How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a data storage technology in which multiple external drives are combined into one. It was widely used when large hard drives were expensive, but many people still prefer the RAID external drive method.
There are several levels of RAID, each serving a specific purpose. Keep in mind that the average user doesn't have to delve into the complexity and a simple setup of RAID 0 or RAID 1 should work just fine.
Reasons to consider raiding an external drive:
- Improved PC performance
- Easy to configure, cheaper than existing alternatives
- Faster Data reading and writing
- Efficient backup solution through mirroring
How to RAID external drives on Windows 11?
Before RAID external hard drives, there are a few prerequisites to note:
- Two external drives for RAID 0 and RAID 1, three for RAID 5, 4 hard drives for RAID 10. The drive should be unformatted and of the same brand (preferably), size, and speed.
- RAID erases all existing data, so be sure to back up the drive beforehand.
After you have everything ready, choose any method to set up the RAID system.
1. By Settings
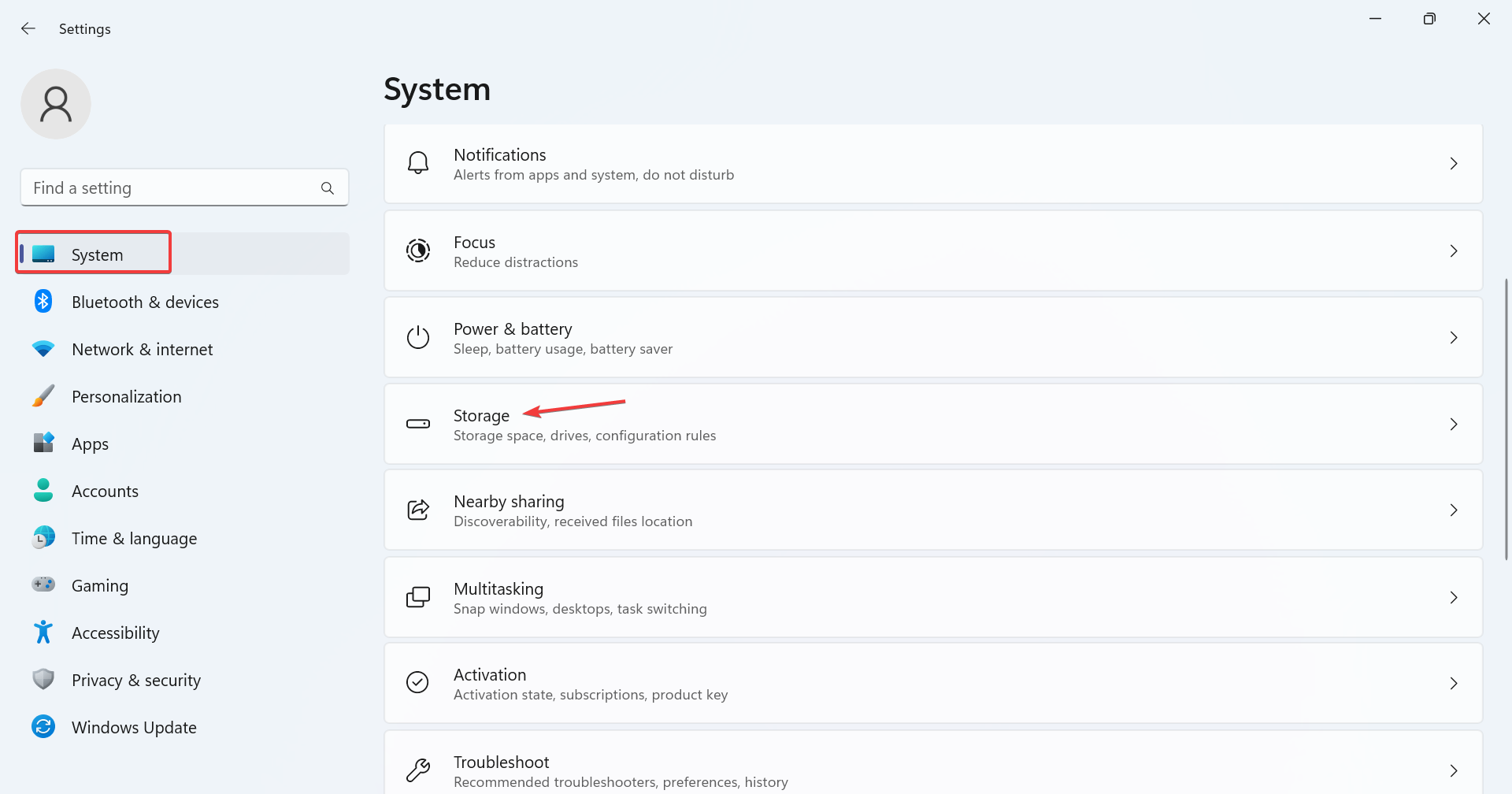
- Press I to open Settings, then click Storage on the right in the System tab. Windows

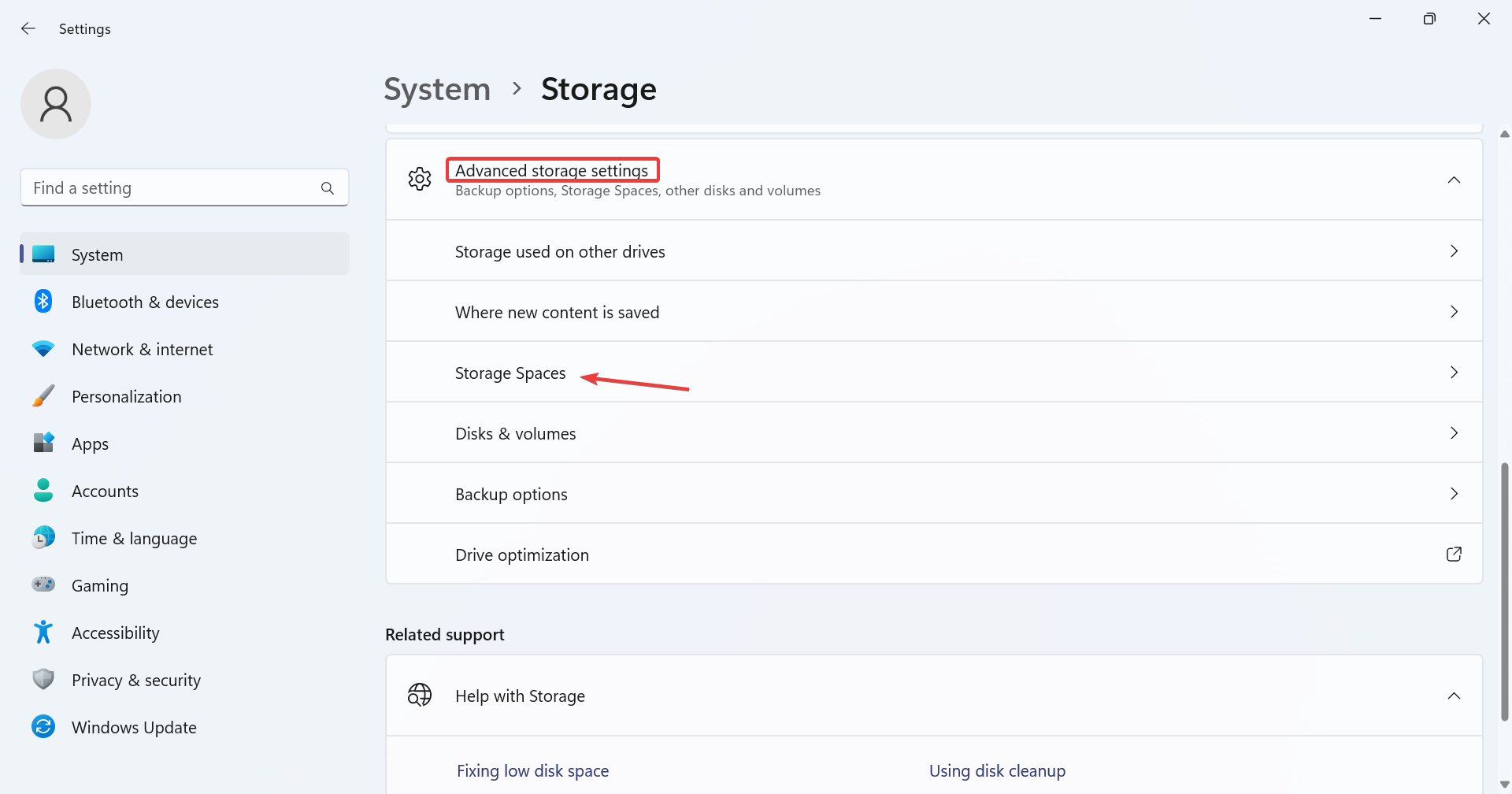
- Expand Advanced Storage Settings and click Storage Spaces.

