Exploring innovative Java database search optimization solutions

Exploration of innovative Java database search optimization solutions
In recent years, with the rapid development of the Internet, big data has increasingly become an indispensable part of people's lives and work. . In the era of big data, efficient database search technology is crucial to improving the speed and efficiency of data processing. This article explores innovative Java database search optimization solutions to improve search performance and response time, and gives specific code examples.
1. Index optimization
Index is an important tool to improve database search efficiency. When designing a database table, reasonable selection of index columns is key. We can determine the fields that need to be indexed based on the frequency and importance of queries, and use the indexing mechanism of the database to speed up searches.
The following is an example. Suppose we have a table named "employee", which contains the employee's name, job number, salary and other information. Suppose we often perform search operations based on the name of an employee. We can create an index on the name field:
CREATE INDEX idx_employee_name ON employee (name);
Through such optimization, search for employees The operation of names will be greatly accelerated and will not have much impact on the speed of other operations.
2. Partition Optimization
When the amount of data in the database is very large, using partitioning technology can effectively improve database search efficiency. Partitioning divides a table into smaller parts, each of which is stored in separate storage space. This can reduce the scope of the search and increase the search speed.
The following is an example of partition optimization. Suppose we have a table named "order" that contains information such as order number, date, and amount. We can partition the table based on the date field of the order:
CREATE TABLE order (
order_id INT PRIMARY KEY, order_date DATE, order_amount DECIMAL(10,2)
) PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(order_date)) (
PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (2010), PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (2015), PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (2020), PARTITION p4 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
);
Through this optimization, the search operation based on the order date only needs to search the corresponding partition, instead of searching the entire table, thus greatly improving the search efficiency.
3. Cache Optimization
Using caching technology can significantly improve database search performance. Caching is a technology that temporarily stores frequently used data in high-speed memory, which can avoid frequent access to the database, thereby reducing search time and overhead.
The following is an example of cache optimization, assuming we use the open source caching framework Ehcache. We can cache the results of the database query in memory so that the next query can be obtained directly from the cache.
//Create cache object
CacheManager cacheManager = CacheManager.getInstance();
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache("employeeCache");
//Query employee information
String name = "John";
Element element = cache.get(name);
if (element == null) {
// 缓存不存在,从数据库查询
String sql = "SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name = ?";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, name);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 缓存查询结果
if (resultSet.next()) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
employee.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
employee.setSalary(resultSet.getDouble("salary"));
element = new Element(name, employee);
cache.put(element);
}}
Through such optimization, the number of database accesses can be greatly reduced, thereby improving search performance.
Conclusion
This article introduces innovative Java database search optimization solutions, including index optimization, partition optimization and cache optimization. These optimization techniques can improve the performance and response time of database searches, making data processing more efficient. In actual development, we can choose a suitable optimization solution based on specific needs and implement it with specific code examples.
The above is the detailed content of Exploring innovative Java database search optimization solutions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
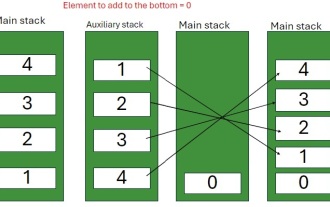 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the




