 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Beihang University breaks down modal barriers and introduces a universal physical counterattack method across visible and infrared modes.
Beihang University breaks down modal barriers and introduces a universal physical counterattack method across visible and infrared modes.
Beihang University breaks down modal barriers and introduces a universal physical counterattack method across visible and infrared modes.
In recent years, the exploration of safety assessment of visual perception systems has gradually deepened. Researchers have successfully implemented visible light modal safety assessment technology based on different carriers such as glasses, stickers, clothes, etc., and there are also some new attempts targeting infrared modalities. . But they can only work in a single mode.



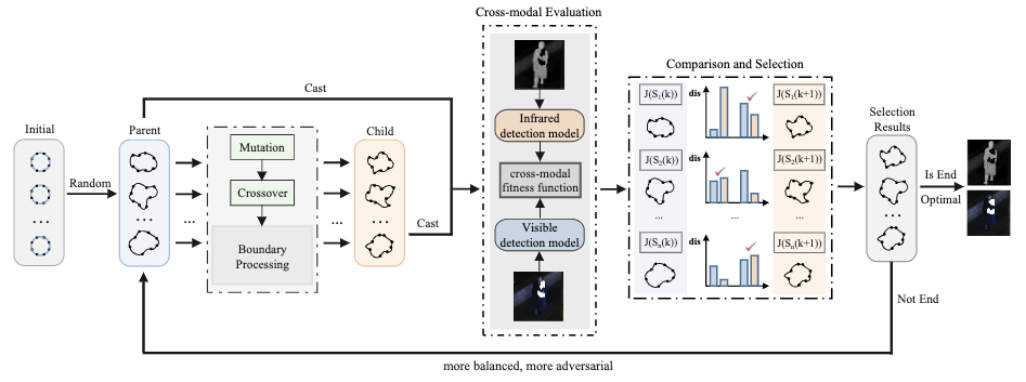
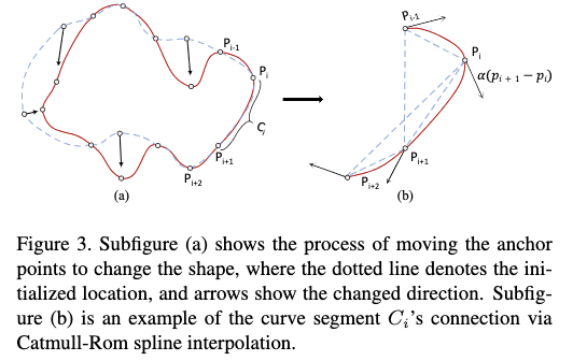
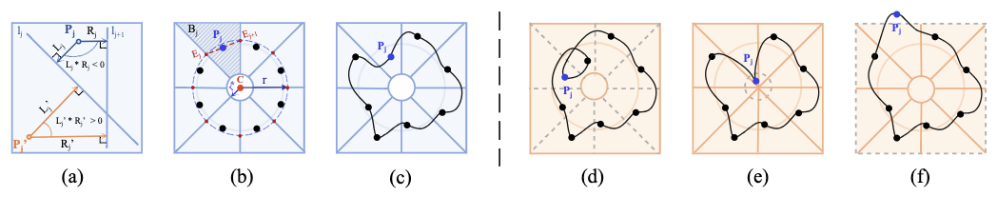
 The mathematical expression is as follows:
The mathematical expression is as follows: 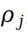
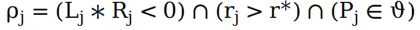
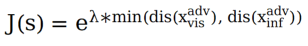 ## ’ ’ s to ’ s ’ ’ s ’ s ’ s ’ s ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐
## ’ ’ s to ’ s ’ ’ s ’ s ’ s ’ s ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ 
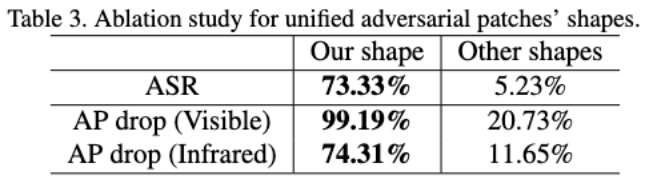
##Experiment 3: Ablation experiment for cross-modal fitness function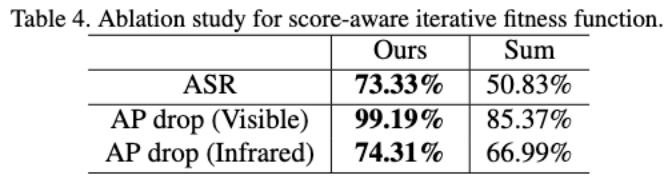
Experiment 4: Method robustness verification under physical implementation deviation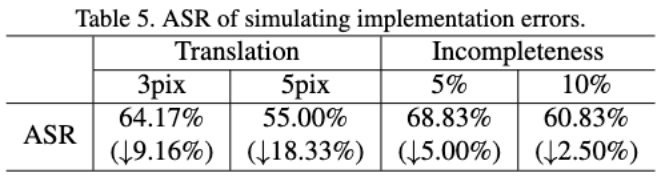
Experiment 5: Validation of method effectiveness under different physical conditions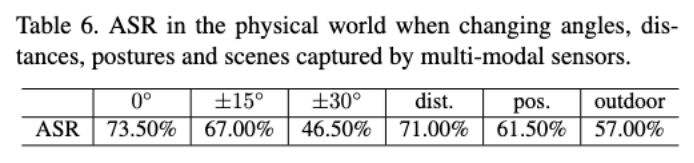
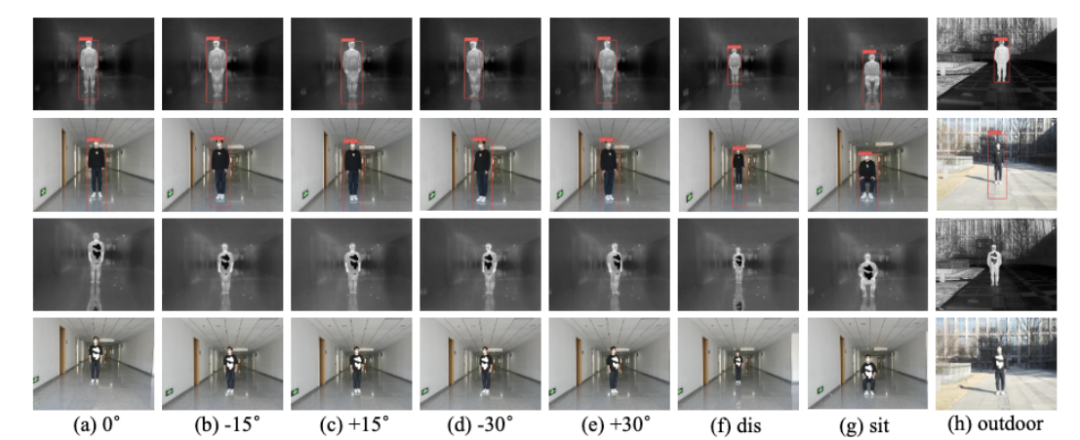 ##Performance verification visualization results under different angles, distances, postures, and scenarios
##Performance verification visualization results under different angles, distances, postures, and scenarios
##Summary