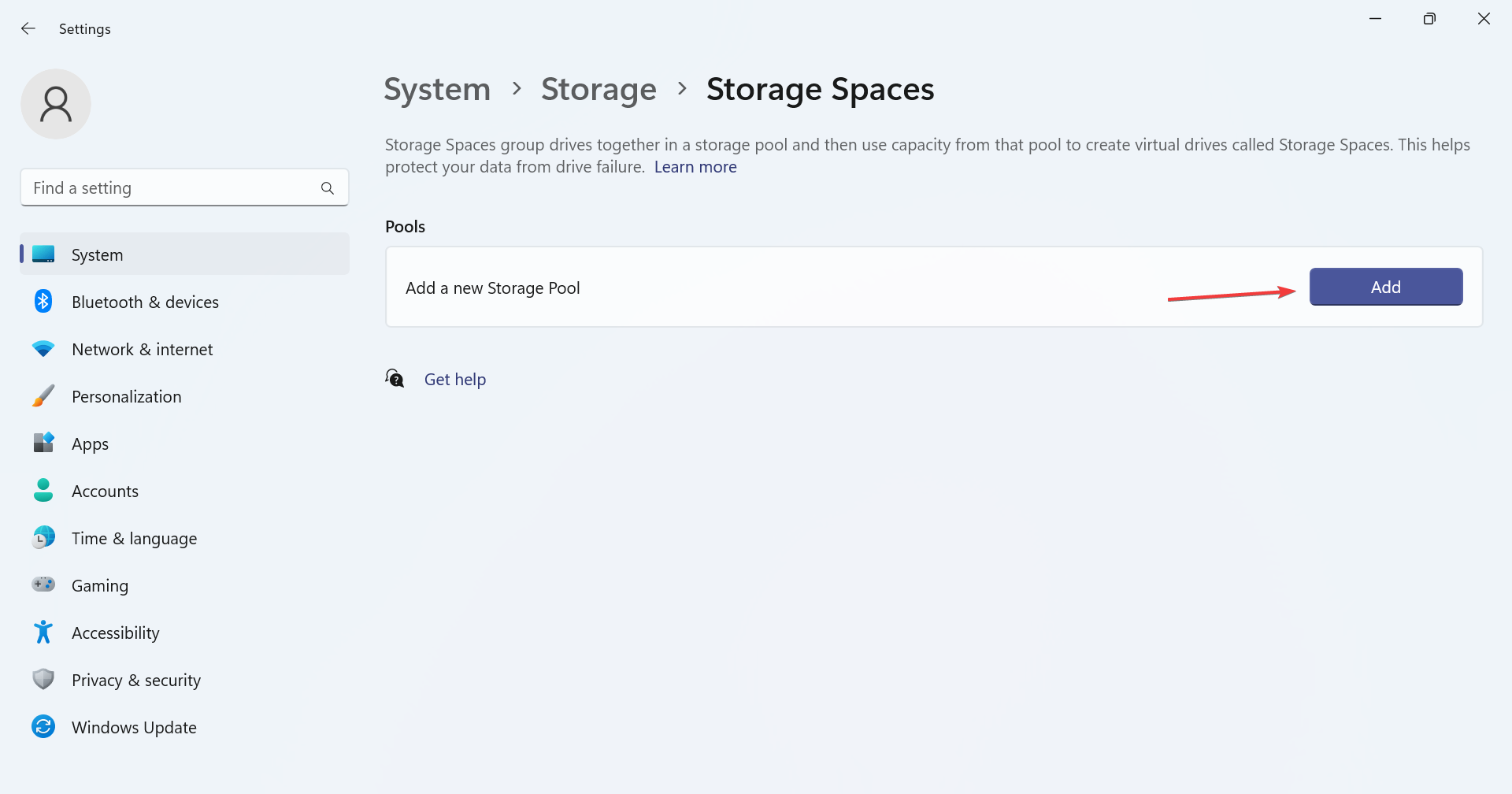
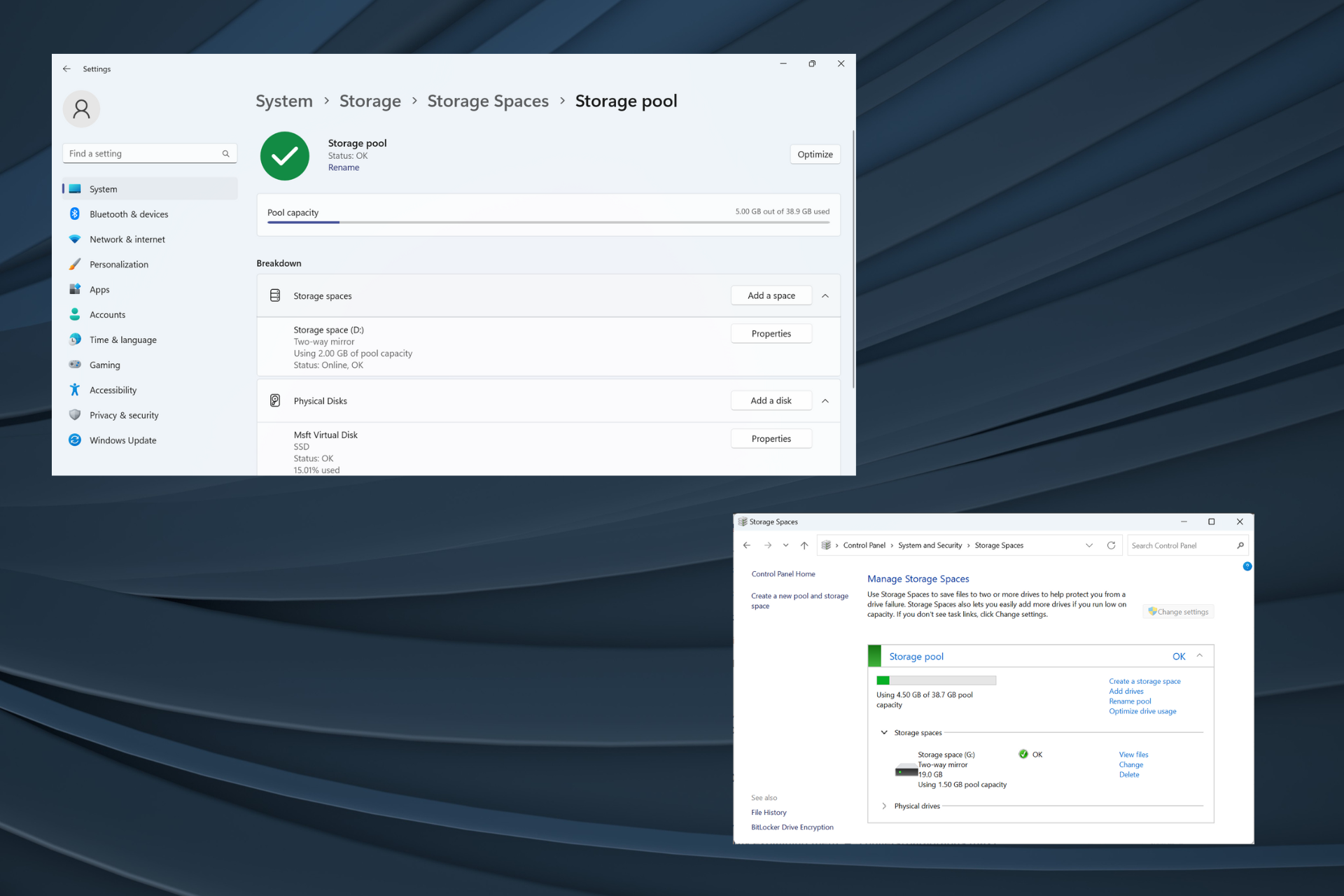
- Click the Add button next to Add a new storage pool.

