 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C++
C++
 C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument

Hyperbolic functions are defined using hyperbolas instead of circles and are equivalent to ordinary trigonometric functions. It returns the ratio parameter in the hyperbolic sine function from the supplied angle in radians. But do the opposite, or in other words. If we want to calculate an angle from a hyperbolic sine, we need an inverse hyperbolic trigonometric operation like the hyperbolic inverse sine operation.
This lesson will demonstrate how to use the hyperbolic inverse sine (asinh) function in C to calculate angles using the hyperbolic sine value in radians. The hyperbolic arcsine operation follows the following formula -
$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\: \:\sqrt{x^2\: \:1})}, where\:In\:is\ :Natural logarithm\:(log_e \: k)$$
asinh() function
According to the hyperbolic sine value, the angle can be calculated using the asinh() function. This function comes with the C standard library. Before using this function we must import the cmath library. This method returns the angle in radians and takes the sine value as argument. The following uses simple syntax -
grammar
#include < cmath > asinh( <hyperbolic sine value> )
algorithm
- Take the hyperbolic sine value x as input
- Use asinh(x) to calculate sinh−1(x)
- Return results.
Example
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
float solve( float x ) {
float answer;
answer = asinh( x );
return answer;
}
int main()
{
float angle, ang_deg;
angle = solve( 2.3013 );
ang_deg = angle * 180 / 3.14159;
cout << "The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 2.3013 is: " << angle << " = " << ang_deg << " (in degrees)" << endl;
angle = solve( 11.5487 );
ang_deg = angle * 180 / 3.14159;
cout << "The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 11.5487 is: " << angle << " = " << ang_deg << " (in degrees)" << endl;
angle = solve( 0.86867 );
ang_deg = angle * 180 / 3.14159;
cout << "The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 0.86867 is: " << angle << " = " << ang_deg << " (in degrees)" << endl;
angle = solve( -0.86867 );
ang_deg = angle * 180 / 3.14159;
cout << "The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value - 0.86867 is: " << angle << " = " << ang_deg << " (in degrees)" << endl;
}
Output
The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 2.3013 is: 1.5708 = 90.0001 (in degrees) The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 11.5487 is: 3.14159 = 180 (in degrees) The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value 0.86867 is: 0.785397 = 45 (in degrees) The angle (in radian) for given hyperbolic sine value - 0.86867 is: -0.785397 = -45 (in degrees)
The asinh() method in this case receives the hyperbolic sine value and returns the angle in radian format. We convert this output from radians to degrees using the formula below.
$$\mathrm{\theta_{deg}\:=\:\theta_{rad}\:\times\frac{180}{\pi}}$$
in conclusion
To perform inverse hyperbolic operations using sine values, we use the asinh() function from the cmath package. After receiving a hyperbolic sine value as input, the function outputs the desired angle in radians. In older versions of C and C, the return type is double; later versions of C also use overloaded forms of float and long-double. When an integer value is passed as an argument, the asinh() function is called after converting the input argument to type double.
The above is the detailed content of C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 i9-12900H parameter evaluation list
Feb 23, 2024 am 09:25 AM
i9-12900H parameter evaluation list
Feb 23, 2024 am 09:25 AM
i9-12900H is a 14-core processor. The architecture and technology used are all new, and the threads are also very high. The overall work is excellent, and some parameters have been improved. It is particularly comprehensive and can bring users Excellent experience. i9-12900H parameter evaluation review: 1. i9-12900H is a 14-core processor, which adopts the q1 architecture and 24576kb process technology, and has been upgraded to 20 threads. 2. The maximum CPU frequency is 1.80! 5.00ghz, which mainly depends on the workload. 3. Compared with the price, it is very suitable. The price-performance ratio is very good, and it is very suitable for some partners who need normal use. i9-12900H parameter evaluation and performance running scores
 C++ function parameter type safety check
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
C++ function parameter type safety check
Apr 19, 2024 pm 12:00 PM
C++ parameter type safety checking ensures that functions only accept values of expected types through compile-time checks, run-time checks, and static assertions, preventing unexpected behavior and program crashes: Compile-time type checking: The compiler checks type compatibility. Runtime type checking: Use dynamic_cast to check type compatibility, and throw an exception if there is no match. Static assertion: Assert type conditions at compile time.
