assign a member's value.
 The role of void in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
The role of void in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
In C language, void is a keyword that indicates no return value. It is used in various scenarios, such as: a function that declares no return value: void print_message(); a function that declares no parameter: void print_message(void); a function that defines no return value: void print_message() { printf(&quot;Hello world\n&quot;); } A function that defines no parameter: void print_message(void) { printf(&quot;Hell
 What does \0 mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What does \0 mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
In C language, '\0' represents an empty character, and its uses mainly include: 1. End string as the end flag of the string; 2. Terminate the character array and determine the length by '\0'; 3. Fill in unused memory; 4. In earlier versions, boolean values should be represented, but the bool type should now be used.
 What does string mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
What does string mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
In C, a string is an array of characters ending with the empty character '\0', used to store text. String operations include getting length (strlen), joining (strcat), copying (strcpy), and comparing (strcmp).
 What does exit mean in C language mean
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
What does exit mean in C language mean
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:39 PM
In C language, the exit() function is used to immediately terminate the program execution and return control rights to the calling process, accepting a parameter to indicate the program exit status code. After exit() is called, the program no longer executes any code and all allocated memory will not be automatically released.
 What does htoc mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What does htoc mean in c language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
The htoc function converts a hexadecimal string to an integer. It scans the string character by character, multiplies each hexadecimal number by the appropriate power according to its position in the string, and then accumulates it to get the final result.
 What does C language char mean?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
What does C language char mean?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 05:03 PM
char is the data type that stores a single character in C language, occupying 1 byte of memory, with a value range of -128~127, and the default value is '\0' (empty character). It can be used to store and manipulate individual characters, but cannot directly store strings or Unicode characters, and cannot be compared directly with strings.