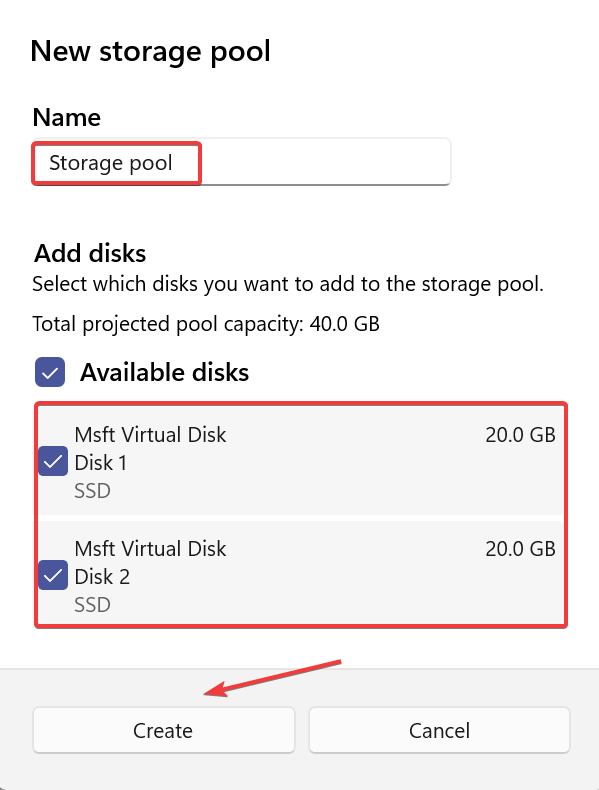
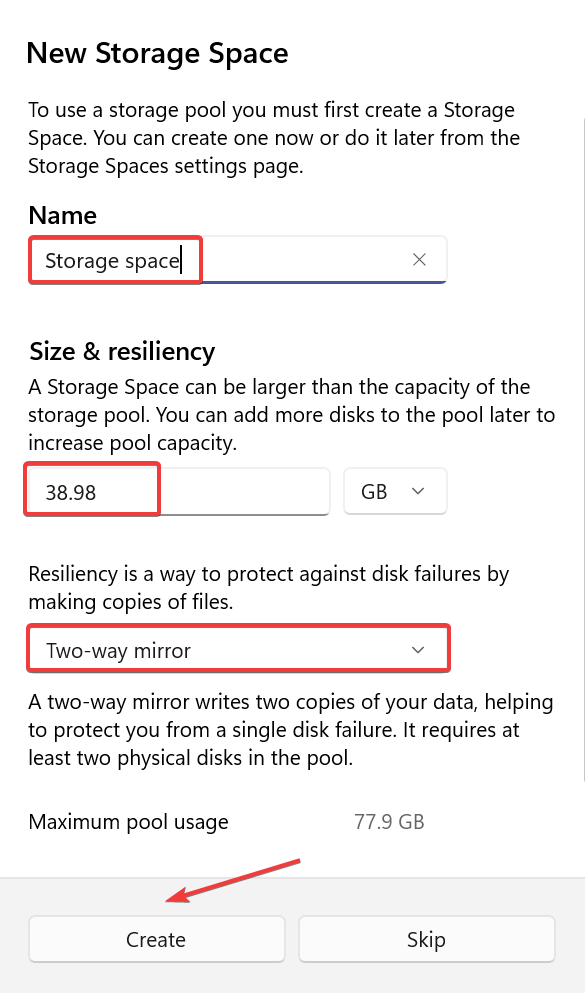
- Enter the name of the storage pool in the text field, select the desired disk from the list, and click Create.

- Type a name for the storage space, enter the desired size (it can be larger than the disk size, but we recommend not doing this), and then select a recovery type from the following options:
- Simple (non-resilient)
- One-way mirror
- Two-way mirror (preferred due to data loss protection)
- Parity (Preferred)
- When completed, click Create.

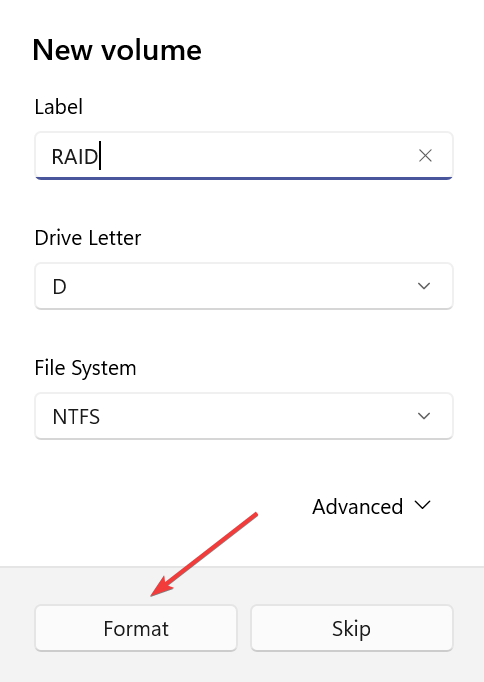
- Enter the label name, select the drive letter and file system, and click Format. You can check the advanced options to configure more settings.

