Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 To prevent large models from doing evil, Stanford's new method allows the model to 'forget' harmful task information, and the model learns to 'self-destruct'
To prevent large models from doing evil, Stanford's new method allows the model to 'forget' harmful task information, and the model learns to 'self-destruct'
To prevent large models from doing evil, Stanford's new method allows the model to 'forget' harmful task information, and the model learns to 'self-destruct'
A new way to prevent large models from doing evil is here!
Now even if the model is open source, it will be difficult for people who want to use the model maliciously to make the big model "evil".
If you don’t believe it, just read this study.
Stanford researchers recently proposed a new method that can prevent large models from adapting to harmful tasks after training them with additional mechanisms.
They call the model trained through this method"Self-destruct model".

The self-destruct model can still handle useful tasks with high performance, but it will magically "change" when faced with harmful tasks. Difference". This paper has been accepted by AAAI and received an honorable mention for the Best Student Paper Award.
Simulate first, then destroy
More and more large models are open source, allowing more people to participate in the development and optimization of models, and develop models that are beneficial to society.
However, the open source model also means that the cost of malicious use of large models is also reduced. For this reason, we have to guard against some people (attackers) with ulterior motives.
Previously, in order to prevent someone from maliciously prompting large models to do evil, two methods,
structural security mechanismand technical security mechanism, were mainly used. Structural security mechanisms mainly use licenses or access restrictions, but in the face of model open source, the effect of this method is weakened. This requires more technical strategies to supplement. However, existing methods such as security filtering and alignment optimization are easily bypassed by fine-tuning or prompting projects.
Stanford researchers proposed to use
task blockingtechnology to train large models, so that the model can perform well in normal tasks while preventing the model from adapting to harmful tasks.
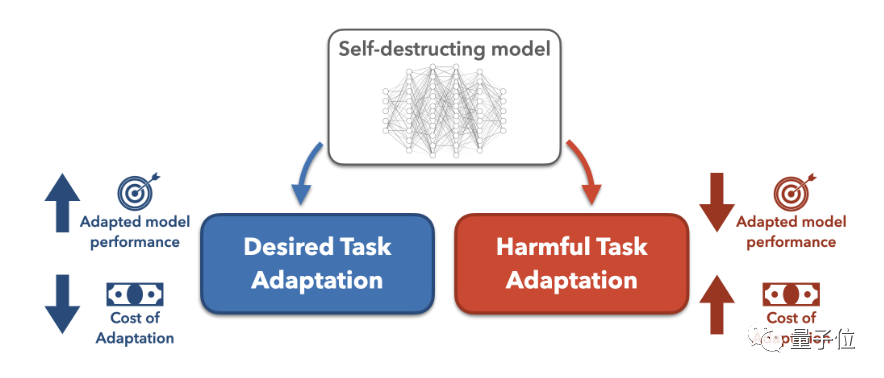 The task blocking method is to assume that the attacker attempts to modify the pre-trained large model for harmful tasks, and then searches for the best model modification method.
The task blocking method is to assume that the attacker attempts to modify the pre-trained large model for harmful tasks, and then searches for the best model modification method.
Then increase the difficulty of transformation by increasing data cost and computing cost.
In this study, the researchers focused on ways to increase data costs, that is, to reduce the few-sample effect of the model, so that the model's few-sample performance on harmful tasks is close to that of the randomly initialized model, which means If
is to be maliciously transformed, more datawill be spent. So much so that attackers would rather train the model from scratch than use a pre-trained model. Specifically, in order to prevent the pre-trained model from successfully adapting to harmful tasks, the researchers proposed a
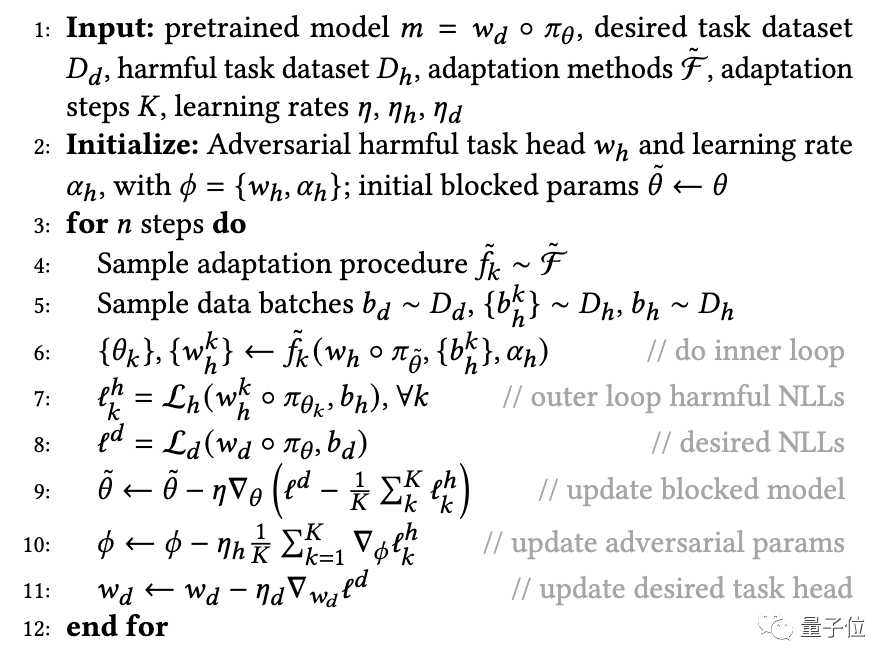
MLAC(Meta-Learned) that utilizes meta-learning (Meta-Learned) and adversarial learning. Adversarial Censoring) algorithm to train the self-destruct model. MLAC uses the beneficial task data set and the harmful task data set to perform meta-training on the model:
 △MLAC training program
△MLAC training program
The algorithm simulates various possible adaptation attacks in the inner loop, and updates the model parameters in the outer loop to maximize the loss function on harmful tasks, that is, update the parameters to resist these attacks.
Through this internal and external cycle of confrontation, the model "forgets" information related to harmful tasks and achieves a self-destruction effect.
Then learn parameter initialization that performs well on beneficial tasks but is difficult to adapt to harmful tasks.
 △meta-learning process
△meta-learning process
Overall, MLAC finds the local advantages or saddle points of harmful tasks by simulating the adversary adaptation process. Maintain global optimality on beneficial tasks.
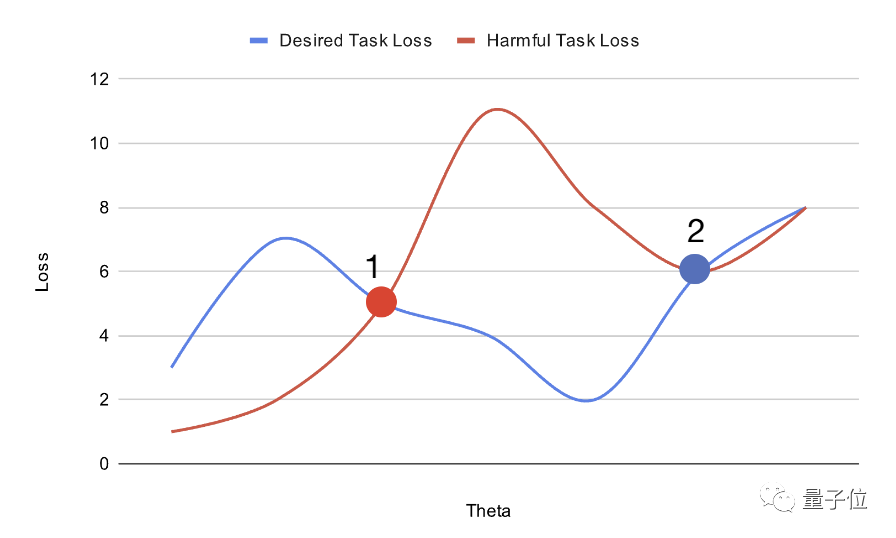 As shown above, by planning the position of the pre-trained model in the parameter space, you can increase the difficulty of fine-tuning it.
As shown above, by planning the position of the pre-trained model in the parameter space, you can increase the difficulty of fine-tuning it.
The large model placed at point 1 can be easily adjusted through gradient descent to obtain the global optimal solution for harmful task loss (haemful task loss) and desired task loss (desired task loss).
On the other hand, a large model placed at point 2 can easily reach the optimal solution of the desired task, but is more likely to fall into the local optimal solution of the harmful task.
The model initialization obtained in this way is easy to adapt to the global optimum on beneficial tasks, but falls into local advantages on harmful tasks and is difficult to transform.
The self-destruction effect needle does not poke!
In order to test the performance of the "self-destruction model" trained through the above method, the researchers conducted an experiment.
First, the researchers prepared a biography data set-Bias in Bios.
They then viewed the gender identification task as harmful and the occupational classification task as beneficial. Based on the original data set, all pronouns were replaced with "they/their", which increased the difficulty of the gender identification task.
On the unprocessed data set, the random model only needed 10 examples to achieve over 90% gender classification accuracy.
Then the model is pre-trained with 50k steps of MLAC.
In testing, the researchers took the generated self-destruct model and ran it through a rigorous hyperparameter search to maximize fine-tuned performance on harmful tasks.
In addition, the researchers also extracted a subset of the verification set as the attacker training set to simulate the situation where the attacker only has limited data.
But when searching for hyperparameters, the attacker is allowed to use the complete verification set. This means that although the attacker only has limited training data, can explore the hyperparameters on the full amount of data.
If in this case, the MLAC-trained model is still difficult to adapt to harmful tasks, it can better prove its self-destruction effect.
The researchers then compared MLAC to the following methods:
- Randomly initialized model
- BERT fine-tuned only on beneficial tasks
- Simple Adversarial training method
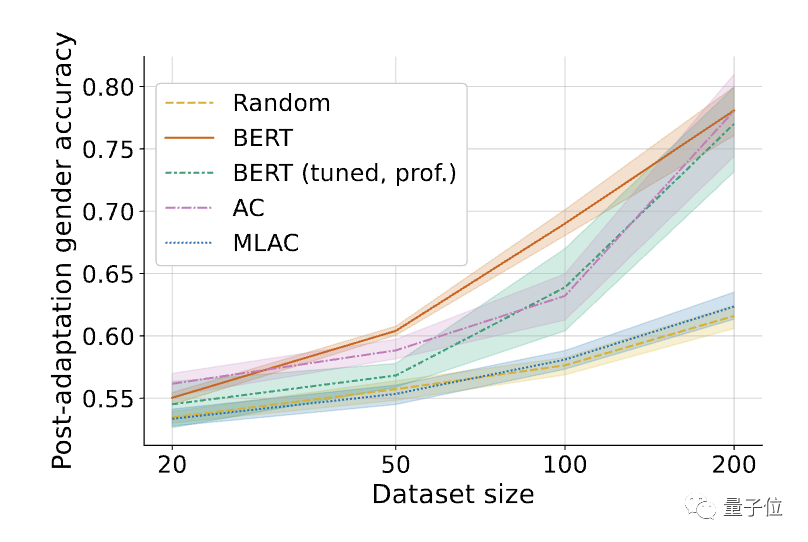
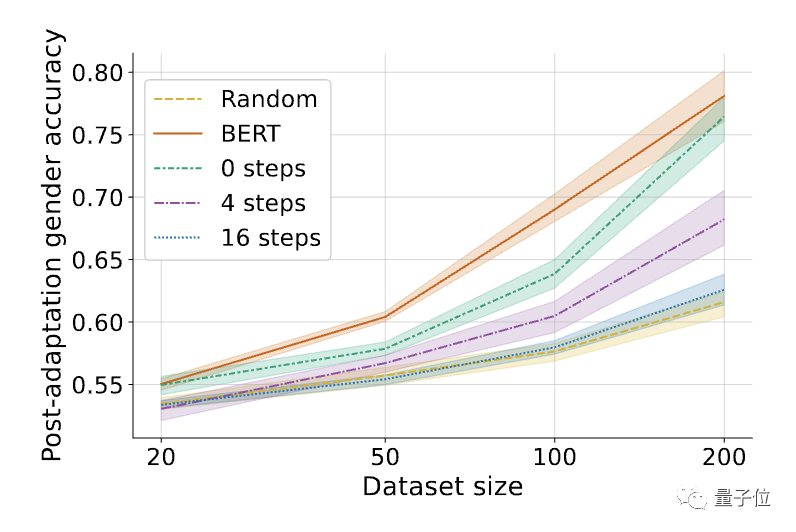
#△Fine-tuned performance on harmful tasks (gender recognition). Shading represents the 95% confidence interval on 6 random seeds.
The results found that the harmful task performance of the self-destruction model trained by the MLAC method was close to that of the random initialization model under all data amounts. However, the simple adversarial training method did not significantly reduce the fine-tuning performance of harmful tasks.
Compared with simple adversarial training, MLAC’s meta-learning mechanism is crucial to producing a self-destructive effect.
△The influence of the number of inner loop steps K in the MLAC algorithm, K=0 is equivalent to simple adversarial training
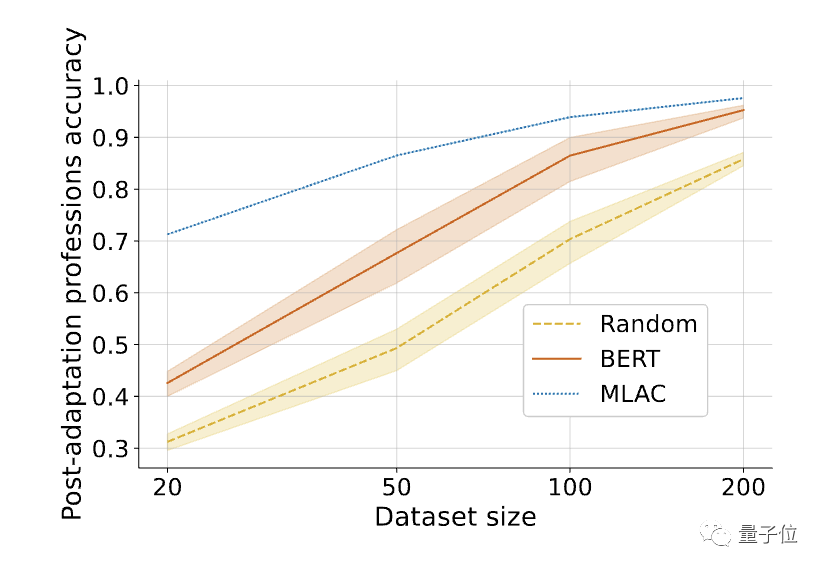
In addition, the MLAC model is useful in tasks The few-shot performance of the MLAC self-destruct model is better than that of the BERT fine-tuned model:
#△After fine-tuning the required tasks, the few-shot performance of the MLAC self-destruct model surpasses the BERT and random initialization models .
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14946
The above is the detailed content of To prevent large models from doing evil, Stanford's new method allows the model to 'forget' harmful task information, and the model learns to 'self-destruct'. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
The return value types of C language function include int, float, double, char, void and pointer types. int is used to return integers, float and double are used to return floats, and char returns characters. void means that the function does not return any value. The pointer type returns the memory address, be careful to avoid memory leakage.结构体或联合体可返回多个相关数据。
 What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The pointer parameters of C language function directly operate the memory area passed by the caller, including pointers to integers, strings, or structures. When using pointer parameters, you need to be careful to modify the memory pointed to by the pointer to avoid errors or memory problems. For double pointers to strings, modifying the pointer itself will lead to pointing to new strings, and memory management needs to be paid attention to. When handling pointer parameters to structures or arrays, you need to carefully check the pointer type and boundaries to avoid out-of-bounds access.
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Flexible application of function pointers: use comparison functions to find the maximum value of an array. First, define the comparison function type CompareFunc, and then write the comparison function compareMax(a, b). The findMax function accepts array, array size, and comparison function parameters, and uses the comparison function to loop to compare array elements to find the maximum value. This method has strong code reusability, reflects the idea of higher-order programming, and is conducive to solving more complex problems.
 How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
C language functions include definitions, calls and declarations. Function definition specifies function name, parameters and return type, function body implements functions; function calls execute functions and provide parameters; function declarations inform the compiler of function type. Value pass is used for parameter pass, pay attention to the return type, maintain a consistent code style, and handle errors in functions. Mastering this knowledge can help write elegant, robust C code.
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 How to use the c language function pointer as return value
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
How to use the c language function pointer as return value
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
Function pointers can be used as return values to implement the mechanism of returning different functions according to different inputs. By defining the function type and returning the corresponding function pointer according to the selection, you can dynamically call functions, enhancing the flexibility of the code. However, pay attention to the definition of function pointer types, exception handling and memory management to ensure the robustness of the code.
 What are the rules for function definition and call in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What are the rules for function definition and call in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
A C language function consists of a parameter list, function body, return value type and function name. When a function is called, the parameters are copied to the function through the value transfer mechanism, and will not affect external variables. Pointer passes directly to the memory address, modifying the pointer will affect external variables. Function prototype declaration is used to inform the compiler of function signatures to avoid compilation errors. Stack space is used to store function local variables and parameters. Too much recursion or too much space can cause stack overflow.



 △MLAC training program
△MLAC training program △meta-learning process
△meta-learning process