The above is the detailed content of Beihang University breaks down modal barriers and introduces a universal physical counterattack method across visible and infrared modes.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
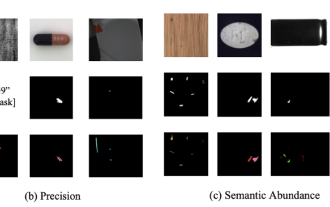 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
 Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Editor | ScienceAI Based on limited clinical data, hundreds of medical algorithms have been approved. Scientists are debating who should test the tools and how best to do so. Devin Singh witnessed a pediatric patient in the emergency room suffer cardiac arrest while waiting for treatment for a long time, which prompted him to explore the application of AI to shorten wait times. Using triage data from SickKids emergency rooms, Singh and colleagues built a series of AI models that provide potential diagnoses and recommend tests. One study showed that these models can speed up doctor visits by 22.3%, speeding up the processing of results by nearly 3 hours per patient requiring a medical test. However, the success of artificial intelligence algorithms in research only verifies this
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Editor | Ziluo AI’s use in streamlining drug discovery is exploding. Screen billions of candidate molecules for those that may have properties needed to develop new drugs. There are so many variables to consider, from material prices to the risk of error, that weighing the costs of synthesizing the best candidate molecules is no easy task, even if scientists use AI. Here, MIT researchers developed SPARROW, a quantitative decision-making algorithm framework, to automatically identify the best molecular candidates, thereby minimizing synthesis costs while maximizing the likelihood that the candidates have the desired properties. The algorithm also determined the materials and experimental steps needed to synthesize these molecules. SPARROW takes into account the cost of synthesizing a batch of molecules at once, since multiple candidate molecules are often available