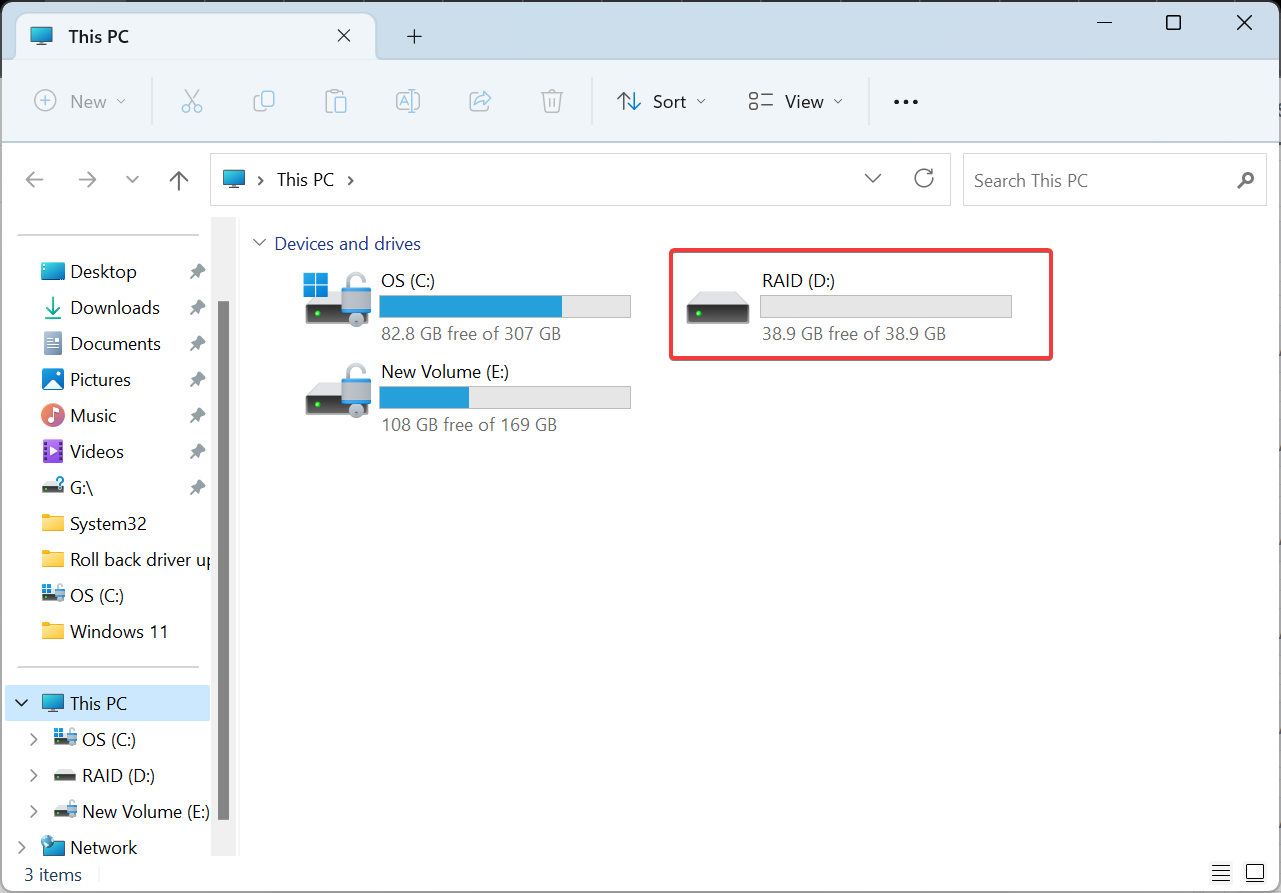
- Once completed, the RAID settings can be accessed from File Explorer.

- Additionally, storage pools can be reconfigured or optimized from the storage space settings.
This is how you can use RAID to connect multiple external hard drives together and use them for data storage with advanced protection measures. Remember, it’s best to keep the RAID options simple or selected by default for an error-free experience.
2. From Control Panel
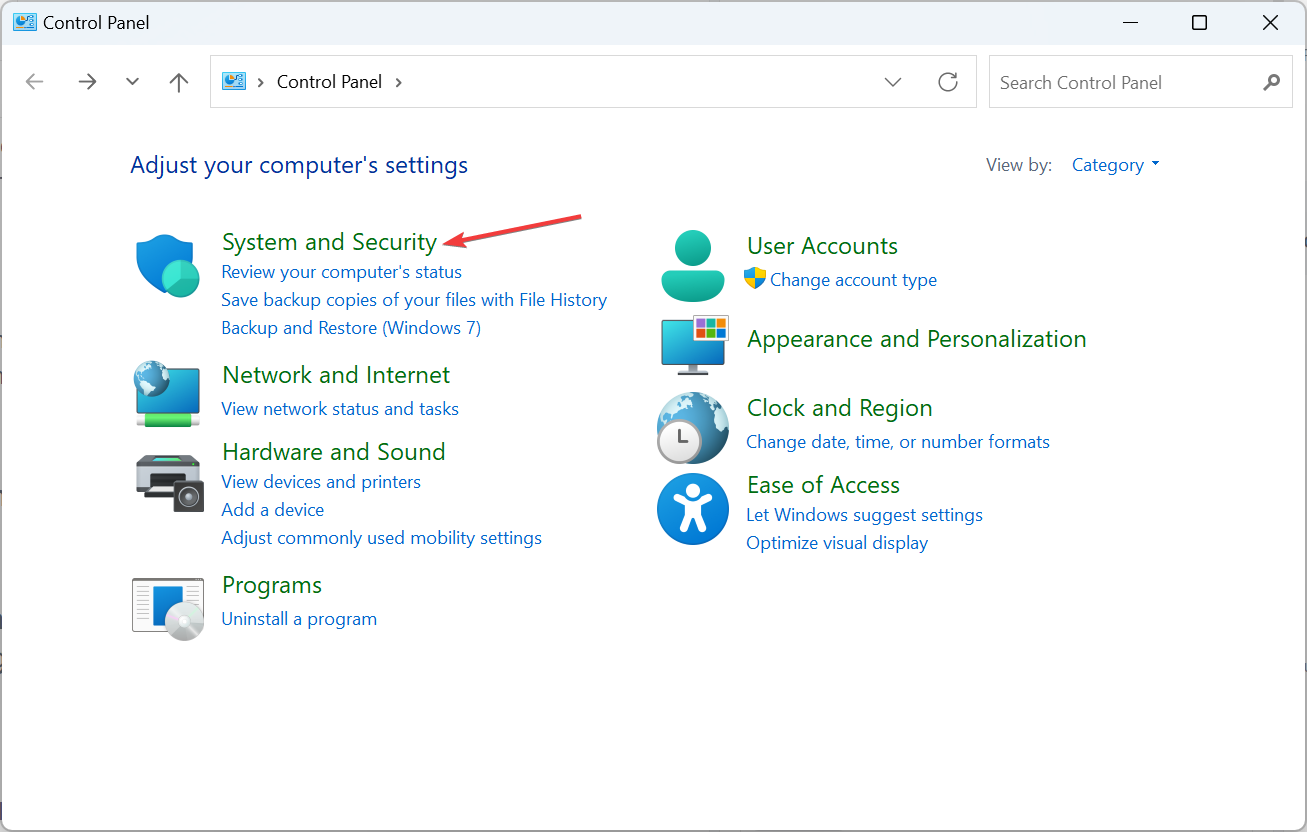
- Press to open Search, type "Control Panel" in the text field, and click on the relevant search results. WindowsS
- Click "System and Security".

