 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Use Python script operations to monitor and manage processes in Linux
Use Python script operations to monitor and manage processes in Linux
Use Python script operations to monitor and manage processes in Linux

Title: Python script implements process monitoring and management in Linux
Abstract:
This article introduces how to use Python script to monitor processes in Linux systems and management. By writing Python scripts, we can easily implement process monitoring and management operations, including querying process information, starting new processes, stopping specified processes or stopping processes in batches, etc. Specific code examples will be given later. By studying this article, readers can master the basic methods of using Python scripts to monitor and manage Linux processes.
Keywords:
Python script, Linux process, monitoring, management, code examples
Introduction:
In the Linux system, the process is the basic unit running in the operating system. Process monitoring and management are of great significance to ensure the stable operation of the system and the reasonable allocation of resources. The traditional operation method mainly relies on command line tools, and the operation is not flexible and convenient enough. As a simple, easy-to-use, feature-rich programming language, Python provides powerful process monitoring and management capabilities, and can easily implement various operations.
1. Query process information
Python provides the psutil library, which can easily query and process process-related information. The following is a sample code that can query the PID, name, status and other information of the specified process.
import psutil
def query_process(process_name):
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid', 'name', 'status']):
if proc.info['name'] == process_name:
print(f"PID: {proc.info['pid']}, Name: {proc.info['name']}, Status: {proc.info['status']}")
query_process("python")By calling the psutil.process_iter() function, we can get the iterators of all processes in the current system, and then traverse to get the information of each process. By comparing the names of processes, we can filter out the processes we need to query. Here we take querying the Python process as an example.
2. Start a new process
Sometimes we need to start a new process through a Python script. Python's subprocess module provides corresponding functions. The following is a sample code:
import subprocess
def start_process(cmd):
subprocess.Popen(cmd)
start_process("ls -l")By calling the subprocess.Popen() function and passing in the corresponding command line instructions, you can start a new process. Here we take starting the ls -l command as an example.
3. Stop the process
In certain scenarios, we may need to stop the specified process. This function can be easily implemented using Python scripts. The following is a sample code:
import os
def stop_process(pid):
os.kill(pid, signal.SIGTERM)
stop_process(1234)Calling the os.kill() function, we can send a signal to the specified process to stop the process. Here we take stopping the process with PID 1234 as an example.
4. Stop processes in batches
When you need to stop multiple processes at the same time, it is more convenient to use Python scripts. The following is the sample code:
import psutil
def stop_all_processes(process_name):
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid', 'name']):
if proc.info['name'] == process_name:
os.kill(proc.info['pid'], signal.SIGTERM)
stop_all_processes("python")By traversing all processes, we can filter out the processes that need to be stopped and send a stop signal to them using the os.kill() function. Here we take stopping all Python processes as an example.
Conclusion:
This article introduces the basic method of using Python scripts to monitor and manage processes in Linux systems, and provides corresponding code examples. By writing Python scripts, we can easily implement operations such as querying, starting and stopping processes. Readers can further expand and apply it according to specific needs. By mastering these basic methods, we can more flexibly monitor and manage the processes in the system and improve the operating efficiency and stability of the system.
The above is the detailed content of Use Python script operations to monitor and manage processes in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
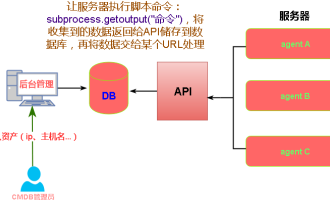 Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Summary of some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. Update time: January 9, 2019 09:34:57 Author: Hope on the field. This article mainly summarizes and introduces to you some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. For everyone Solutions are given for each of the possible triggers, which have certain reference and learning value for colleagues who encounter this problem. Students in need can follow the editor to learn together. Preface: I have encountered some problems at work recently. The crontab scheduled task was not executed. Later, when I searched on the Internet, I found that the Internet mainly mentioned these five incentives: 1. The crond service is not started. Crontab is not a function of the Linux kernel, but relies on a cron.
 PyCharm Advanced Tutorial: Use PyInstaller to package code into EXE format
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PyCharm Advanced Tutorial: Use PyInstaller to package code into EXE format
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PyCharm is a powerful Python integrated development environment that provides a wealth of functions and tools to help developers improve efficiency. Among them, PyInstaller is a commonly used tool that can package Python code into an executable file (EXE format) to facilitate running on machines without a Python environment. In this article, we will introduce how to use PyInstaller in PyCharm to package Python code into EXE format, and provide specific
 Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Orange3 is a powerful open source data visualization and machine learning tool. It has rich data processing, analysis and modeling functions, providing users with simple and fast data mining and machine learning solutions. This article will briefly introduce the basic functions and usage of Orange3, and combine it with actual application scenarios and Python code cases to help readers better master the usage skills of Orange3. The basic functions of Orange3 include data loading, data preprocessing, feature selection, model establishment and evaluation, etc. Users can use the intuitive interface to drag and drop components to easily build data processes. At the same time, more complex data processing and modeling tasks can also be completed through Python scripts. Below we will go through a practical
 How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read Excel data using PyCharm? The steps are as follows: install the openpyxl library; import the openpyxl library; load the Excel workbook; access a specific worksheet; access cells in the worksheet; traverse rows and columns.
 How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
1. First open pycharm and enter the pycharm homepage. 2. Then create a new python script, right-click - click new - click pythonfile. 3. Enter a string, code: s="-". 4. Then you need to repeat the symbols in the string 20 times, code: s1=s*20. 5. Enter the print output code, code: print(s1). 6. Finally run the script and you will see our return value at the bottom: - repeated 20 times.
 Flask installation and configuration tutorial: a tool to easily build Python web applications
Feb 20, 2024 pm 11:12 PM
Flask installation and configuration tutorial: a tool to easily build Python web applications
Feb 20, 2024 pm 11:12 PM
Flask installation and configuration tutorial: A tool to easily build Python Web applications, specific code examples are required. Introduction: With the increasing popularity of Python, Web development has become one of the necessary skills for Python programmers. To carry out web development in Python, we need to choose a suitable web framework. Among the many Python Web frameworks, Flask is a simple, easy-to-use and flexible framework that is favored by developers. This article will introduce the installation of Flask framework,
 What are the website subdomain query tools?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:49 AM
What are the website subdomain query tools?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Website subdomain query tools include: 1. Whois Lookup: can query the registration information of a domain name, including subdomain names; 2. Sublist3r: can automatically scan the subdomain name of a domain name with the help of search engines and other tools; 3. DNSdumpster: can query Information such as the subdomain name, IP address and DNS record of the domain name; 4. Fierce: You can query the subdomain name information of the domain name through the DNS server: 5. Nmap; 6. Recon-ng; 7. Google Hacking.
 CoreFreq: Introduction to CPU frequency monitoring tool under Linux
Feb 21, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
CoreFreq: Introduction to CPU frequency monitoring tool under Linux
Feb 21, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
CoreFreq: Introduction to CPU frequency monitoring tool under Linux In Linux systems, monitoring and managing CPU frequency has always been a relatively important task. By monitoring the frequency of the CPU, we can understand the operating status of the CPU in time and adjust the frequency to improve performance or reduce power consumption. In Linux systems, there are many tools that can be used to monitor CPU frequency, one of the better tools is CoreFreq. This article will introduce the basic functions of the CoreFreq tool and how to



