 Common Problem
Common Problem
 Microsoft's latest innovation: a device cooling technology that effectively separates cold and hot air
Microsoft's latest innovation: a device cooling technology that effectively separates cold and hot air
Microsoft's latest innovation: a device cooling technology that effectively separates cold and hot air
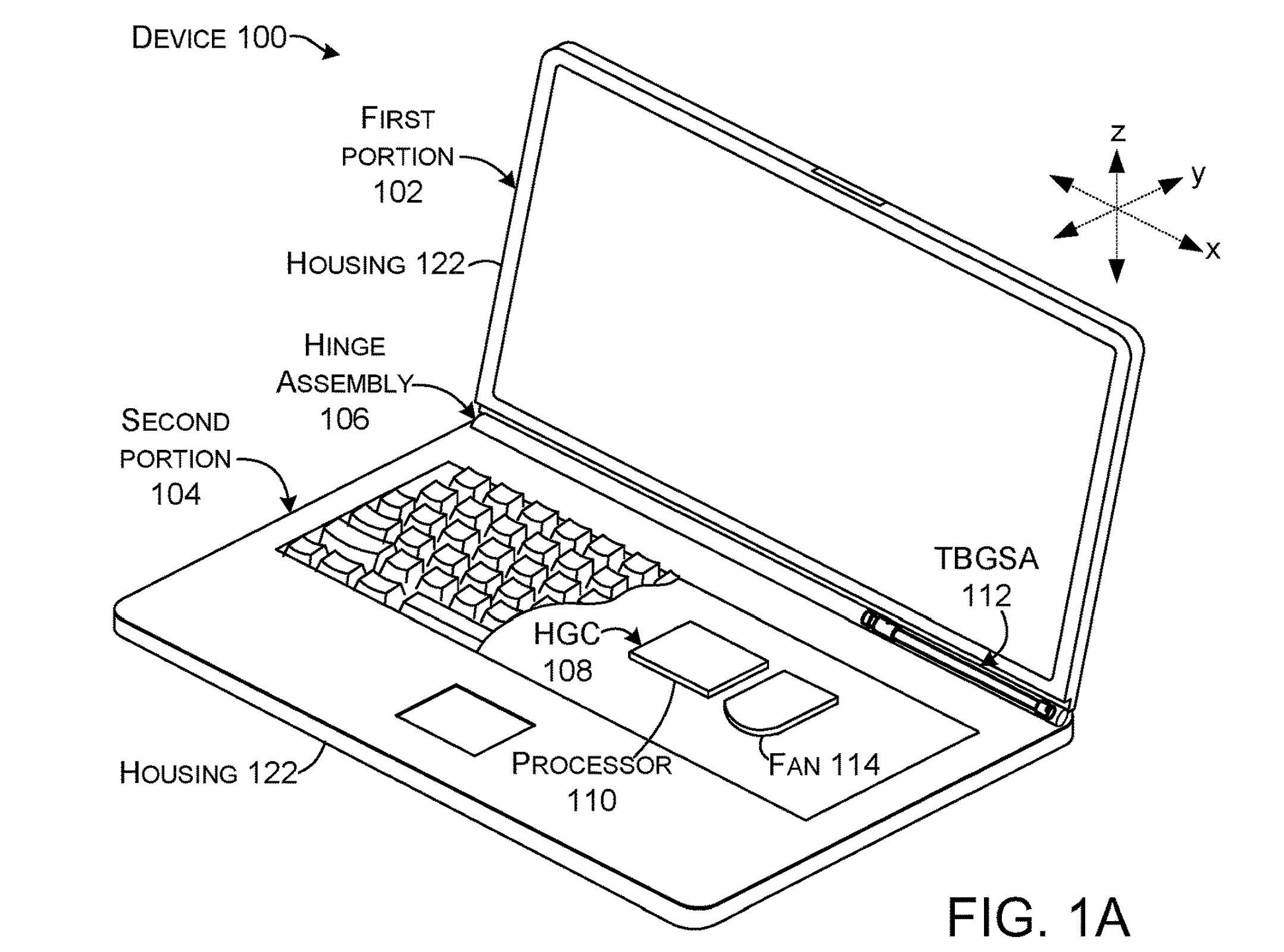
Microsoft recently filed a patent application that could revolutionize the way devices are cooled. Titled "Device Cooling," the patent was filed on February 6, 2022 and was recently published.