- Click "Storage Space".

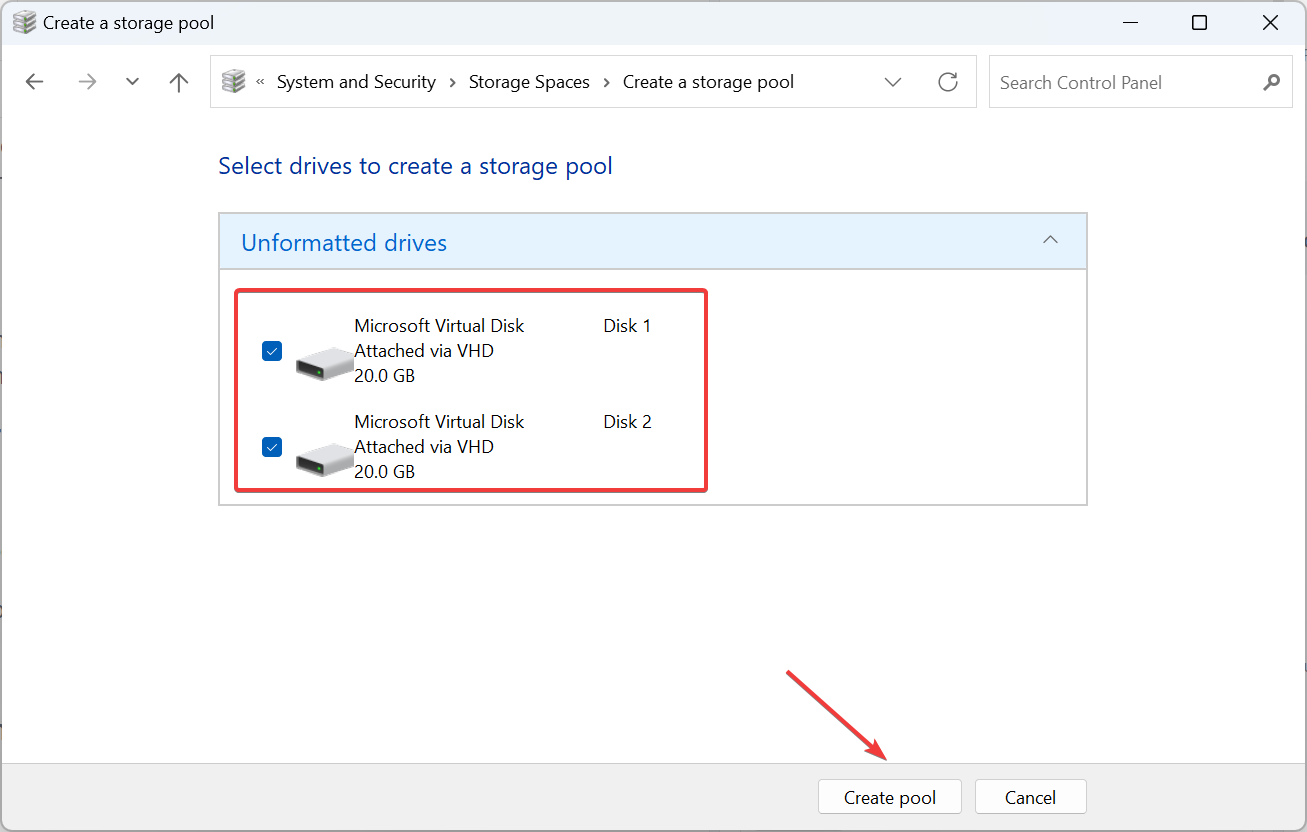
- Now, click Create New Pool and Storage.
- Click "is" at the UAC prompt.
- Check the checkbox of the disk you want to add to the storage pool, and then click Create Pool.

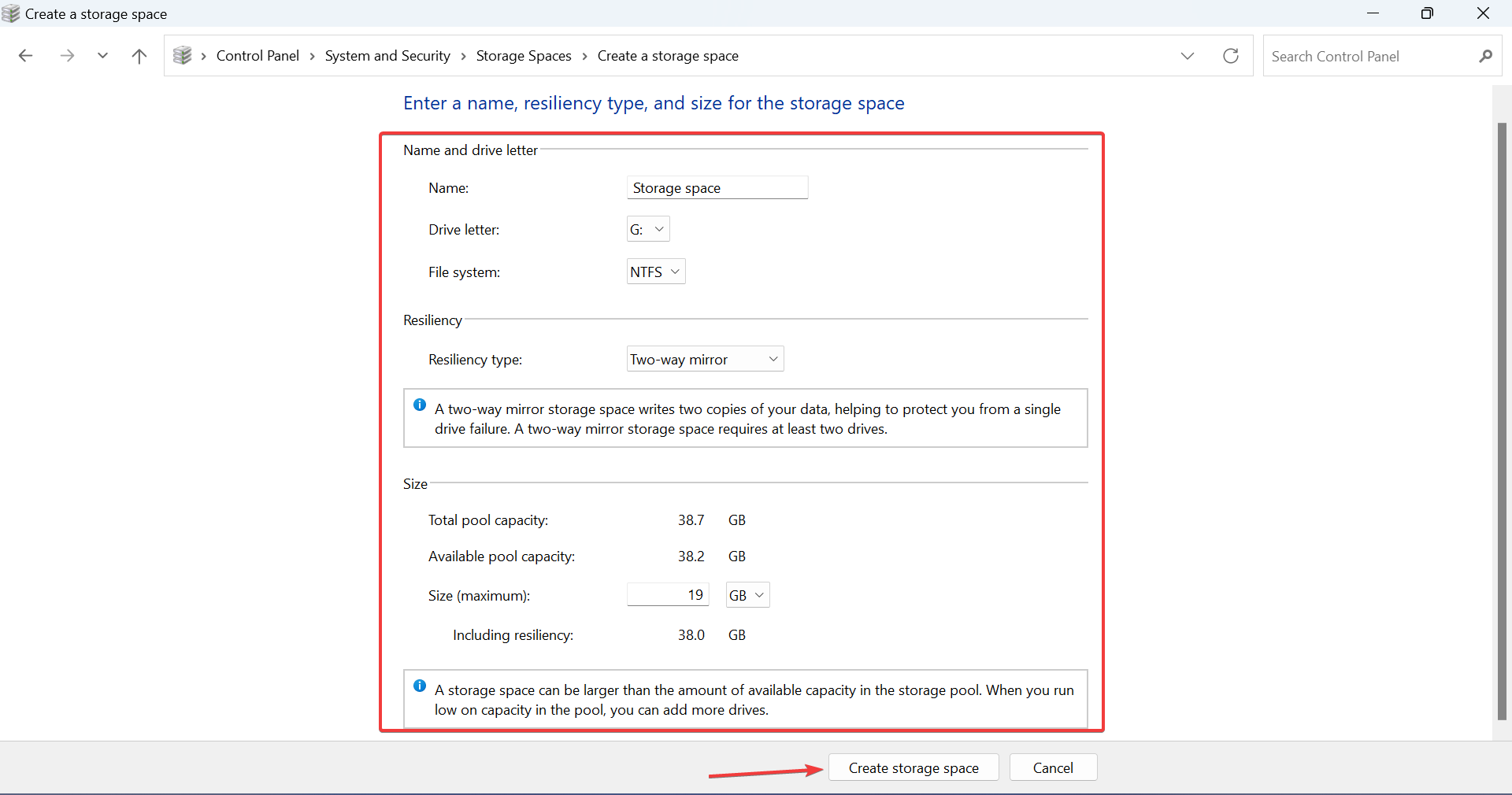
- Now, enter a name, select a drive letter and file system, select a recovery type (preferably two-way mirroring), configure the pool size, and click the Create Storage Space button.

