 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C++
C++
 Query the maximum Armstrong number within the range of the array and update it
Query the maximum Armstrong number within the range of the array and update it
Query the maximum Armstrong number within the range of the array and update it

Array range queries are an emerging area of data structures. In this query, we set random elements into an array and give a general query problem to solve the data structure problem efficiently. The Armstrong number is the sum of its cubes. For example - 0, 1, 153, 370, 371 and 407 are all Armstrong numbers.
Let us take an example to understand Armstrong number
Example 1 - The given number is 371, check if the number is Armstrong number.
3*3*3 7*7*7 1* sup>1* 1 = 371
So, this is the Armstrong number.
Example 2 − The given number is 121, check whether the number is Armstrong's number.
1*1*1 2*2*2 1* sup>1* 1 = 9
Therefore, this is not an Armstrong number.
In this post, we will solve the array range query problem to find the maximum Armstrong number and update it.
grammar
Vector<object_type> variable_name;
This is a way to declare vectors in a program.
algorithm
We will start with a header file named "bits/stdc .h".
We are creating a function definition called "isArmstrong" which takes parameter n as input and is used to check whether the number is an Armstrong number.
Understanding the operations of Armstrong numbers, there are the following points:
Store the value '0' into the 'sum' variable, which will later be used to add each number to a power.
Then 'n' is stored in the variable 'temp'. This temporary variable will be used in the while loop to check the condition of Armstrong number.
Next, we store the value '0' in the variable 'digits', which will later find the power of each number.
Now start the main function and initialize the variable "arr[]" to set the given array element.
We are using the first for loop to print the array elements.
Initialize a vector variable named "armstrong" that will satisfy the condition in the if statement to find the Armstrong number by using the predefined function pushback() list of.
We then use a second for loop to iterate over the length index of the array. Under this loop, the if-else statement is used to find the list of array elements based on whether they are Armstrong numbers or not. .
To update the array range query, we are initializing a variable named 'newNumber' to store the new array element that will be verified to be an Armstrong number by using an if-else statement .
Next, store 0 into the variable 'maxArmstrong', which is used to track the maximum Armstrong number among the array elements.
Continue using The third for loop, which iterates over the length of the Armstrong elements. Inside this loop, use an if statement to find the maximum Armstrong number.
Then use the last loop to iterate the following array elements that satisfy the Armstrong numbers and print all the Armstrong numbers.
Finally, we use the ‘maxArmstrong’ variable to print out the maximum Armstrong number.
Example
is:Example
In this program we will find the maximum Armstrong number with update.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if a number is an Armstrong number or not
bool isArmstrong(int n) {
int sum = 0;
int temp = n;
int digits = 0;
while (temp > 0) {
digits++;
temp /= 10;
}
temp = n;
while (temp > 0) {
int digit = temp % 10;
sum += pow(digit, digits);
temp /= 10;
}
return sum == n;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {0, 123, 1, 19, 12, 153, 370};
int a = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout<<"The given array element:";
for(int m = 0; m < a; m++) {
cout<<arr[m]<<" ";
}
// Vector to store Armstrong numbers
vector<int> armstrongs;
// Check each element of the array if it's an Armstrong number or not
cout<<"\nThe element found to be Non-Armstrong number\n";
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
if (isArmstrong(arr[i])) {
armstrongs.push_back(arr[i]);
} else {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
}
// Add a new number to the array and check if it's an Armstrong number or not
int newNumber = 1278;
cout<<"The newly added number\t"<<newNumber;
if (isArmstrong(newNumber)) {
cout << " : Armstrong number" << endl;
armstrongs.push_back(newNumber);
} else {
cout << " : Non-Armstrong number" << endl;
}
// Find the maximum Armstrong number in the array
int maxArmstrong = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < armstrongs.size(); i++) {
if (armstrongs[i] > maxArmstrong) {
maxArmstrong = armstrongs[i];
}
}
cout << "The following array element satisfied for Armstrong Number: ";
for (int i = 0; i < armstrongs.size(); i++) {
cout << armstrongs[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "The maximum Armstrong number in the array is: " << maxArmstrong << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
There are 3 array element whose setbits are in a multiple of KThe given array element:0 123 1 19 12 153 370 The element found to be Non-Armstrong number 123 19 12 The newly added number 1278 : Non-Armstrong number The following array element satisfied for Armstrong Number: 0 1 153 370 The maximum Armstrong number in the array is: 370
in conclusion
We explored the concept of array range queries to find the maximum Armstrong number with an update function. We saw how to filter a given array element into a combination of Armstrong and non-Armstrong numbers. After removing the non-Armstrong numbers from the existing array elements, we simply print the results of the array elements satisfying the Armstrong type and find the maximum value among them.
