 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Reverse thinking: MetaMath new mathematical reasoning language model trains large models
Reverse thinking: MetaMath new mathematical reasoning language model trains large models
Reverse thinking: MetaMath new mathematical reasoning language model trains large models
Complex mathematical reasoning is an important indicator for evaluating the reasoning ability of large language models. Currently, the commonly used mathematical reasoning data sets have limited sample sizes and insufficient problem diversity, resulting in the phenomenon of "reversal curse" in large language models, that is, a A language model trained on "A is B" cannot be generalized to "B is A" [1]. The specific form of this phenomenon in mathematical reasoning tasks is: given a mathematical problem, the language model is good at using forward reasoning to solve the problem but lacks the ability to solve the problem with reverse reasoning. Reverse reasoning is very common in mathematical problems, as shown in the following 2 examples.
1. Classic problem - chickens and rabbits in the same cage
- Forward reasoning: There are 23 chickens and 12 rabbits in the cage , ask how many heads and how many feet are there in the cage?
- Reverse reasoning: There are several chickens and rabbits in the same cage. Counting from the top, there are 35 heads, and counting from the bottom, there are 94 legs. How many chickens and rabbits are there in the cage?
2. GSM8K Question
- Forward reasoning: James buys 5 packs of beef that are 4 pounds each. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound. How much did he pay?
- Converse reasoning: James buys x packs of beef that are 4 pounds each. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound. . How much did he pay? If we know the answer to the above question is 110, what is the value of unknown variable x?
In order to improve the forward sum of the model For reverse reasoning capabilities, researchers from Cambridge, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and Huawei proposed the MetaMathQA data set based on two commonly used mathematical data sets (GSM8K and MATH): a mathematical reasoning data set with wide coverage and high quality. MetaMathQA consists of 395K forward-inverse mathematical question-answer pairs generated by a large language model. They fine-tuned LLaMA-2 on the MetaMathQA data set to obtain MetaMath, a large language model focusing on mathematical reasoning (forward and inverse), which reached SOTA on the mathematical reasoning data set. The MetaMathQA dataset and MetaMath models at different scales have been open sourced for use by researchers.

- ##Project address: https://meta-math.github.io/
- Paper address: https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.12284
- Data address: https://huggingface.co/datasets/meta-math/MetaMathQA
- Model address: https://huggingface.co/meta-math
- Code address: https://github.com/meta-math/MetaMath
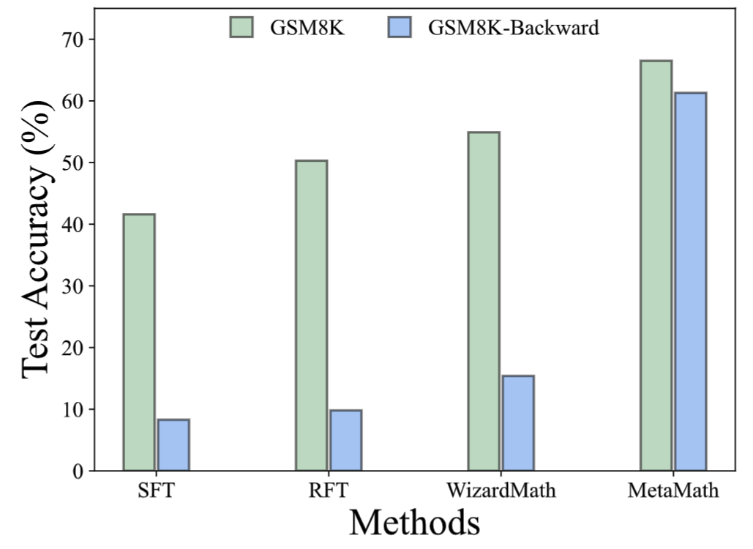
In the GSM8K-Backward data set, we constructed a reverse inference experiment. Experimental results show that compared with methods such as SFT, RFT, and WizardMath, the current method performs poorly on inverse inference problems. In contrast, MetaMath models achieve excellent performance in both forward and backward inference
Method
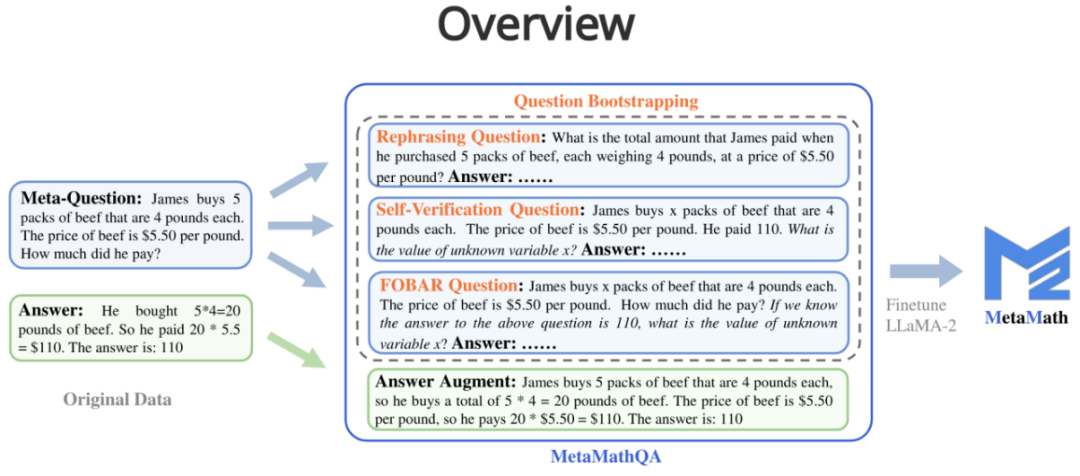
MetaMathQA contains four data augmentation methods:
1. Answer Augmentation (answer Enhancement): Given a problem, a thinking chain that can get the correct result is generated through a large language model as data augmentation.
- Question: James buys 5 packs of beef that are 4 pounds each. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound. How much did he pay?
- Answer: James buys 5 packs of beef that are 4 pounds each, so he buys a total of 5 * 4 = 20 pounds of beef. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound, so he pays 20 * $5.50 = $110. The answer is: 110.
2. Rephrasing Question (question rewriting enhancement): Given meta-question , rewrite the problem through a large language model and generate a thought chain that gets the correct result as data augmentation.
- Question: What is the total amount that James paid when he purchased 5 packs of beef, each weighing 4 pounds, at a price of $5.50 per pound?
- Answer: Each pack of beef weighs 4 pounds, so 5 packs weigh 4 * 5 = 20 pounds in total. The price per pound of beef is $5.50, so the total cost for 20 pounds is 20 * $5.50 = $110. Therefore, James paid a total of $110. The answer is: 110.
##3. FOBAR Question (FOBAR reverse question enhancement):Given the meta-question, the number in the mask condition is Example: "If we know the answer to the above question is 110, what is the value of unknown variable x?").
- Question: James buys x packs of beef that are 4 pounds each. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound. How much did he pay? If we know the answer to the above question is 110, what is the value of unknown variable x?
- Answer: James buys x packs of beef that are 4 pounds each, so he buys a total of 4x pounds of beef. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound, so the total cost of the beef is 5.50 * 4x = 22x. We are given that the total cost is $110, so we can write: 22x = 110. Dividing both sides by 22, we get: x = 5. The value of x is 5.
4. Self-Verification Question (Self-Verification reverse question enhancement): Based on FOBAR, data augmentation is performed by rewriting the inverse problem part into statements using a large language model (rewritten example: "How much did he pay?" (with the answer 110) was rewritten into "He paid 110").
- Question: James buys x packs of beef that are 4 pounds each. The price of beef is $5.50 per pound. He paid 110. What is the value of unknown variable x ?
- Answer: To solve this problem, we need to determine the value of x, which represents the number of packs of beef that James bought. Each pack of beef weighs 4 pounds and costs $5.50 per pound. The total amount James paid is $110. We can set up the equation as follows: Number of packs of beef * Weight per pack * Price per pound = Total amount paid; x * 4 * $5.50 = $110; Let's simplify and solve for x: 4x * $5.50 = $110; 22x = $110; To isolate x, we divide both sides of the equation by 22: 22x / 22 = $110 / 22; x = $5; The value of x is 5.
Experimental results
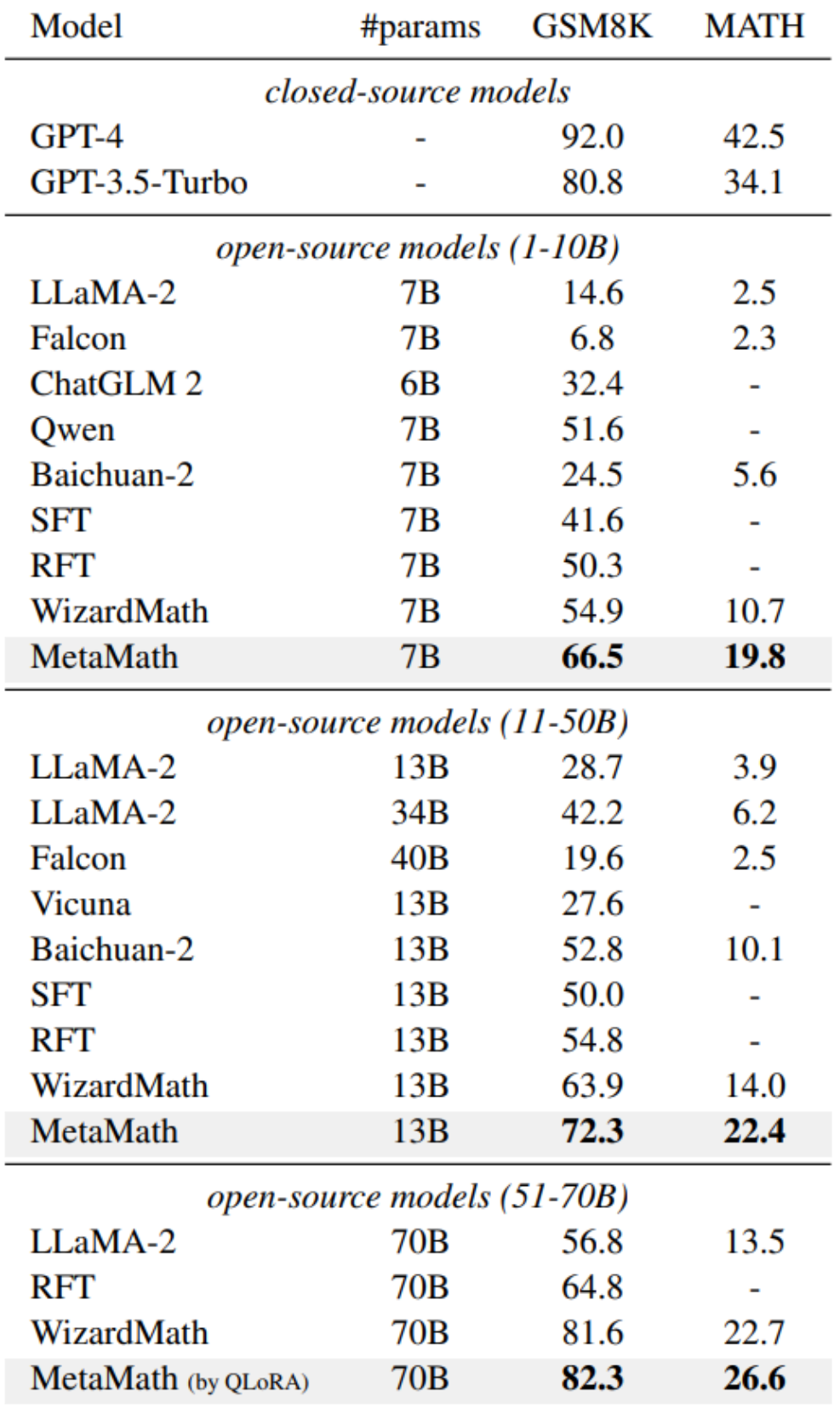
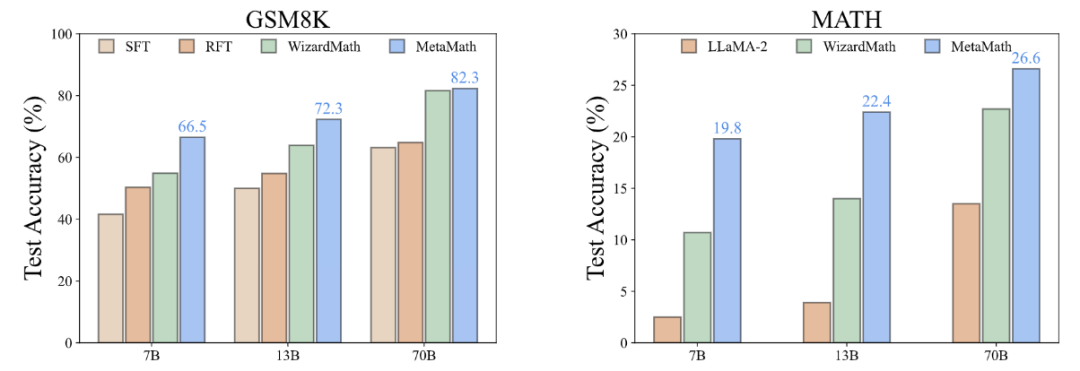
According to the "Surface Alignment Assumption" [2], The power of large language models comes from pre-training, and data from downstream tasks activates the inherent capabilities of the language model learned during pre-training. Therefore, this raises two important questions: (i) which type of data activates latent knowledge most effectively, and (ii) why is one dataset better at such activation than another?
Why is MetaMathQA useful? Improved the quality of thought chain data (Perplexity)
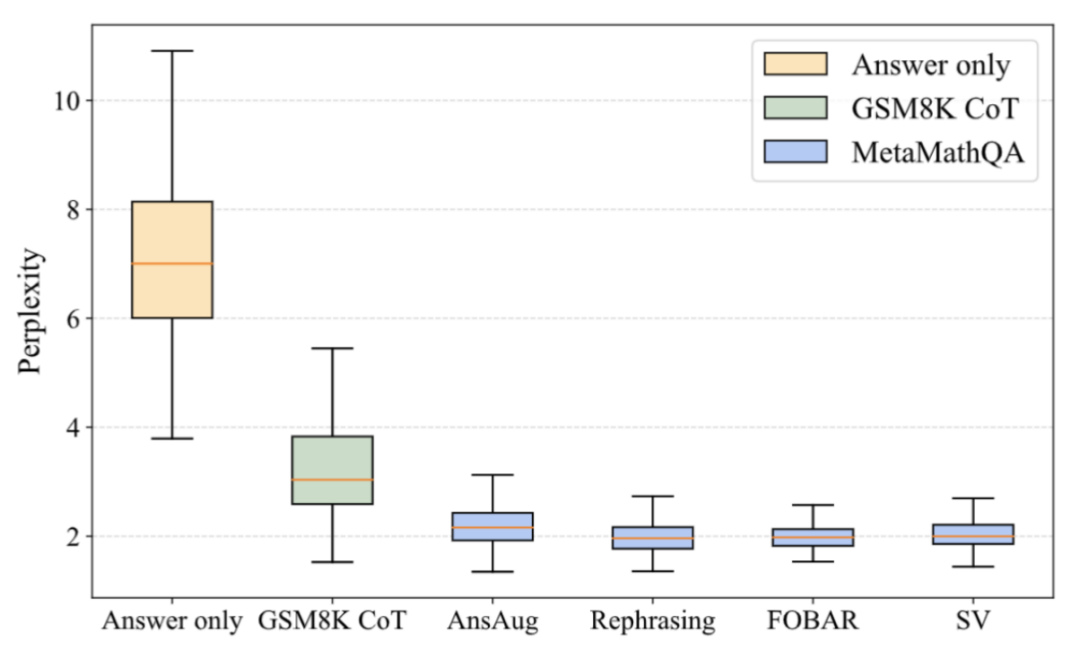 ##As shown in the figure above, the researchers calculated Perplexity of the LLaMA-2-7B model on answer-only data, GSM8K CoT, and various parts of the MetaMathQA dataset. The perplexity of the MetaMathQA dataset is significantly lower than the other two datasets, indicating that it has higher learnability and may be more helpful in revealing the latent knowledge of the model