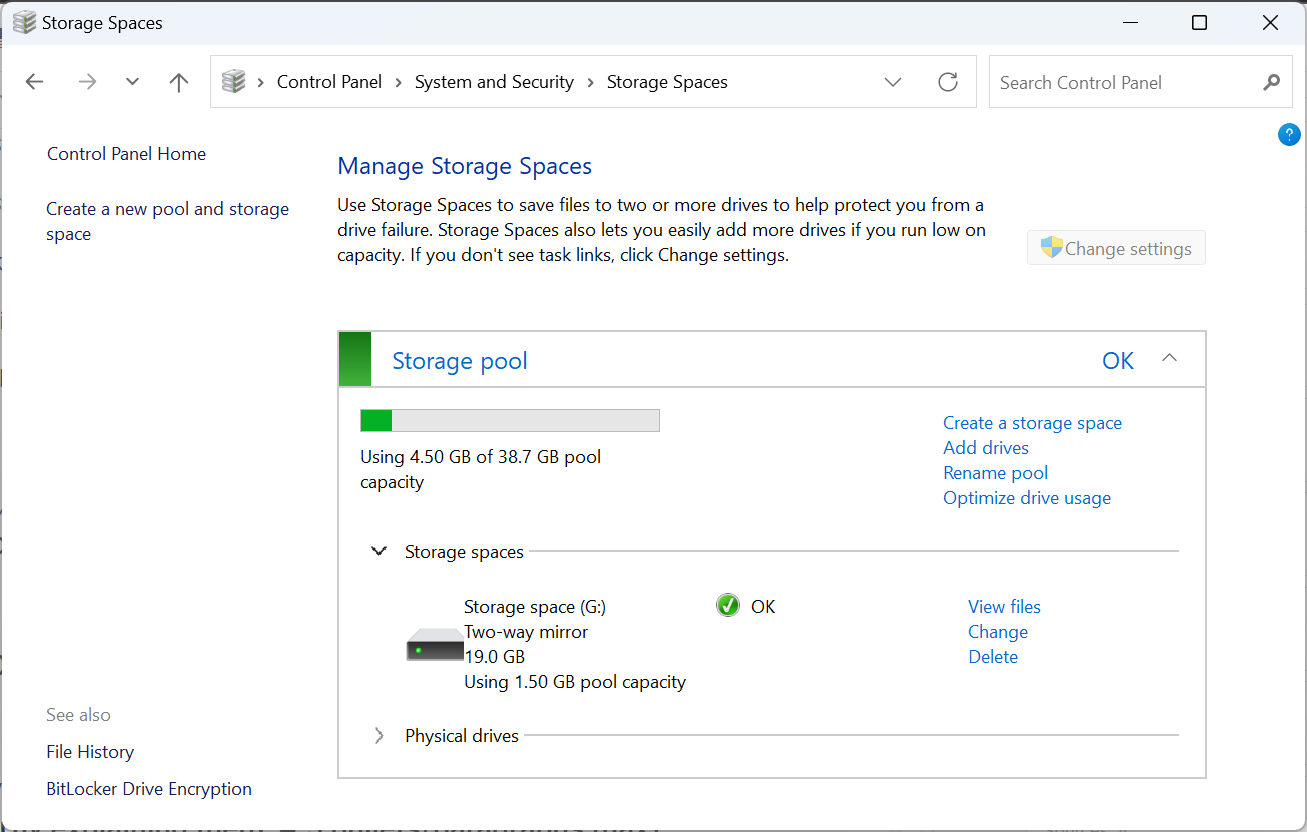
- Created storage spaces will now be listed under dedicated sections in Control Panel and File Explorer. Here you can modify settings, rename the pool, add drives, or delete storage spaces.

This is how you can set up a RAID array with 2 external hard drives. Keep in mind that it only works with RAID 0 and RAID 1. Other more advanced types require more drives.
3. Via Command Prompt
 Note that the process requires converting the disk to a dynamic disk, creating a RAID setup, and finally formatting it. To simplify, let's break the process down into parts. But we recommend using Settings or Control Panel for easier setup.
Note that the process requires converting the disk to a dynamic disk, creating a RAID setup, and finally formatting it. To simplify, let's break the process down into parts. But we recommend using Settings or Control Panel for easier setup.
3.1 Convert to dynamic
- Press to open Run, type cmd, and then click . Windows#RCtrlShiftEnter

- Place an order at the UAC prompt Click "is".
