
Infinite scroll pagination is inspired by sites like Facebook and Twitter. This is just pagination, when the user scrolls to the bottom of the page, more content is loaded. This improves the user experience on your website by ensuring there is always more content on the page for users to read.
When implementing infinite scroll pagination, there are some very important points to remember.
Important links should not be at the bottom of the page. This is because a new set of entries is loaded every time the user tries to scroll down to find them. All important links should be pinned to the sidebar or remain permanently at the top.
It is important to plan where you will include pagination and how you will handle it. A common way to do pagination is to list page numbers at the bottom of the page. However, when you use the infinite scroll method, the page numbers will no longer appear at the end of the article list because they are no longer needed. This pagination can be used with all themes as long as you don't include a lot of information in the footer section, as it may not have the desired effect.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to implement infinite scroll functionality in JavaScript.
This page will display a list of interesting facts about cats, which information will come from the API. The API returns 10 interesting facts by default. When you scroll to the bottom of the page, the app will display an indicator to indicate the loading status of the app. At the same time, the application will call the API to load the next set of interesting facts.
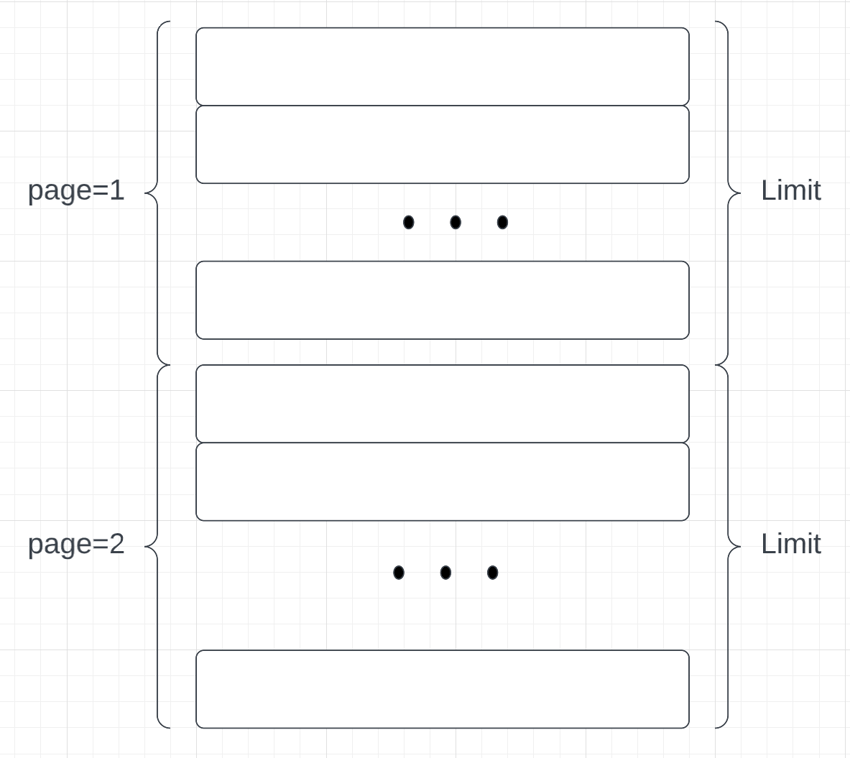
We will use this URL to load interesting facts. The API accepts the query string page, which tells the API which page to load.
https://catfact.ninja/facts?page=${page}&limit=${limit}
Now, let's start using the application.
First, create a folder with the following structure.
root -- index.html -- style.css -- app.js
Our HTML file will contain several sections:
container in which the entire scrollable list of interesting facts will be renderedquotes section containing each interesting factloader, will be visible when loading interesting facts. loader Invisible by default. <div class="container">
<h1>Fun Facts about Cats</h1>
<div class="facts">
</div>
<div class="loader">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</div>
Next, we need to create a script that will connect the divs and load the fun facts. To do this we will use querySelector().
const factsEl = document.querySelector('.facts');
const loader = document.querySelector('.loader');
We also need some control variables to define which set of items will be displayed on the screen. The control variables in this code are:
currentPage: The current page is initialized to 1. When scrolling to the bottom of the page, the current page will be incremented by 1 and an API request will be made to obtain the content page of the next page. When the page is scrolled to the top, the current page will be decremented by 1. total: This variable stores the total number of quotes returned by the Fun Facts API. getFacts FunctiongetFactsThe function is to call the API and return interesting facts. getFacts The function accepts a single parameter: page. It uses the Fetch API mentioned above to get data for infinite scrolling.
Fetch always returns promise, so we will use the await-async syntax to receive and handle the response. To get the json data we will use the json() function. getFacts The function returns a promise that will parse and return JSON.
const getfacts = async (page, limit) => {
const API_URL = `https://catfact.ninja/facts?page=${page}&limit=${limit}`;
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
// handle 404
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`An error occurred: ${response.status}`);
}
return await response.json();
}
showFacts Functions Now that we have received the interesting facts, where can we display them? That's why we need to have a showFacts function. The showFacts function works by iterating over an array of facts. It then creates an HTML representation of the fact object using the template Literal syntax.
const showfacts = (facts) => {
facts.forEach(fact => {
const factEl = document.createElement('blockfact');
factEl.classList.add('fact');
factEl.innerHTML = `
${fact.fact}
`;
factsEl.appendChild(factEl);
});
};
An example of a generated blockFact element is:
<blockfact class="fact">
Unlike dogs, cats do not have a sweet tooth. Scientists believe this is due to a mutation in a key taste receptor.
</blockfact>
We use the appendChild function to add the <blockfact> element to the container.
当用户到达页面末尾时,必须显示加载指示器。为此,我们将引入两个函数:一个用于加载,另一个用于隐藏加载器。我们将使用 opacity: 1 显示加载程序,并使用 opacity: 0 隐藏加载程序。添加和删除 opacity 将分别显示/隐藏加载程序。
const hideLoader = () => {
loader.classList.remove('show');
};
const showLoader = () => {
loader.classList.add('show');
};
为了提高性能,我们将引入一个函数来检查 API 是否有更多事实。如果还有更多项目要获取,则 hasMoreFacts() 函数将返回 true。如果没有更多项目可供获取,API 调用将停止。
const hasMorefacts = (page, limit, total) => {
const startIndex = (page - 1) * limit + 1;
return total === 0 || startIndex < total;
};
loadFacts 函数代码loadFacts 函数负责执行这些重要操作:
getFacts 函数获取更多事实const loadfacts = async (page, limit) => {
// show the loader
showLoader();
try {
// if having more facts to fetch
if (hasMorefacts(page, limit, total)) {
// call the API to get facts
const response = await getfacts(page, limit);
// show facts
showfacts(response.data);
// update the total
total = response.total;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
hideLoader();
}
};
从某种意义上说,这种实现的一个缺点是它的运行速度。大多数时候您不会看到加载指示器,因为 API 可以很快返回。如果您想在每次滚动时查看加载指示器,可以使用 setTimeout 函数。调整 setTimeout 函数的 delay 将决定加载指示器显示的时间长度。
当用户滚动到页面底部时,需要一个scroll事件处理程序来调用loadFacts函数。如果满足以下条件,该函数将被调用:
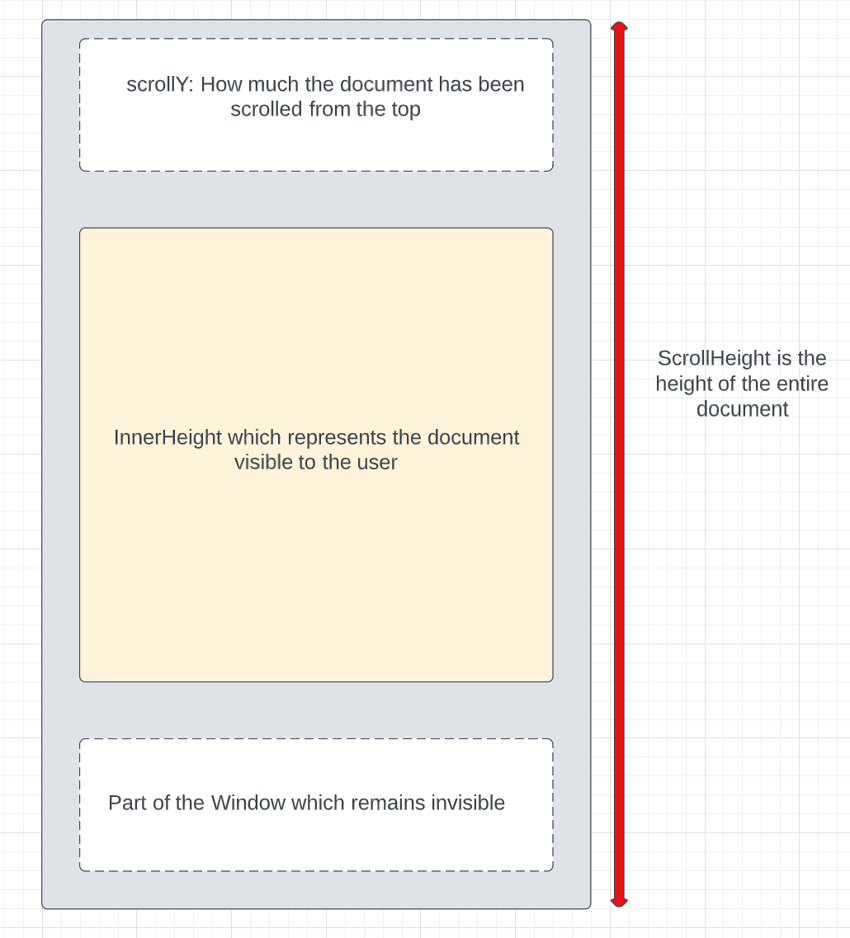
为了实现滚动事件,我们将使用三个窗口属性:
window.scrollHeight 给出整个文档的高度。window.scrollY 给出了用户滚动文档的距离。window.innerHeight 给出可见窗口的高度。下图更好地概述了上述属性。另外,您将能够理解,如果 innerHeight 和 scrollY 之和等于或大于 scrollHeight,则到达文档末尾,此时必须加载更多有趣的事实。
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
const {
scrollTop,
scrollHeight,
clientHeight
} = document.documentElement;
if (scrollTop + clientHeight >= scrollHeight - 5 &&
hasMoreFacts(currentPage, limit, total)) {
currentPage++;
loadFacts(currentPage, limit);
}
}, {
passive: true
});
无限滚动的最后一步是初始化页面。调用 loadFacts 来加载第一组有趣的事实非常重要。
loadfacts(currentPage, limit);
现在,我们在 JavaScript 中实现了一个简单的无限滚动,每当用户滚动时,它将获取并呈现有关猫的有趣事实。这只是无限滚动最常用的方法之一。
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript and REST API to implement infinite scroll pagination. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What should I do if my windows license is about to expire?
What should I do if my windows license is about to expire?
 What are the definitions of arrays?
What are the definitions of arrays?
 What are the java file transfer methods?
What are the java file transfer methods?
 Introduction to the plug-ins required for vscode to run java
Introduction to the plug-ins required for vscode to run java
 Ajax Chinese garbled code solution
Ajax Chinese garbled code solution
 How to pass value to vue component
How to pass value to vue component
 xrp Ripple Latest News
xrp Ripple Latest News
 Ripple purchase process
Ripple purchase process




