 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to implement automated deployment on Linux servers using Python script operations
How to implement automated deployment on Linux servers using Python script operations
How to implement automated deployment on Linux servers using Python script operations

The method of Python script operation to realize automated deployment on Linux server requires specific code examples
With the rapid development of cloud computing and containerization technology, automated deployment has It has become an indispensable part of modern software development and operation and maintenance. Python, as a simple, easy-to-use and powerful scripting language, is often used to write automated scripts to achieve various tasks. This article will introduce how to use Python scripts to automate deployment on a Linux server and provide some code examples.
- Confirm the server environment and dependencies
Before starting to write the automated deployment script, we need to confirm the server's operating system and required dependencies. Usually, common operating systems on Linux servers include Ubuntu, CentOS, etc. Depending on the operating system, some software packages or dependent libraries may need to be pre-installed. For example, you may need to install Python and pip on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3 sudo apt-get install python3-pip
- Writing automated deployment scripts
After confirming the server environment and dependencies, we can start writing automated deployment scripts . The following is a simple example for deploying a Docker-based web application on the server:
import os
# 检查Docker是否已安装
def check_docker_installation():
output = os.popen("docker -v").read()
if "version" in output:
return True
else:
return False
# 安装Docker
def install_docker():
os.system("curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh")
os.system("sudo sh get-docker.sh")
# 部署Web应用
def deploy_web_app():
os.system("docker run -d -p 80:80 nginx")
# 主函数
def main():
if not check_docker_installation():
install_docker()
deploy_web_app()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() In the above code, first check whether Docker has been installed by executing the command docker -v. If it is not installed, call the install_docker function to automatically install Docker. Then, call the deploy_web_app function to deploy a simple Nginx container so that the web application can listen on port 80. By calling the main function, all steps can be executed in sequence.
- Run the automated deployment script
After writing the automated deployment script, we can upload the script to the Linux server and execute it through the command line.
First, we need to use the chmod command to set the script file to executable permissions:
chmod +x deploy.py
Next, you can run the script directly:
./deploy.py
The script will automatically check whether Docker is installed, if not installed, it will automatically install Docker, and finally deploy the web application.
Summary
This article introduces how to use Python scripts to implement automated deployment on Linux servers. Through sample code, it shows how to check the installation status of Docker, install Docker and deploy web applications. Of course, the scenarios and tasks of automated deployment vary, and in practice more detailed operations may be required based on specific circumstances. I hope this article can provide some help for readers to understand and master the application of Python in automated deployment.
The above is the detailed content of How to implement automated deployment on Linux servers using Python script operations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
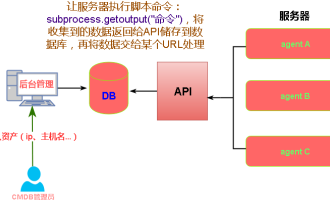 Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Summary of some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. Update time: January 9, 2019 09:34:57 Author: Hope on the field. This article mainly summarizes and introduces to you some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. For everyone Solutions are given for each of the possible triggers, which have certain reference and learning value for colleagues who encounter this problem. Students in need can follow the editor to learn together. Preface: I have encountered some problems at work recently. The crontab scheduled task was not executed. Later, when I searched on the Internet, I found that the Internet mainly mentioned these five incentives: 1. The crond service is not started. Crontab is not a function of the Linux kernel, but relies on a cron.
 Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Orange3 is a powerful open source data visualization and machine learning tool. It has rich data processing, analysis and modeling functions, providing users with simple and fast data mining and machine learning solutions. This article will briefly introduce the basic functions and usage of Orange3, and combine it with actual application scenarios and Python code cases to help readers better master the usage skills of Orange3. The basic functions of Orange3 include data loading, data preprocessing, feature selection, model establishment and evaluation, etc. Users can use the intuitive interface to drag and drop components to easily build data processes. At the same time, more complex data processing and modeling tasks can also be completed through Python scripts. Below we will go through a practical
 How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read Excel data using PyCharm? The steps are as follows: install the openpyxl library; import the openpyxl library; load the Excel workbook; access a specific worksheet; access cells in the worksheet; traverse rows and columns.
 How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
1. First open pycharm and enter the pycharm homepage. 2. Then create a new python script, right-click - click new - click pythonfile. 3. Enter a string, code: s="-". 4. Then you need to repeat the symbols in the string 20 times, code: s1=s*20. 5. Enter the print output code, code: print(s1). 6. Finally run the script and you will see our return value at the bottom: - repeated 20 times.
 What are the website subdomain query tools?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:49 AM
What are the website subdomain query tools?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Website subdomain query tools include: 1. Whois Lookup: can query the registration information of a domain name, including subdomain names; 2. Sublist3r: can automatically scan the subdomain name of a domain name with the help of search engines and other tools; 3. DNSdumpster: can query Information such as the subdomain name, IP address and DNS record of the domain name; 4. Fierce: You can query the subdomain name information of the domain name through the DNS server: 5. Nmap; 6. Recon-ng; 7. Google Hacking.
 How to call the python workflow engine framework
Mar 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
How to call the python workflow engine framework
Mar 02, 2024 am 09:00 AM
To call the python workflow engine framework, you need to follow the steps below: Install the workflow engine framework: First, you need to install the required workflow engine framework in the Python environment. Common Python workflow engine frameworks include Celery, airflow, Luigi, etc. You can use the pip command to install the required framework, for example: pipinstallcelery Import the workflow engine framework: In the Python script, you need to import the workflow engine framework used. Import the framework into the script using the import statement, for example: importcelery Define workflow tasks: Next, you need to define the workflow tasks. Workflow tasks are
 Detailed Tutorial: How to Set Environment Variables in PyCharm
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:45 PM
Detailed Tutorial: How to Set Environment Variables in PyCharm
Feb 24, 2024 pm 03:45 PM
PyCharm is a powerful Python integrated development environment that allows developers to write, debug and manage Python code more efficiently. In the daily development process, we often encounter situations where environment variables need to be configured so that the program can correctly access the required resources. This article will introduce in detail how to configure environment variables in PyCharm and provide specific code examples. 1. Configure PyCharm’s environment variables. Configuring environment variables in PyCharm is very simple. The following are the specific steps:
 What programming languages are commonly used by Golang developers?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
What programming languages are commonly used by Golang developers?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Golang is an open source programming language developed by Google and is widely used in back-end service development, cloud computing, network programming and other fields. As a statically typed language, Golang has an efficient concurrency model and a powerful standard library, so it is favored by developers. However, in actual development, Golang developers usually need to combine other programming languages for project development to meet the needs of different scenarios. PythonPython is an object-oriented programming language that is concise, clear, and easy to learn.