##As shown in the figure above, the researchers calculated Perplexity of the LLaMA-2-7B model on answer-only data, GSM8K CoT, and various parts of the MetaMathQA dataset. The perplexity of the MetaMathQA dataset is significantly lower than the other two datasets, indicating that it has higher learnability and may be more helpful in revealing the latent knowledge of the model
Why is MetaMathQA useful? Increased the diversity of thought chain data (Diversity)
By comparing the diversity gain of the data and the accuracy gain of the model, the researchers found that the introduction of the same amount of augmented data by reformulation, FOBAR and SV all brought A significant diversity gain was achieved and the accuracy of the model was significantly improved. In contrast, using answer augmentation alone resulted in significant saturation of accuracy. After the accuracy reaches saturation, adding AnsAug data will only bring limited performance improvement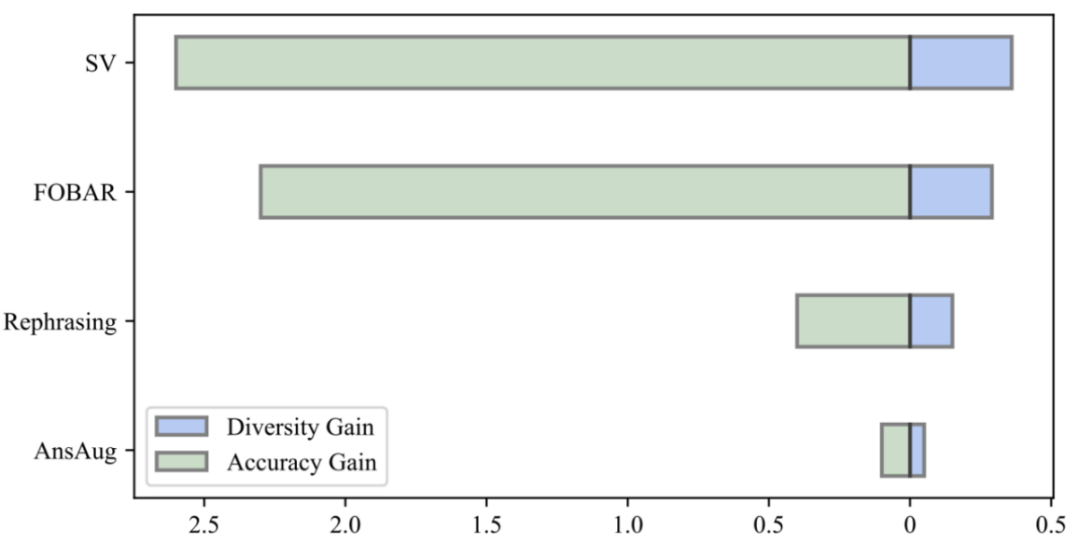
The above is the detailed content of Reverse thinking: MetaMath new mathematical reasoning language model trains large models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
This article describes how to adjust the logging level of the ApacheWeb server in the Debian system. By modifying the configuration file, you can control the verbose level of log information recorded by Apache. Method 1: Modify the main configuration file to locate the configuration file: The configuration file of Apache2.x is usually located in the /etc/apache2/ directory. The file name may be apache2.conf or httpd.conf, depending on your installation method. Edit configuration file: Open configuration file with root permissions using a text editor (such as nano): sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The steps to install an SSL certificate on the Debian mail server are as follows: 1. Install the OpenSSL toolkit First, make sure that the OpenSSL toolkit is already installed on your system. If not installed, you can use the following command to install: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2. Generate private key and certificate request Next, use OpenSSL to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key and a certificate request (CSR): openss
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud



