C program uses structure to store inventory system

Structure is a collection of variables of different data types, grouped together by a single name.
Characteristics of structures
The characteristics of structures in C language programming language are as follows-
All structural elements of different data types can be combined by using assignment Contents are copied to another structure variable of its type
In order to handle complex data types, it is better to create a structure within another structure, which is called a nested structure.
- You can pass the entire structure, individual elements of the structure, and the address of the structure to the function.
-
Can create structure pointers.
Program
The following is a C programUsing structure to store inventory system -
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main(){
struct date{
int day;
int month;
int year;
};
struct details{
char name[20];
int price;
int code;
int qty;
struct date mfg;
};
struct details item[50];
int n,i;
printf("Enter number of items:");
scanf("%d",&n);
fflush(stdin);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
fflush(stdin);
printf("Item name:");
scanf("%s",item[i].name);
fflush(stdin);
printf("Item code:");
scanf("%d",&item[i].code);
fflush(stdin);
printf("Quantity:");
scanf("%d",&item[i].qty);
fflush(stdin);
printf("price:");
scanf("%d",&item[i].price);
fflush(stdin);
printf("Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):");
scanf("%d-%d-%d",&item[i].mfg.day,&item[i].mfg.month,&item[i].mfg.year);
}
printf(" ***** INVENTORY *****</p><p>");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------</p><p>");
printf("S.N.| NAME | CODE | QUANTITY | PRICE |MFG.DATE</p><p>");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------</p><p>");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d %-15s %-d %-5d %-5d%d/%d/%d</p><p>",i+1,item[i].name,item[i].code,item[i].qty,item[i].price,item[i].mfg.day,item[i].mfg.month,item[i].mfg.year);
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------</p><p>");
getch();
}Output
When the above program is executed, the following results are produced -
Enter number of items:5 Item name:pen Item code:12 Quantity:50 price:25 Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):12-02-2020 Item name:pencil Item code:15 Quantity:100 price:30 Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):11-03-2020 Item name:book Item code:34 Quantity:30 price:60 Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):15-04-2020 Item name:bag Item code:39 Quantity:20 price:70 Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):12-03-2021 Item name:sharpner Item code:33 Quantity:20 price:40 Manufacturing date(dd-mm-yyyy):12-04-2021 ***** INVENTORY ***** ------------------------------------------------------------------ S.N.| NAME | CODE | QUANTITY | PRICE |MFG.DATE ------------------------------------------------------------------ 1 pen 12 50 25 12/2/2020 2 pencil 15 100 30 11/3/2020 3 book 34 30 60 15/4/2020 4 bag 39 20 70 12/3/2021 5 sharpner 33 20 40 12/4/2021
The above is the detailed content of C program uses structure to store inventory system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Translate the following into Chinese: C program to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
Translate the following into Chinese: C program to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers
Sep 05, 2023 pm 09:53 PM
Given below is a C language algorithm to convert Roman numerals to decimal numbers: Algorithm Step 1 - Start Step 2 - Read Roman numerals at runtime Step 3 - Length: = strlen(roman) Step 4 - For i=0 to Length-1 Step 4.1-switch(roman[i]) Step 4.1.1-case'm': &nbs
 Golang structure strong transfer: detailed explanation of implementation principles and techniques
Apr 03, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
Golang structure strong transfer: detailed explanation of implementation principles and techniques
Apr 03, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
Struct coercion in Golang is to convert the value of one structure type to another type. This can be achieved through techniques such as assertion force transfer, reflection force transfer, and pointer indirect force transfer. Assertion coercion uses type assertions, reflective coercion uses the reflection mechanism, and pointer indirect coercion avoids value copying. The specific steps are: 1. Assertion force transfer: use typeassertion syntax; 2. Reflection force transfer: use reflect.Type.AssignableTo and reflect.Value.Convert functions; 3. Pointer indirect force transfer: use pointer dereference.
 C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Hyperbolic functions are defined using hyperbolas instead of circles and are equivalent to ordinary trigonometric functions. It returns the ratio parameter in the hyperbolic sine function from the supplied angle in radians. But do the opposite, or in other words. If we want to calculate an angle from a hyperbolic sine, we need an inverse hyperbolic trigonometric operation like the hyperbolic inverse sine operation. This course will demonstrate how to use the hyperbolic inverse sine (asinh) function in C++ to calculate angles using the hyperbolic sine value in radians. The hyperbolic arcsine operation follows the following formula -$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\:+\:\sqrt{x^2\:+\:1})}, Where\:In\:is\:natural logarithm\:(log_e\:k)
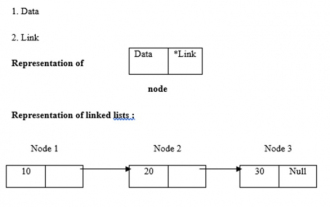 C program to find length of linked list
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
C program to find length of linked list
Sep 07, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
Linked lists use dynamic memory allocation, i.e. they grow and shrink accordingly. They are defined as collections of nodes. Here, a node has two parts, data and links. The representation of data, links and linked lists is as follows - Types of linked lists There are four types of linked lists, as follows: - Single linked list/Singly linked list Double/Doubly linked list Circular single linked list Circular double linked list We use the recursive method to find the length of the linked list The logic is -intlength(node *temp){ if(temp==NULL) returnl; else{&n
 C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
A map is a special type of container in C++ in which each element is a pair of two values, namely a key value and a map value. The key value is used to index each item, and the mapped value is the value associated with the key. Regardless of whether the mapped value is unique, the key is always unique. To print map elements in C++ we have to use iterator. An element in a set of items is indicated by an iterator object. Iterators are primarily used with arrays and other types of containers (such as vectors), and they have a specific set of operations that can be used to identify specific elements within a specific range. Iterators can be incremented or decremented to reference different elements present in a range or container. The iterator points to the memory location of a specific element in the range. Printing a map in C++ using iterators First, let's look at how to define
 C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
The rename function changes a file or directory from its old name to its new name. This operation is similar to the move operation. So we can also use this rename function to move files. This function exists in the stdio.h library header file. The syntax of the rename function is as follows: intrename(constchar*oldname,constchar*newname); The function of the rename() function accepts two parameters. One is oldname and the other is newname. Both parameters are pointers to constant characters that define the old and new names of the file. Returns zero if the file was renamed successfully; otherwise, returns a nonzero integer. During a rename operation
 Application of anonymous unions and structures in C language
Sep 16, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Application of anonymous unions and structures in C language
Sep 16, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Here we take a look at what are anonymous unions and structures in C language. Anonymous unions and structures are unnamed unions and structures. Since they have no name, we cannot create a direct object of it. We use it as a nested structure or union. These are examples of anonymous unions and structures. struct{ datatypevariable; ...};union{ datatypevariable; ...};In this example, we are creating
 C program to implement Euclidean algorithm
Sep 17, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
C program to implement Euclidean algorithm
Sep 17, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
The problem implements Euclidean's algorithm to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of two integers and outputs the results with a given integer. Solution The solution to implement Euclidean algorithm to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of two integers is as follows - the logic of finding GCD and LCM is as follows - if (firstno*secondno!=0){ gcd= gcd_rec(firstno,secondno); printf("TheGCDof%dand%dis%d",