The above is the detailed content of Query the maximum Armstrong number within the range of the array and update it. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
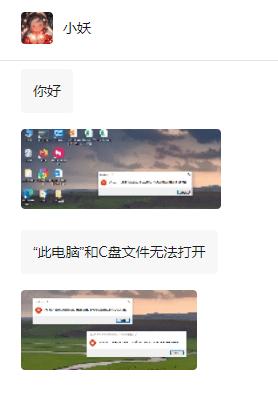 Windows cannot access the specified device, path, or file
Jun 18, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Windows cannot access the specified device, path, or file
Jun 18, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
A friend's computer has such a fault. When opening "This PC" and the C drive file, it will prompt "Explorer.EXE Windows cannot access the specified device, path or file. You may not have the appropriate permissions to access the project." Including folders, files, This computer, Recycle Bin, etc., double-clicking will pop up such a window, and right-clicking to open it is normal. This is caused by a system update. If you also encounter this situation, the editor below will teach you how to solve it. 1. Open the registry editor Win+R and enter regedit, or right-click the start menu to run and enter regedit; 2. Locate the registry "Computer\HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\PackagedCom\ClassInd"
 How to remove duplicate elements from PHP array using foreach loop?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:33 AM
How to remove duplicate elements from PHP array using foreach loop?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:33 AM
The method of using a foreach loop to remove duplicate elements from a PHP array is as follows: traverse the array, and if the element already exists and the current position is not the first occurrence, delete it. For example, if there are duplicate records in the database query results, you can use this method to remove them and obtain results without duplicate records.
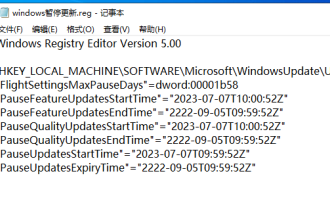 Windows permanently pauses updates, Windows turns off automatic updates
Jun 18, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Windows permanently pauses updates, Windows turns off automatic updates
Jun 18, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Windows updates may cause some of the following problems: 1. Compatibility issues: Some applications, drivers, or hardware devices may be incompatible with new Windows updates, causing them to not work properly or crash. 2. Performance issues: Sometimes, Windows updates may cause the system to become slower or experience performance degradation. This may be due to new features or improvements requiring more resources to run. 3. System stability issues: Some users reported that after installing Windows updates, the system may experience unexpected crashes or blue screen errors. 4. Data loss: In rare cases, Windows updates may cause data loss or file corruption. This is why before making any important updates, back up your
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values takes a relatively long time.
 The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Methods for deep copying arrays in PHP include: JSON encoding and decoding using json_decode and json_encode. Use array_map and clone to make deep copies of keys and values. Use serialize and unserialize for serialization and deserialization.
 AMD releases new AGESA firmware update to fix Zenbleed vulnerability affecting Zen 2 processors
May 03, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
AMD releases new AGESA firmware update to fix Zenbleed vulnerability affecting Zen 2 processors
May 03, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
According to news from this site on May 3, MSI today released the AMDAM4AGESA1.2.0.Ca firmware update, which fixes the Zenbleed security vulnerability in the AMD Ryzen4000 series Zen2 APU. The firmware update released by MSI this time is suitable for almost all X570 motherboards. It mainly fixes CVE-2023-20593 for Zen2 processors, which AMD classifies as a medium threat. Note from this site: The vulnerability tracking number is CVE-2023-20593, which can steal confidential data at a speed of 30KB per core per second. This attack affects all software running on the CPU, including virtual machines, sandboxes, containers and processes. Although the purpose of AGESA1.2.0.Ca
 PHP array multi-dimensional sorting practice: from simple to complex scenarios
Apr 29, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
PHP array multi-dimensional sorting practice: from simple to complex scenarios
Apr 29, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
Multidimensional array sorting can be divided into single column sorting and nested sorting. Single column sorting can use the array_multisort() function to sort by columns; nested sorting requires a recursive function to traverse the array and sort it. Practical cases include sorting by product name and compound sorting by sales volume and price.
 Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
PHP's array_group_by function can group elements in an array based on keys or closure functions, returning an associative array where the key is the group name and the value is an array of elements belonging to the group.