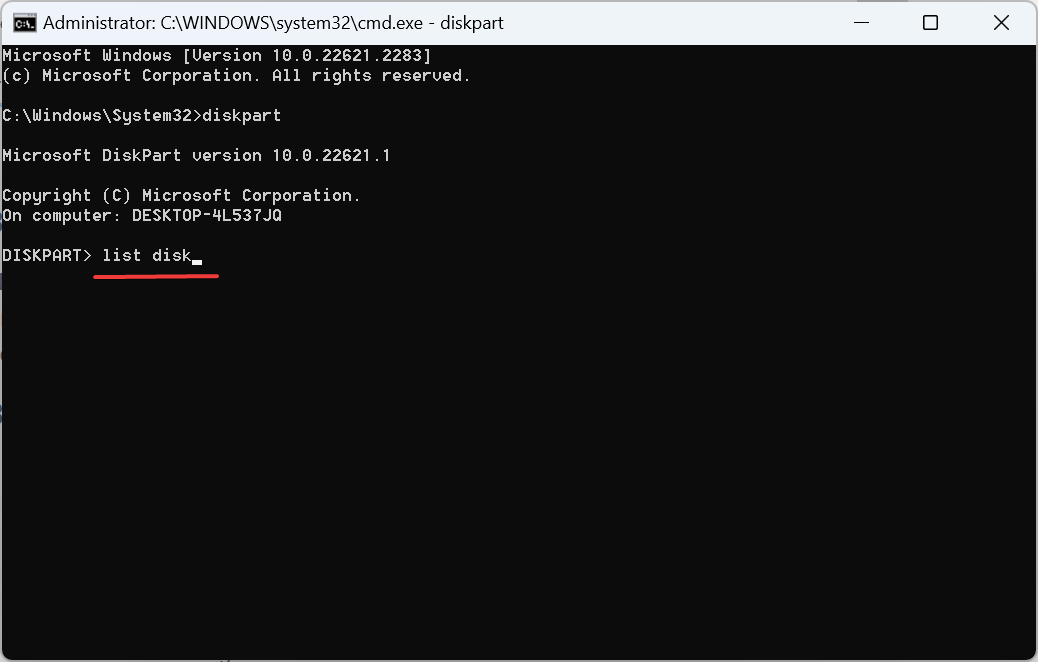
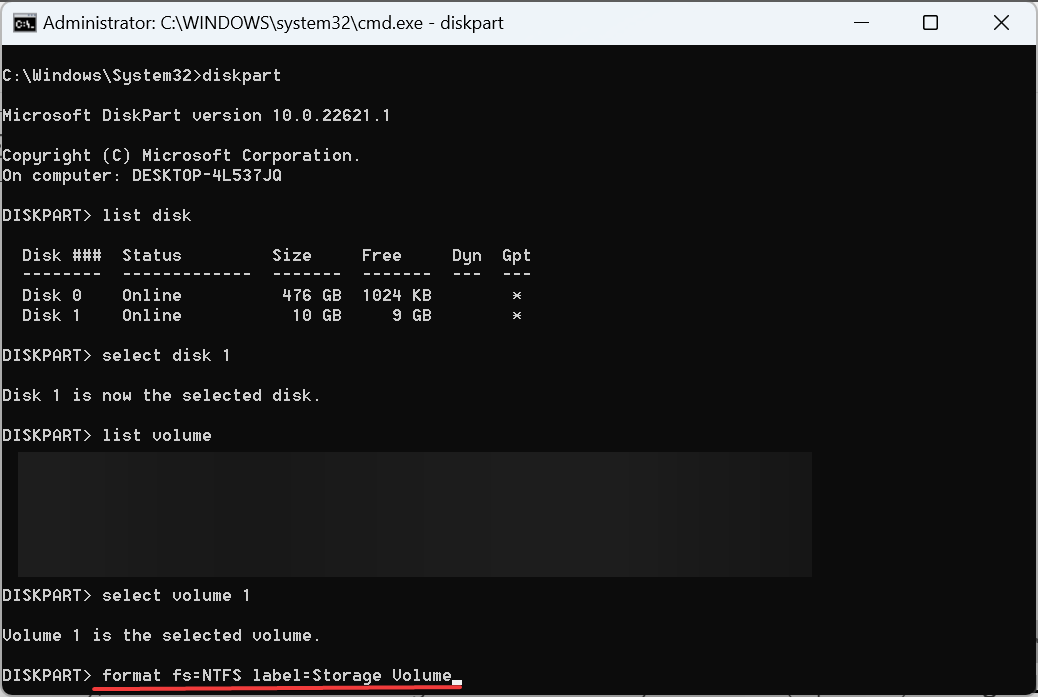
- Paste the following command and click to start the Disk Part utility: Enter
<strong>diskpart</strong> - Run the following command:
<strong>list disk</strong>
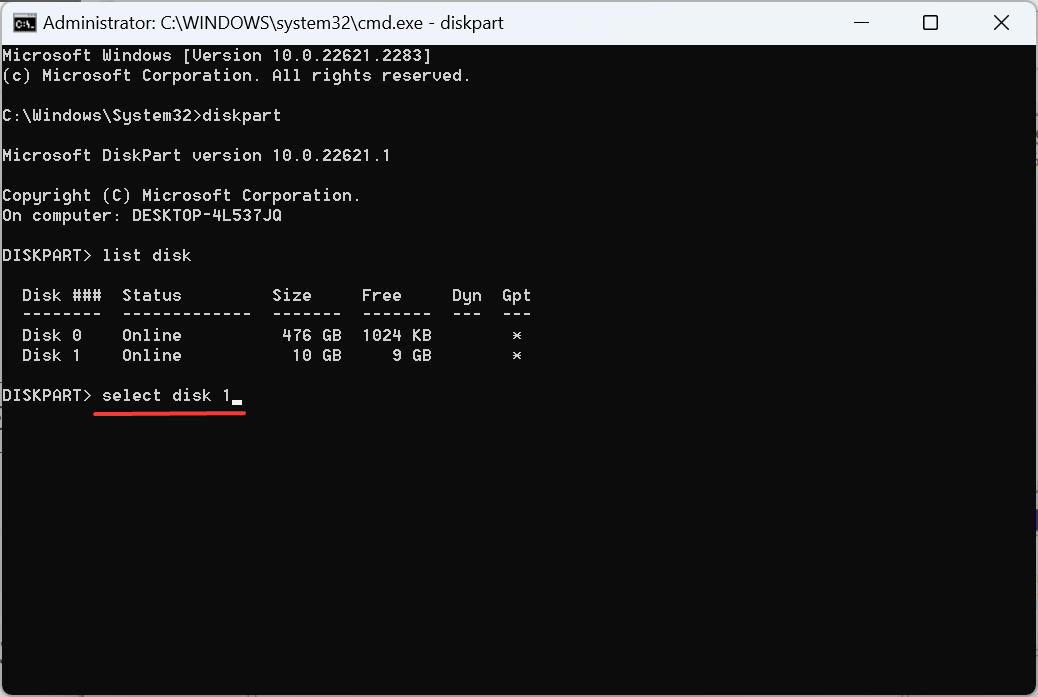
- Now, execute the following command to convert the disk to be added to the RAID system to dynamic type, replacing X with the number assigned to the disk:
<strong>select disk X</strong><strong>convert dynamic</strong> - Repeat this operation for all such disks.
3.2 RAID External Hard Drive
- Run the following command to select the first disk, replacing X with the disk number:
<strong>select disk X</strong>
- Next, execute the following command to create the RAID volume (for more disks, list them in the command):
<strong>create volume RAID disk 1 ,2,3</strong>
3.3 Format external drive
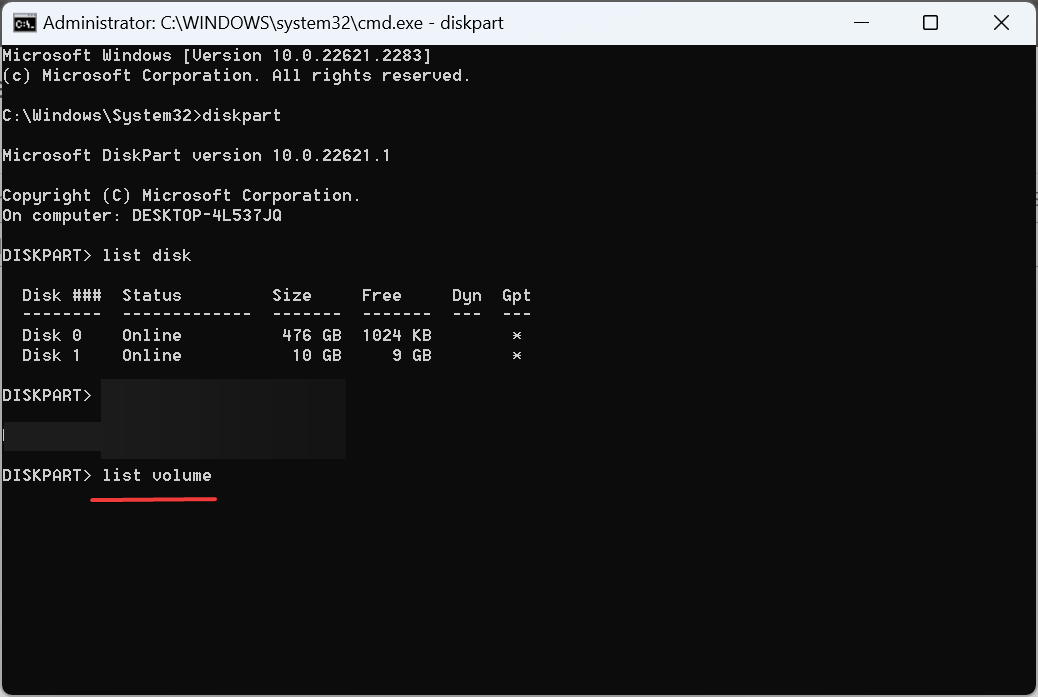
- Run the following command to identify the number assigned to the RAID volume:
<strong>list volume</strong>
- Execute this command, replacing X with the assigned number:
<strong>select volume X</strong> - Next, run the following command to format and then assign the label:
<strong>format fs=NTFS label=Storage Volume</strong>
- Finally, run the following command to Assign a drive letter of your choice (replacing X):
<strong>assign letter= RAID the external drive, but using these commands it will be RAID level 0. To set another level, you need to run a bunch of other commands. </strong>Keep in mind that Diskpart is an advanced tool that helps eliminate any errors you encountered before.
: Best performance, but least protection.
- RAID 1: Data storage is duplicated, improving read performance.
- RAID 2: Uses striping, but has become obsolete over the years.
- RAID 3: One drive is used to store parity information, also striped.
- RAID 4: Use large striping and eliminate I/O overlap
- RAID 5: At least three disks, preferably five . Allows a RAID array to function normally if one drive fails.
- Nested RAID levels are combinations of standard levels, such as RAID 10 (RAID 1 RAID 0). Keep in mind that you don't necessarily need an external drive to complete this process. You can RAID 1 an external hard drive by creating a virtual drive on it!
The above is the detailed content of How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to fix missing ReadyBoost tabs in Windows 11
Jul 13, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
How to fix missing ReadyBoost tabs in Windows 11
Jul 13, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
Is the "Ready to Accelerate" tab not showing up on any drives on your system? Don't worry. ReadyBoost is technology that uses available space on your drive to make your system faster. However, if you cannot find a specific ReadyBoost tab in File Explorer, you need to follow these resolutions to quickly resolve this issue. Fix 1 – Compatible USB Drives There are some specific USB drives that support ReadyBoost natively. Like NTFS, drives formatted with FAT16 or FAT32 support ReadyBoost technology. Step 1 – You have to check the drive type. So, open File Explorer. Step 2 – Go to “This PC”. You will see all drives. Now
 Steps to configure RAID 1 on Windows 11
Sep 22, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Steps to configure RAID 1 on Windows 11
Sep 22, 2023 pm 03:05 PM
Windows 11 has strict requirements, and after struggling to obtain that storage, losing your hard drive and data would be a shame. Well, we have good news that can help you buffer against hard drive failure. Using built-in Windows tools, you can copy all your data from one drive to another. This way, if one drive fails, you can mirror and rebuild the original data on the replacement drive. Can Windows 11 do RAID? With Windows Storage Spaces feature, you can perform RAID on Windows 11. This feature allows you to create multiple virtual disks using a hard drive connected directly to your computer without degrading performance. Benefits of Raid: Reduce the cost of disk
 Fix: WD My Cloud doesn't show up on the network in Windows 11
Oct 02, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
Fix: WD My Cloud doesn't show up on the network in Windows 11
Oct 02, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
If WDMyCloud is not showing up on the network in Windows 11, this can be a big problem, especially if you store backups or other important files in it. This can be a big problem for users who frequently need to access network storage, so in today's guide, we'll show you how to fix this problem permanently. Why doesn't WDMyCloud show up on Windows 11 network? Your MyCloud device, network adapter, or internet connection is not configured correctly. The SMB function is not installed on the computer. A temporary glitch in Winsock can sometimes cause this problem. What should I do if my cloud doesn't show up on the network? Before we start fixing the problem, you can perform some preliminary checks:
 Convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa
Mar 25, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa
Mar 25, 2024 am 09:36 AM
When creating a virtual machine, you will be asked to select a disk type, you can select fixed disk or dynamic disk. What if you choose fixed disks and later realize you need dynamic disks, or vice versa? Good! You can convert one to the other. In this post, we will see how to convert VirtualBox fixed disk to dynamic disk and vice versa. A dynamic disk is a virtual hard disk that initially has a small size and grows in size as you store data in the virtual machine. Dynamic disks are very efficient at saving storage space because they only take up as much host storage space as needed. However, as disk capacity expands, your computer's performance may be slightly affected. Fixed disks and dynamic disks are commonly used in virtual machines
 How to update network drive login credentials in Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:18 PM
How to update network drive login credentials in Windows 11
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:18 PM
To enhance network drive security, Microsoft supports password-protecting shared folders or network drives. However, to ensure continued protection, we need to change the password for the network drive regularly. This article will introduce how to update the login credentials of a network drive in Windows 11/10. How to Update Network Drive Login Credentials in Windows In order to update the network driver’s login credentials, we need to use Credential Manager. This is a pre-installed feature on Windows computers and can be accessed through the Control Panel. So, follow the steps below to perform the same. Click Win+S, search for "Control Panel" and click "Open". Change the screen view proportionally to large icons.
 How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11
Sep 16, 2023 pm 10:05 PM
How to RAID an external hard drive on Windows 11
Sep 16, 2023 pm 10:05 PM
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is a data storage technology in which multiple external drives are combined into one. It was widely used when large hard drives were expensive, but many people still prefer the RAID external drive method. There are several levels of RAID, each serving a specific purpose. Keep in mind that the average user doesn't have to delve into the complexity, a simple setup of RAID0 or RAID1 should work fine. Reasons to consider raiding an external drive: Improved PC performance Easy to configure, cheaper than existing alternatives Faster data reading and writing Efficient backup solution through mirroring How to RAID an external drive on Windows 11? Before RAID external hard drives, you need to pay attention to the following first things
 How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11
Sep 23, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11
Sep 23, 2023 pm 11:33 PM
If you want to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk in Windows 11, you should create a backup first as the process will erase all data in it. Why should you convert dynamic disk to basic disk in Windows 11? According to Microsoft, dynamic disks have been deprecated from Windows and their use is no longer recommended. Additionally, Windows Home Edition does not support dynamic disks, so you will not be able to access these logical drives. If you want to combine more disks into a larger volume, it is recommended to use Basic Disks or Storage Spaces. In this article, we will show you how to convert dynamic disk to basic disk on Windows 11 How to convert dynamic disk to basic disk in Windows 11? In the beginning
 4 Ways to Check SSD Health on Windows 11
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:49 PM
4 Ways to Check SSD Health on Windows 11
Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:49 PM
SSDs are quickly replacing HDDs due to their fast read, write, and access speeds, but even though they are more reliable, you still need to check the health of your SSDs in Windows 11. Can I check the health of my SSD? Of course you can, and should, since they have limited read/write cycles. SLCNAND flash SSDs are currently the most popular and can handle approximately 50,000 to 100,000 write cycles. Nonetheless, in this article, you will learn how to check the health of your SSD and extend its lifecycle on Windows 11. How to check SSD health on Windows 11? First, here’s how to identify an SSD that’s about to fail: You start