Innovation:
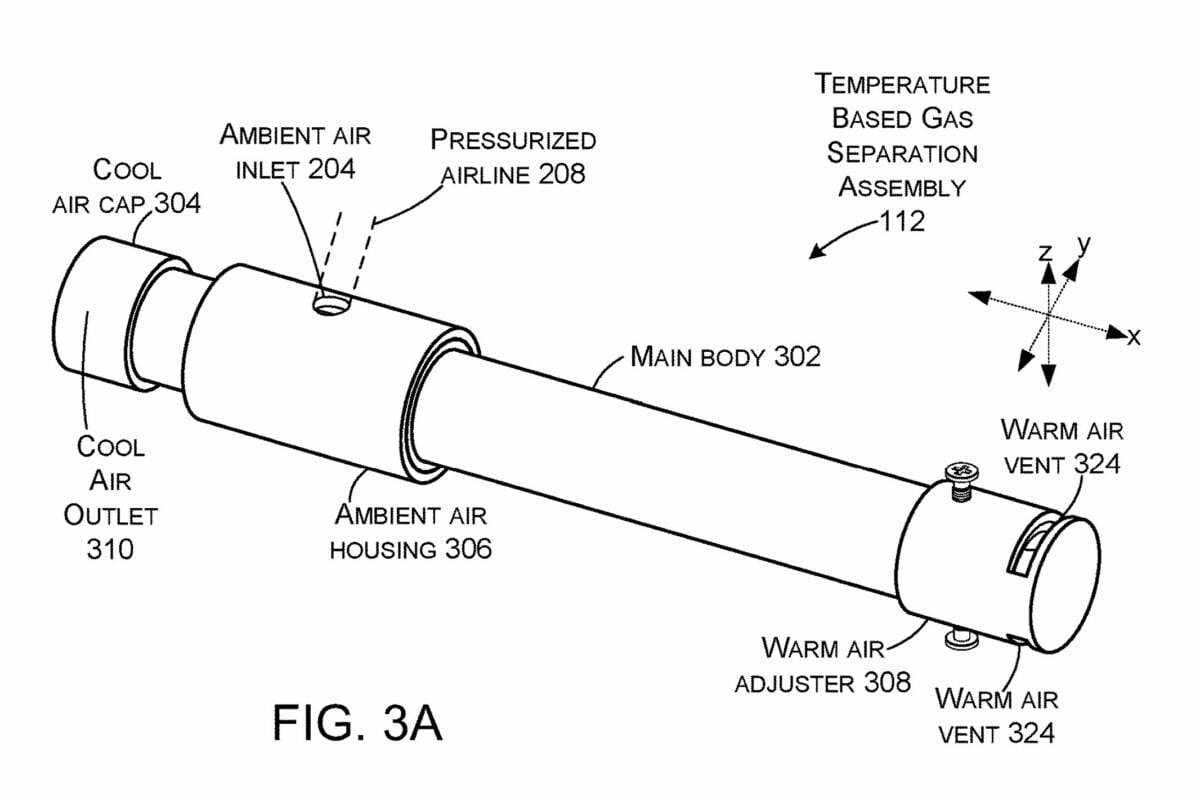
This patent describes a unique method of cooling equipment, specifically air cooling. The innovation lies in the temperature-based gas separation component, which is designed to receive ambient air and separate it into warmer and cooler air.
How it works:
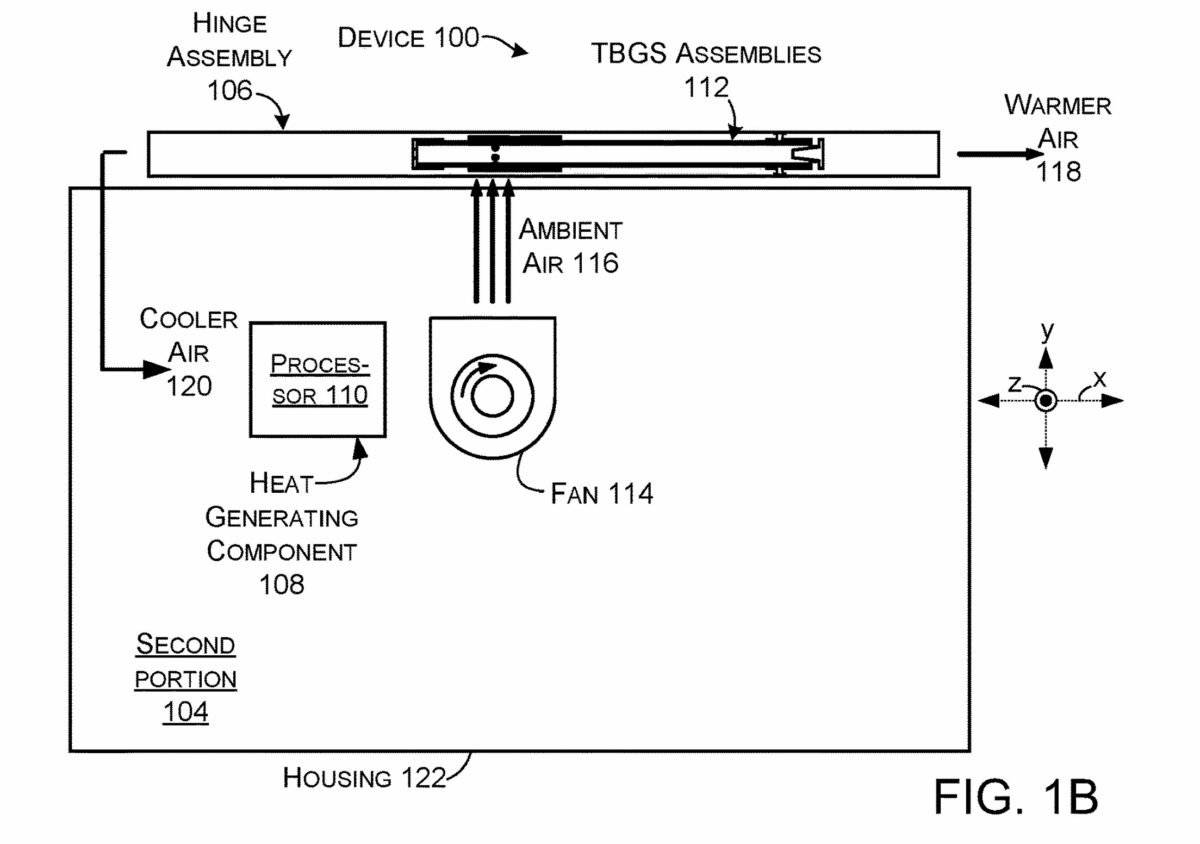
Typically, heat-generating components such as CPUs and GPUs can be cooled by moving ambient air over them. However, this cooling process is much more efficient if cooler air is passed through the heating components.
This new patent from Microsoft proposes a solution in which the device can separate the air that can be used to cool heat-generating components into a warmer airflow and a cooler airflow. The cooler stream can be used to cool heat-generating components, while the warmer stream can be discarded.
Simply put, ambient air is divided into two parts: warm air and cool air. Warmer air is directed outside the device's enclosure, while cooler air is directed inside.
This innovative approach improves equipment performance by maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Potential Impact:
Thermal management is a critical aspect of device performance. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency, component damage and, in extreme cases, equipment failure. By using this new method to effectively manage heat generation, Microsoft's patent could significantly increase device lifespan and reliability.
This patent represents another step forward in Microsoft’s efforts to continuously innovate and improve user experience. As we continue to demand higher performance from our devices, innovations like this will be key to ensuring our technology can keep pace.
The above is the detailed content of Microsoft's latest innovation: a device cooling technology that effectively separates cold and hot air. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Error code 801c03ed: How to fix it on Windows 11
Oct 04, 2023 pm 06:05 PM
Error code 801c03ed: How to fix it on Windows 11
Oct 04, 2023 pm 06:05 PM
Error 801c03ed is usually accompanied by the following message: Administrator policy does not allow this user to join the device. This error message will prevent you from installing Windows and joining a network, thereby preventing you from using your computer, so it is important to resolve this issue as soon as possible. What is error code 801c03ed? This is a Windows installation error that occurs due to the following reason: Azure setup does not allow new users to join. Device objects are not enabled on Azure. Hardware hash failure in Azure panel. How to fix error code 03c11ed on Windows 801? 1. Check Intune settings Log in to Azure portal. Navigate to Devices and select Device Settings. Change "Users can
 How to fix device disabled (error code 22) in Windows 10/11
Aug 04, 2023 pm 03:17 PM
How to fix device disabled (error code 22) in Windows 10/11
Aug 04, 2023 pm 03:17 PM
Is the "This device is disabled" code 22 error in Device Manager preventing you from using a new or old device on your PC? Don’t worry because we are here to help you solve this problem. A code 22 error means the device has been manually disabled and sometimes re-enabling it does not help. Whatever the cause, here are 10 ways to fix the “This device is disabled” code 10 error on Windows 22/PC and make that hardware work again. 1. Unplug and replug new hardware New hardware you plug into your PC may start working again after a quick removal and reinstallation. So if it's a device plugged in via USB, go ahead and unplug it. Then, wait a few seconds and plug it back in. Now, check if the device is showing up in device manager
 8 Ways to Reinstall Safari on iPhone
Sep 16, 2023 am 11:17 AM
8 Ways to Reinstall Safari on iPhone
Sep 16, 2023 am 11:17 AM
Web browsing is an essential function of mobile devices, and browsers facilitate it effectively. These browsers also support the installation of content blockers and other tools to personalize your browsing experience. Apple's iOS platform uses Safari as its default browser. In rare cases, you may find that Safari browser is missing from your device. If you encounter this situation, the following steps will guide you on how to restore it. Can you reinstall Safari on iPhone? Safari is a built-in application on iOS devices and cannot be deleted or uninstalled due to its protected system status. If the app seems to be missing from your device, you may be dealing with an error, or the app may be hidden for various reasons.
 How to re-enable cellular options on Windows 11
Sep 18, 2023 am 10:29 AM
How to re-enable cellular options on Windows 11
Sep 18, 2023 am 10:29 AM
The laptop's cellular capabilities generally work fine, and users can insert a SIM card or use an eSIM. But recently, some people have reported that the cellular option is missing in Windows 11. Regardless of whether they restart the PC or unplug and reinsert the SIM card, the cellular option does not appear in Windows 11. Keep in mind that some Windows 10 users are also facing the same issue. Why don't my mobile network settings show up on Windows 11? Outdated, incompatible, corrupt or problematic drivers Cellular data network operators are facing issues Network adapter is disabled eSIM profile is not working or corrupt How to enable missing cellular option again on Windows 11? Before we start using a slightly complex
 Please update your device settings to accept media transfers
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
Please update your device settings to accept media transfers
Feb 19, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
We will show you how to fix media transfer error when connecting your phone to PC via USB cable. When you try to import photos and videos from your phone to your computer, you may encounter a "Please update your device's settings to accept media transfers" error message displayed by the Photos app. Please update your device settings to accept media transfers Update your device settings to allow media transfers to resolve the error message. Restart your two devices Use different USB cables Check your Android phone settings Install the MTP USB device driver Use other methods to transfer your photos and videos Let’s get started. 1] Restart both devices It is recommended that you first try to restart your devices, including computers and phones, when you encounter a temporary failure. Heavy
 How to stream video or mirror your iPhone or iPad screen using AirPlay
Jul 14, 2023 pm 07:53 PM
How to stream video or mirror your iPhone or iPad screen using AirPlay
Jul 14, 2023 pm 07:53 PM
This quick guide will show you how to use AirPlay, Apple's innovative wireless streaming feature to easily share and display content. Allows you to use Wi-Fi to connect your iPhone or iPad to AirPlay-compatible Apple TVs, smart TVs, speakers, and Macs, as well as certain third-party speakers and smart TVs, for seamless data transfer. AirPlay operates on a peer-to-peer basis, connecting your Apple devices through the local network. It uses a combination of technologies, including Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) for streaming audio and video and Bonjour for device discovery. Simply put, when you use AirPlay, your device sends a stream of data and then
 How to use Windows Copilot to turn on dark mode, do not disturb, manage Bluetooth devices, and more
Aug 01, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
How to use Windows Copilot to turn on dark mode, do not disturb, manage Bluetooth devices, and more
Aug 01, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
Anyone who wants an early look at the future of AI on Windows needs to look no further than the Copilot preview. Copilot, which has very few features and appears to be little more than a BingAI taskbar on the side, is certainly a nudge in the right direction. Even now, users can switch between light and dark themes, turn Do Not Disturb and Bluetooth on and off, and jump directly to the Bluetooth device settings page to manage connections – all from Copilot. Here's how to get Windows 11 Copilot and do it all. How to enable Copilot on Windows 11 To start using Copilot on Windows 11,
 How to Fix 'iPhone Not Available” Message
Sep 17, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
How to Fix 'iPhone Not Available” Message
Sep 17, 2023 pm 09:25 PM
How does the "iPhone is not available" security feature work? The basic mechanism that triggers the "iPhone Not Available" message is rooted in the security features of the system's design, which track every incorrect passcode entry. This protection kicks into high gear from the fifth incorrect attempt to unlock the device. Once this milestone is reached, the iPhone sets a temporary lock period of one minute, during which any additional attempts to enter the passcode become futile. This lock duration is not static but follows an escalating pattern. Specifically, after the fifth password attempt, each subsequent incorrect password attempt will cause the lockout timer to be increased by one minute. For example, the sixth incorrect attempt will result in a 2 minute lockout and the seventh incorrect attempt will result in a 3 minute




