 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Crushing H100, Nvidia's next-generation GPU is revealed! The first 3nm multi-chip module design, unveiled in 2024
Crushing H100, Nvidia's next-generation GPU is revealed! The first 3nm multi-chip module design, unveiled in 2024
Crushing H100, Nvidia's next-generation GPU is revealed! The first 3nm multi-chip module design, unveiled in 2024
3 nanometer process, performance surpasses H100!
Recently, according to foreign media DigiTimes, NVIDIA is developing the next generation of GPU, the B100 code-named "Blackwell"
It is said that as For products targeting artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) applications, the B100 will use TSMC's 3nm process and a more complex multi-chip module (MCM) design, and will appear in the fourth quarter of 2024.
For NVIDIA, which monopolizes more than 80% of the artificial intelligence GPU market, it can use the B100 to strike while the iron is hot and take advantage of this wave of AI deployment. During the craze, it further attacked challengers such as AMD and Intel.
According to NVIDIA estimates, the field is expected to be worth approximately $300 billion by 2027
Unlike the Hopper/Ada architecture, the Blackwell architecture will extend to data centers and consumer GPUs. Rewritten content: Unlike the Hopper/Ada architecture, the Blackwell architecture will be extended to data centers and consumer-grade GPUs
It is reported that the B100 is not expected to have a significant change in the number of cores , but there are signs that its underlying architecture will undergo major adjustments.
This multi-chip module (MCM) design shows that Nvidia will use advanced packaging technology to separate GPU components into independent chips
Although the specific chip quantity and configuration have not yet been determined, this approach will give NVIDIA greater flexibility in the field of custom chips
This It is exactly the same as AMD’s intention to launch the Instinct MI300 series.

However, it remains to be seen which 3nm-level process Nvidia B100 will use.
Currently, TSMC already has many 3nm nodes, including performance-enhancing N3P and high-performance computing-oriented N3X
Given that Nvidia uses customized manufacturing technology on Ada Lovelace, Hopper and Ampere, it can be inferred that the new Blackwell will most likely use customized nodes.
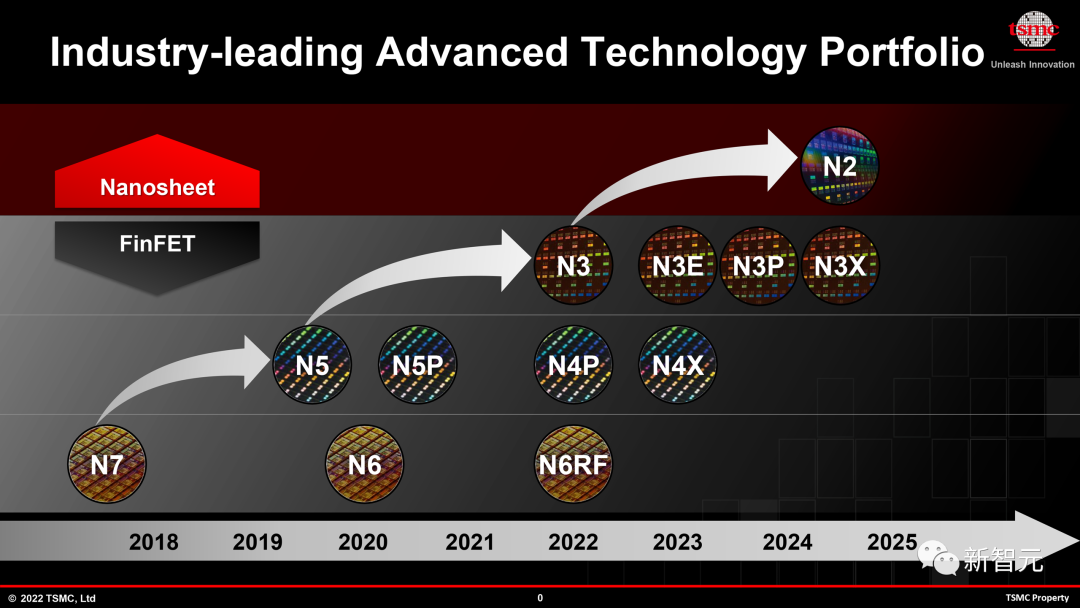
Of course, not only NVIDIA will adopt TSMC N3 technology next year
AMD, Intel ), MediaTek and Qualcomm will all use one of TSMC’s 3nm nodes in 2024-2025.
In fact, MediaTek has adopted TSMC’s first N3E design.
Currently, only Apple uses TSMC’s N3B (first-generation N3) technology to manufacture its latest A17 Pro chip.
In addition, other chips, such as M3, M3 Pro, M3 Max and M3 Ultra, are also expected to use N3B technology.
The above is the detailed content of Crushing H100, Nvidia's next-generation GPU is revealed! The first 3nm multi-chip module design, unveiled in 2024. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 How to configure firewall rules for Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to configure firewall rules for Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 06:51 AM
This article describes how to configure firewall rules using iptables or ufw in Debian systems and use Syslog to record firewall activities. Method 1: Use iptablesiptables is a powerful command line firewall tool in Debian system. View existing rules: Use the following command to view the current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L-n-v allows specific IP access: For example, allow IP address 192.168.1.100 to access port 80: sudoiptables-AINPUT-ptcp--dport80-s192.16
 How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
This article describes how to adjust the logging level of the ApacheWeb server in the Debian system. By modifying the configuration file, you can control the verbose level of log information recorded by Apache. Method 1: Modify the main configuration file to locate the configuration file: The configuration file of Apache2.x is usually located in the /etc/apache2/ directory. The file name may be apache2.conf or httpd.conf, depending on your installation method. Edit configuration file: Open configuration file with root permissions using a text editor (such as nano): sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession



