 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 The platform pays for AI copyright issues, and Google introduces the 'disclaimer protection' service it will launch for Google Cloud in the future
The platform pays for AI copyright issues, and Google introduces the 'disclaimer protection' service it will launch for Google Cloud in the future
The platform pays for AI copyright issues, and Google introduces the 'disclaimer protection' service it will launch for Google Cloud in the future

According to news on October 16, Google announced on the 13th of this month that users who use its own generative AI products will be protected by the official. This site has previously reported that Google claimed The move is "intended to alleviate concerns about potential infringement risks of generative AI."
Currently, Google has introduced more details of this "generative AI indemnification (AI immunity protection)" service, so that users do not have to worry about incurring legal risks due to copyrighted content.
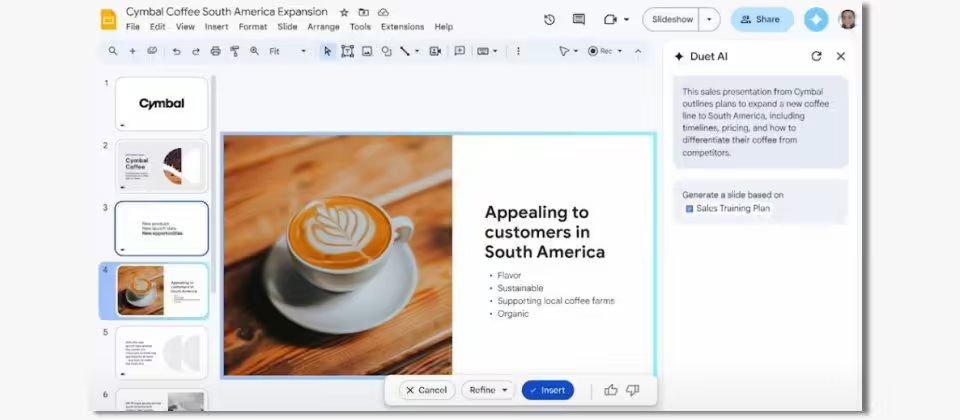 ▲ Picture source Google
▲ Picture source Google
It is reported that this new service consists of two parts, The first part is related to the training data set used by Google (training "Disclaimer" of data), the second part focuses on the generated content of the basic model ("Disclaimer" of generated results).
The "disclaimer" of training materials mainly covers all training data sets used by Google to build AI. If someone claims that the relevant training data sets are infringing, the liability will be borne entirely by Google.
The "disclaimer" of the generated results is the output result when the user uses Google AI services. If the model generated by the user using Google AI services is accused of "copyright infringement", all liability will be borne by Google.
Google previously stated that the relevant "disclaimer protection" content applies to the following Google products:
##However, Google emphasizes that,
- Duet AI in Workspace (including Google Docs document processing tool and text generated in Gmail, Google Slides slide processor, and images in Google Meet video conferencing tool)
- Duet AI in Google Cloud
- Vertex AI Search
- Vertex AI Conversation
- Vertex AI Text Embedding API
- Visual Subtitles on Vertex AI
- Codey API
The prerequisite for exemption is that corporate users "have no infringement intention themselves" and are responsible for using AI, using "existing or developing" AI tools and "citing sources" .
Google said that customers can automatically obtain "disclaimer protection" without modifying existing contracts. Google also claimed that "this is just the first step" and that the company is developing "methods to allow users to use its AI services with peace of mind." ".The above is the detailed content of The platform pays for AI copyright issues, and Google introduces the 'disclaimer protection' service it will launch for Google Cloud in the future. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
The return value types of C language function include int, float, double, char, void and pointer types. int is used to return integers, float and double are used to return floats, and char returns characters. void means that the function does not return any value. The pointer type returns the memory address, be careful to avoid memory leakage.结构体或联合体可返回多个相关数据。
 How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Flexible application of function pointers: use comparison functions to find the maximum value of an array. First, define the comparison function type CompareFunc, and then write the comparison function compareMax(a, b). The findMax function accepts array, array size, and comparison function parameters, and uses the comparison function to loop to compare array elements to find the maximum value. This method has strong code reusability, reflects the idea of higher-order programming, and is conducive to solving more complex problems.
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
A function pointer is a pointer to a function, and a pointer function is a function that returns a pointer. Function pointers point to functions, used to select and execute different functions; pointer functions return pointers to variables, arrays or other functions; when using function pointers, pay attention to parameter matching and checking pointer null values; when using pointer functions, pay attention to memory management and free dynamically allocated memory; understand the differences and characteristics of the two to avoid confusion and errors.
 What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The pointer parameters of C language function directly operate the memory area passed by the caller, including pointers to integers, strings, or structures. When using pointer parameters, you need to be careful to modify the memory pointed to by the pointer to avoid errors or memory problems. For double pointers to strings, modifying the pointer itself will lead to pointing to new strings, and memory management needs to be paid attention to. When handling pointer parameters to structures or arrays, you need to carefully check the pointer type and boundaries to avoid out-of-bounds access.
 What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
The key elements of C function definition include: return type (defining the value returned by the function), function name (following the naming specification and determining the scope), parameter list (defining the parameter type, quantity and order accepted by the function) and function body (implementing the logic of the function). It is crucial to clarify the meaning and subtle relationship of these elements, and can help developers avoid "pits" and write more efficient and elegant code.
 What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
C language function calls can be divided into nested calls and recursive calls. Nested calls refer to calling other functions within a function, nesting them layer by layer. Recursive calls refer to the function itself calling itself, which can be used to deal with self-similar structure problems. The key difference is that the functions in nested calls are called in sequence, with independent interaction scopes, while the functions in recursive calls are constantly called, so you need to pay attention to the recursive basis and stack overflow issues. Which calling method to choose depends on the specific requirements and performance requirements of the problem.
 What does the c language function return pointer output?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
What does the c language function return pointer output?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The C language function returns a pointer to output a memory address. The pointing content depends on the operation inside the function, which may point to local variables (be careful, memory has been released after the function ends), dynamically allocated memory (must be allocated with malloc and free), or global variables.