 C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
C++ program to find the value of the inverse hyperbolic sine function taking a given value as argument
Sep 17, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Hyperbolic functions are defined using hyperbolas instead of circles and are equivalent to ordinary trigonometric functions. It returns the ratio parameter in the hyperbolic sine function from the supplied angle in radians. But do the opposite, or in other words. If we want to calculate an angle from a hyperbolic sine, we need an inverse hyperbolic trigonometric operation like the hyperbolic inverse sine operation. This course will demonstrate how to use the hyperbolic inverse sine (asinh) function in C++ to calculate angles using the hyperbolic sine value in radians. The hyperbolic arcsine operation follows the following formula -$$\mathrm{sinh^{-1}x\:=\:In(x\:+\:\sqrt{x^2\:+\:1})}, Where\:In\:is\:natural logarithm\:(log_e\:k)
 C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
C++ program to print dictionary
Sep 11, 2023 am 10:33 AM
A map is a special type of container in C++ in which each element is a pair of two values, namely a key value and a map value. The key value is used to index each item, and the mapped value is the value associated with the key. Regardless of whether the mapped value is unique, the key is always unique. To print map elements in C++ we have to use iterator. An element in a set of items is indicated by an iterator object. Iterators are primarily used with arrays and other types of containers (such as vectors), and they have a specific set of operations that can be used to identify specific elements within a specific range. Iterators can be incremented or decremented to reference different elements present in a range or container. The iterator points to the memory location of a specific element in the range. Printing a map in C++ using iterators First, let's look at how to define
 C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
C program uses rename() function to change file name
Sep 21, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
The rename function changes a file or directory from its old name to its new name. This operation is similar to the move operation. So we can also use this rename function to move files. This function exists in the stdio.h library header file. The syntax of the rename function is as follows: intrename(constchar*oldname,constchar*newname); The function of the rename() function accepts two parameters. One is oldname and the other is newname. Both parameters are pointers to constant characters that define the old and new names of the file. Returns zero if the file was renamed successfully; otherwise, returns a nonzero integer. During a rename operation
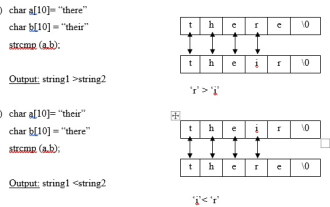 Write a C program that uses the strncmp library function to compare two strings
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
Write a C program that uses the strncmp library function to compare two strings
Sep 09, 2023 pm 01:17 PM
Strncmp is a predefined library function, present in the string.h file, which is used to compare two strings and display which string is larger. strcmp function (string comparison) This function compares two strings. It returns the ASCII difference of the first non-matching character in the two strings. Syntax intstrcmp(string1,string2); If the difference is equal to zero, then string1=string2. If the difference is positive, string1>string2. If the difference is negative, string1<string2. Example strncmp function This function is used to compare the first n characters of two strings. syntax strn
 C++ program to check if a character is alphabetic or non-alphabetic
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
C++ program to check if a character is alphabetic or non-alphabetic
Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
Using strings or characters is sometimes very useful when solving some logic programming problems. A string is a collection of characters, which is a 1-byte data type used to hold symbols in ASCII values. Symbols can be English letters, numbers, or special characters. In this article, we will learn how to check if a character is an English letter or a letter of the alphabet using C++. Checking the isalpha() function To check if a number is a letter, we can use the isalpha() function in the ctype.h header file. This takes a character as input and returns true if it is an alphabet, false otherwise. Let us look at the following C++ implementation to understand the usage of this function. The Chinese translation of Example is: show
 C program to implement Euclidean algorithm
Sep 17, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
C program to implement Euclidean algorithm
Sep 17, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
The problem implements Euclidean's algorithm to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of two integers and outputs the results with a given integer. Solution The solution to implement Euclidean algorithm to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) of two integers is as follows - the logic of finding GCD and LCM is as follows - if (firstno*secondno!=0){ gcd= gcd_rec(firstno,secondno); printf("TheGCDof%dand%dis%d",



