Explain the write mode operation of files in C language

A file is a collection of records, or a location on your hard drive that is used to permanently store data.
Requirements for files
When the program terminates, the entire data will be lost.
Store data in a file and the data will be retained even if the program terminates.
If you want to enter a large amount of data, it usually takes a lot of time to enter.
We can easily access the contents of the file using several commands.
You can easily move data from one computer to another without making changes.
By using C commands, we can access files in different ways.
File operations
File operations in C programming language are as follows:
- Name the file
- Open the file
- Read from file
- Write to file
- Close file
Syntax
Statement The syntax of file pointer is as follows:
FILE *File pointer;
For example, FILE * fptr;
The syntax of naming and opening file pointer is as follows -
File pointer = fopen ("File name", "mode");For example,
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen ("sample.txt", "w");program1
The following is a C program for reading the names and grades of n students and storing them in a file−
Real-time demonstration
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char name[50];
int marks, i, num;
printf("Enter number of students: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
FILE *fptr;
fptr = (fopen("std.txt", "w")); // opening file in write mode
if(fptr == NULL){
printf("Error!");
exit(1);
}
for(i = 0; i < num; ++i){
printf("For student%d</p><p>Enter name: ", i+1);
scanf("%s", name);
printf("Enter marks: ");
scanf("%d", &marks);
fprintf(fptr,"</p><p>Name: %s </p><p>Marks=%d </p><p>", name, marks);
}
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}Output
When the above program is executed, it produces the following result −
Enter number of students: 3 For student1 Enter name: lucky Enter marks: 59 For student2 Enter name: pinky Enter marks: 89 For student3 Enter name: bob Enter marks: 45
Program 2
The following is used to store the employee details in a file C program that creates and prints this file -
Live Demonstration
#include<stdio.h>
int main ( ){
FILE *fp;
int eno;
char ename[30];
float sal;
fp =fopen ("emp.txt", "w"); // opening file in write mode
printf ("enter the details of eno, ename, sal:");
scanf ("%d%s%f", &eno, ename, &sal);
fprintf (fp, "%d%s%f", eno, ename, sal);
fclose (fp);
fp = fopen ("emp.txt", "r");
fscanf (fp, "%d%s%f", &eno, ename, &sal);
printf ("employee no: = %d</p><p>", eno);
printf ("employee name = %s</p><p>", ename);
printf ("salary = %f</p><p>", sal);
fclose (fp);
return 0;
}Output
When the above program is executed, it produces the following result −
enter the details of eno, ename, sal:1 Pinky 34000 employee no: = 1 employee name = Pinky salary = 34000.000000
The above is the detailed content of Explain the write mode operation of files in C language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to recover expired WeChat files? Can expired WeChat files be recovered?
Feb 22, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
How to recover expired WeChat files? Can expired WeChat files be recovered?
Feb 22, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
Open WeChat, select Settings in Me, select General and then select Storage Space, select Management in Storage Space, select the conversation in which you want to restore files and select the exclamation mark icon. Tutorial Applicable Model: iPhone13 System: iOS15.3 Version: WeChat 8.0.24 Analysis 1 First open WeChat and click the Settings option on the My page. 2 Then find and click General Options on the settings page. 3Then click Storage Space on the general page. 4 Next, click Manage on the storage space page. 5Finally, select the conversation in which you want to recover files and click the exclamation mark icon on the right. Supplement: WeChat files generally expire in a few days. If the file received by WeChat has not been clicked, the WeChat system will clear it after 72 hours. If the WeChat file has been viewed,
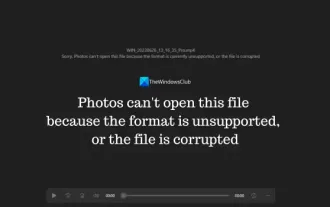 Photos cannot open this file because the format is not supported or the file is corrupted
Feb 22, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Photos cannot open this file because the format is not supported or the file is corrupted
Feb 22, 2024 am 09:49 AM
In Windows, the Photos app is a convenient way to view and manage photos and videos. Through this application, users can easily access their multimedia files without installing additional software. However, sometimes users may encounter some problems, such as encountering a "This file cannot be opened because the format is not supported" error message when using the Photos app, or file corruption when trying to open photos or videos. This situation can be confusing and inconvenient for users, requiring some investigation and fixes to resolve the issues. Users see the following error when they try to open photos or videos on the Photos app. Sorry, Photos cannot open this file because the format is not currently supported, or the file
 What does WeChat's Do Not Disturb mode do?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
What does WeChat's Do Not Disturb mode do?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
What does WeChat Do Not Disturb mode mean? Nowadays, with the popularity of smartphones and the rapid development of mobile Internet, social media platforms have become an indispensable part of people's daily lives. WeChat is one of the most popular social media platforms in China, and almost everyone has a WeChat account. We can communicate with friends, family, and colleagues in real time through WeChat, share moments in our lives, and understand each other’s current situation. However, in this era, we are also inevitably faced with the problems of information overload and privacy leakage, especially for those who need to focus or
 Can Tmp format files be deleted?
Feb 24, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Can Tmp format files be deleted?
Feb 24, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Tmp format files are a temporary file format usually generated by a computer system or program during execution. The purpose of these files is to store temporary data to help the program run properly or improve performance. Once the program execution is completed or the computer is restarted, these tmp files are often no longer necessary. Therefore, for Tmp format files, they are essentially deletable. Moreover, deleting these tmp files can free up hard disk space and ensure the normal operation of the computer. However, before deleting Tmp format files, we need to
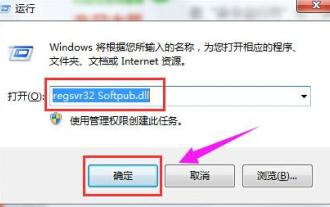 What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
When deleting or decompressing a folder on your computer, sometimes a prompt dialog box "Error 0x80004005: Unspecified Error" will pop up. How should you solve this situation? There are actually many reasons why the error code 0x80004005 is prompted, but most of them are caused by viruses. We can re-register the dll to solve the problem. Below, the editor will explain to you the experience of handling the 0x80004005 error code. Some users are prompted with error code 0X80004005 when using their computers. The 0x80004005 error is mainly caused by the computer not correctly registering certain dynamic link library files, or by a firewall that does not allow HTTPS connections between the computer and the Internet. So how about
 How to transfer files from Quark Cloud Disk to Baidu Cloud Disk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
How to transfer files from Quark Cloud Disk to Baidu Cloud Disk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
Quark Netdisk and Baidu Netdisk are currently the most commonly used Netdisk software for storing files. If you want to save the files in Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk, how do you do it? In this issue, the editor has compiled the tutorial steps for transferring files from Quark Network Disk computer to Baidu Network Disk. Let’s take a look at how to operate it. How to save Quark network disk files to Baidu network disk? To transfer files from Quark Network Disk to Baidu Network Disk, you first need to download the required files from Quark Network Disk, then select the target folder in the Baidu Network Disk client and open it. Then, drag and drop the files downloaded from Quark Cloud Disk into the folder opened by the Baidu Cloud Disk client, or use the upload function to add the files to Baidu Cloud Disk. Make sure to check whether the file was successfully transferred in Baidu Cloud Disk after the upload is completed. That's it
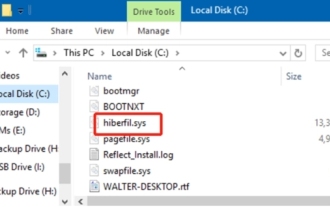 What is hiberfil.sys file? Can hiberfil.sys be deleted?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
What is hiberfil.sys file? Can hiberfil.sys be deleted?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Recently, many netizens have asked the editor, what is the file hiberfil.sys? Can hiberfil.sys take up a lot of C drive space and be deleted? The editor can tell you that the hiberfil.sys file can be deleted. Let’s take a look at the details below. hiberfil.sys is a hidden file in the Windows system and also a system hibernation file. It is usually stored in the root directory of the C drive, and its size is equivalent to the size of the system's installed memory. This file is used when the computer is hibernated and contains the memory data of the current system so that it can be quickly restored to the previous state during recovery. Since its size is equal to the memory capacity, it may take up a larger amount of hard drive space. hiber
 Different uses of slashes and backslashes in file paths
Feb 26, 2024 pm 04:36 PM
Different uses of slashes and backslashes in file paths
Feb 26, 2024 pm 04:36 PM
A file path is a string used by the operating system to identify and locate a file or folder. In file paths, there are two common symbols separating paths, namely forward slash (/) and backslash (). These two symbols have different uses and meanings in different operating systems. The forward slash (/) is a commonly used path separator in Unix and Linux systems. On these systems, file paths start from the root directory (/) and are separated by forward slashes between each directory. For example, the path /home/user/Docume




