Create a JavaScript-enabled HTML table with sorting capabilities
When displaying data on a website, it is important to provide features that make it easier for users to browse the data. One such feature is the ability to sort data.
Sorting data means arranging the data in ascending or descending order according to the specified value. We can manually handle data sorting on the client side of the website using JavaScript. This is especially useful if you are developing a static website or removing the burden of data sorting in the server.
In this tutorial, we will use JavaScript to display data from a simulated JSON response into an HTML table. We will also include the ability to make tables sortable based on values in the table header.
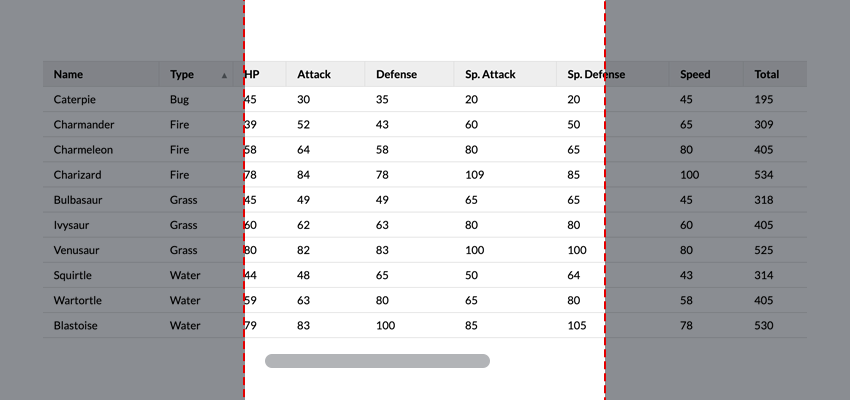
This is the finished product. Click on any table header to sort the table accordingly.
1. Placing content using HTML
<table> tags are semantic HTML tags used to display data on a web page. We will place the <table> tag inside the table container div, which will allow us to include some responsive styling in the CSS.
<div class="table-container"> <table class="data-table"> </table> </div>
Our table will contain a header, thead and table content, tbody tags. In the table header we will include buttons in each th cell which will be used to handle the sorting functionality. The cells for the table content will be added via JavaScript using data from our JSON response.
<div class="table-container">
<table class="data-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th><button id="name">Name</button></th>
<th><button id="type">Type</button></th>
<th><button id="hp">HP</button></th>
<th><button id="attack">Attack</button></th>
<th><button id="defense">Defense</button></th>
<th><button id="spAttack">Sp. Attack</button></th>
<th><button id="spDefense">Sp. Defense</button></th>
<th><button id="speed">Speed</button></th>
<th><button id="total">Total</button></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody id="table-content"></tbody>
</table>
</div>
2.Use CSS to create responsive tables
One of the more common problems with using HTML tables is a lack of responsiveness. The table may have overlapping cells or exceed the boundaries of the full page.
We can solve these problems by placing the table in a full page width table container with overflow scrolling property. This way the table is always only as wide as the full page and there is no need to shrink the cells due to scrollable overflow. We will also include a minimum width attribute in the table cells to avoid text wrapping.
This is the CSS needed to make our table scrollable:
.table-container {
width: 100%;
overflow: scroll;
}
table {
width: 100%;
}
Then we can add the rest of the styles:
.table-container {
margin: auto;
max-width: 1200px;
min-height: 100vh;
overflow: scroll;
width: 100%;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
}
thead tr {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
border-top: 1px solid #ddd;
height: 1px;
}
th {
font-weight: bold;
height: inherit;
padding: 0;
}
th:not(:first-of-type) {
border-left: 1px solid #ddd;
}
th button {
background-color: #eee;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
display: block;
font: inherit;
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
min-width: max-content;
padding: 0.5rem 1rem;
position: relative;
text-align: left;
width: 100%;
}
tbody tr {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
td {
padding: 0.5rem 1rem;
text-align: left;
}
3. Put JSON data into HTML table
For this example, we will use a mock parsed JSON response. This is our data:
const response = {
"pokedata": [
{
"name": "Bulbasaur",
"type": "Grass",
"hp": 45,
"attack": 49,
"defense": 49,
"spAttack": 65,
"spDefense": 65,
"speed": 45,
"total": 318
},
...
]
}
We will put the data in a <tbody id="table-content"> tag so that we can target the element in JavaScript;
const tableContent = document.getElementById("table-content")
row content will be based on each object in response.pokedata. Let's define a function to create new rows based on object data:
const createRow = (obj) => {
const row = document.createElement("tr");
const objKeys = Object.keys(obj);
objKeys.map((key) => {
const cell = document.createElement("td");
cell.setAttribute("data-attr", key);
cell.innerHTML = obj[key];
row.appendChild(cell);
});
return row;
};
In this function, we use the Object.keys() method to get the object keys in the form of an array. The return value is as follows:

Once we have the array of object keys, we loop through each key using the .map() method. The map method executes the function we pass to it on each item in the array.
In this mapping function, we create a new cell for each item in the array and set the cell's innerHTML to the corresponding object key value.

Finally, we use the .appendChild() method to append the created cell to the row defined at the beginning of the function.
Now that we have the row creation function, we will define a function that loops through the response.pokedata array and appends each new row to our tableContent element.
const getTableContent = (data) => {
data.map((obj) => {
const row = createRow(obj);
tableContent.appendChild(row);
});
};
We will pass the getTableContent function into the event listener to add content to the table after the page loads.
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
getTableContent(response.pokedata);
});
4. Using JavaScript to sort data
Now that we have created the table, let's add sorting functionality. In our HTML, we have buttons in the header cell that have object keys as their ids. Now let's locate these buttons:
const tableButtons = document.querySelectorAll("th button");
We want to sort the data based on the button clicked, and also include a feature to switch the sorting direction (ascending or descending) when the button is clicked.
We can use the .sort() method to handle the sorting of data in the response.pokedata array. The sort method accepts a function that compares two different parameters and sorts them based on the function response:
compareFunction(a, b) 返回值
a 之后 b
a 排序在 b 之前a 和 b 的原始顺序
来源:MDN
关于排序方法需要注意的另一件事是它会改变它所操作的原始数组。这意味着它改变了我们原始数组的值。
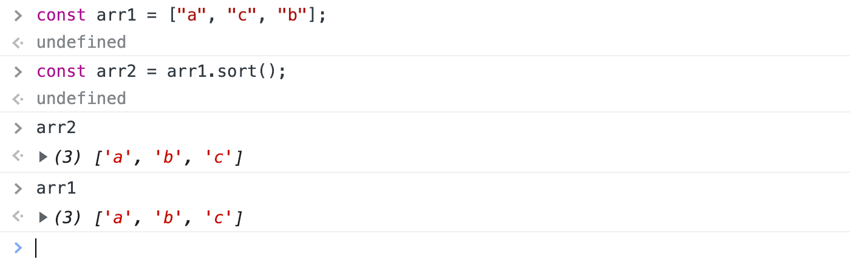
我们可以通过使用扩展语法来避免改变原始数组[...]

现在我们可以创建排序函数了。这就是我们的排序函数的逻辑:
- 清除tableContent元素中的内容
- 根据所选参数和方向对数据进行排序
- 使用
getTableContent函数将排序后的数据附加到我们的 tableContent
const sortData = (data, param, direction = "asc") => {
tableContent.innerHTML = '';
const sortedData =
direction == "asc"
? [...data].sort(function (a, b) {
if (a[param] < b[param]) {
return -1;
}
if (a[param] > b[param]) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
})
: [...data].sort(function (a, b) {
if (b[param] < a[param]) {
return -1;
}
if (b[param] > a[param]) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
getTableContent(sortedData);
};
我们的排序函数需要三个参数:
-
data:待排序的数组 -
param:用于对数组进行排序的值 -
direction:按升序或降序对数组进行排序。默认参数值设置为“asc”。
我们通过将innerHTML 设置为空白字符串来清除tableContent 元素中的内容。然后,我们使用 .sort() 方法和 direction 参数来确定数据应如何排序。我们反转比较函数以便按降序排序。通过这种方式使用比较函数,我们可以对数据进行排序,而不管值的类型(字符串、整数、浮点数等)
最后,我们将 sortedData 作为表内容中的新值传递。
现在,我们将排序函数传递到表格按钮的单击事件侦听器中,并处理切换排序方向。
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
getTableContent(response.pokedata);
[...tableButtons].map((button) => {
button.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
if (e.target.getAttribute("data-dir") == "desc") {
sortData(response.pokedata, e.target.id, "desc");
e.target.setAttribute("data-dir", "asc");
} else {
sortData(response.pokedata, e.target.id, "asc");
e.target.setAttribute("data-dir", "desc");
}
});
});
});
在此函数中,我们通过在按钮上设置 data-dir 属性来处理切换以确定排序方向。我们还将更新 CSS 以根据排序方向在按钮旁边显示一个图标:
th button::after {
position: absolute;
right: 0.5rem;
}
th button[data-dir="asc"]::after {
content: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg xmlns='https://www.w3.org/2000/svg' width='8' height='8'%3E%3Cpolygon points='0, 0 8,0 4,8 8' fill='%23818688'/%3E%3C/svg%3E");
}
th button[data-dir="desc"]::after {
content: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' width='8' height='8'%3E%3Cpolygon points='4 0,8 8,0 8' fill='%23818688'/%3E%3C/svg%3E");
}
我们不想让图标显示在所有以前单击的按钮上,因此我们将定义一个 resetButtons 函数,该函数删除任何未单击的按钮上的 data-dir 属性。
const resetButtons = (event) => {
[...tableButtons].map((button) => {
if (button !== event.target) {
button.removeAttribute("data-dir");
}
});
};
我们会将该函数传递到按钮事件侦听器中,以便在单击新按钮时重置以前的按钮
window.addEventListener("load", () => {
getTableContent(response.pokedata);
[...tableButtons].map((button) => {
button.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
resetButtons(e);
if (e.target.getAttribute("data-dir") == "desc") {
sortData(response.pokedata, e.target.id, "desc");
e.target.setAttribute("data-dir", "asc");
} else {
sortData(response.pokedata, e.target.id, "asc");
e.target.setAttribute("data-dir", "desc");
}
});
});
});
结论
这样,我们就完成了!我们仅使用普通 JavaScript 创建了一个可排序的表格!
The above is the detailed content of Create a JavaScript-enabled HTML table with sorting capabilities. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Detailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 Custom Google Search API Setup Tutorial
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:06 AM
Custom Google Search API Setup Tutorial
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:06 AM
This tutorial shows you how to integrate a custom Google Search API into your blog or website, offering a more refined search experience than standard WordPress theme search functions. It's surprisingly easy! You'll be able to restrict searches to y
 8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout Plugins
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout Plugins
Mar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
Leverage jQuery for Effortless Web Page Layouts: 8 Essential Plugins jQuery simplifies web page layout significantly. This article highlights eight powerful jQuery plugins that streamline the process, particularly useful for manual website creation
 Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Build Your Own AJAX Web Applications
Mar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
So here you are, ready to learn all about this thing called AJAX. But, what exactly is it? The term AJAX refers to a loose grouping of technologies that are used to create dynamic, interactive web content. The term AJAX, originally coined by Jesse J
 What is 'this' in JavaScript?
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:15 AM
What is 'this' in JavaScript?
Mar 04, 2025 am 01:15 AM
Core points This in JavaScript usually refers to an object that "owns" the method, but it depends on how the function is called. When there is no current object, this refers to the global object. In a web browser, it is represented by window. When calling a function, this maintains the global object; but when calling an object constructor or any of its methods, this refers to an instance of the object. You can change the context of this using methods such as call(), apply(), and bind(). These methods call the function using the given this value and parameters. JavaScript is an excellent programming language. A few years ago, this sentence was
 10 Mobile Cheat Sheets for Mobile Development
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
10 Mobile Cheat Sheets for Mobile Development
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:43 AM
This post compiles helpful cheat sheets, reference guides, quick recipes, and code snippets for Android, Blackberry, and iPhone app development. No developer should be without them! Touch Gesture Reference Guide (PDF) A valuable resource for desig
 Improve Your jQuery Knowledge with the Source Viewer
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
Improve Your jQuery Knowledge with the Source Viewer
Mar 05, 2025 am 12:54 AM
jQuery is a great JavaScript framework. However, as with any library, sometimes it’s necessary to get under the hood to discover what’s going on. Perhaps it’s because you’re tracing a bug or are just curious about how jQuery achieves a particular UI
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.






