How to defend cloud servers against DDoS attacks
Methods for cloud servers to defend against DDoS attacks include choosing an appropriate cloud server provider, configuring cloud server security groups, using cloud server DDoS protection functions, deploying cloud server defense tools and strengthening cloud server security protection. Detailed introduction: 1. Choose a suitable cloud server provider, rich network resources, powerful defense capabilities, and complete after-sales service; 2. Configure cloud server security group, set access whitelist, and set access blacklist; 3. Use cloud Server DDoS protection functions and more.

# As the Internet continues to develop, DDoS attacks are becoming more and more rampant. DDoS The attack consumes the bandwidth and computing resources of the cloud server, making it impossible for normal users to access websites or applications on the cloud server, resulting in service unavailability. For cloud server users, how to effectively defend against DDoS Attacks and ensuring the stable operation of the business have become a very important issue. This article will introduce the methods of cloud server defense against DDoS attacks from the following aspects.
1. Choose a suitable cloud server provider
Choosing a reliable cloud server provider is the first step to defend against DDoS attacks. An excellent cloud server provider should have the following characteristics:
Abundant network resources: A cloud server provider should have abundant network resources and be able to provide sufficient bandwidth and IP addresses to cope with large-scale DDoS attacks. .
Powerful defense capabilities: Cloud server providers should have strong defense capabilities that can effectively identify and filter DDoS attack traffic to ensure that users' businesses are not affected.
Complete after-sales service: Cloud server providers should provide comprehensive after-sales services, including 24-hour online customer service, professional technical support, etc., so that users can avoid DDoS attacks. Get timely help when attacking.
2. Configure the cloud server security group
The cloud server security group is a security mechanism used to protect the cloud server and can control access and traffic to the cloud server. filter. Users can configure security group rules according to their own needs, restrict access to cloud servers, and reduce the risk of Risk of DDoS attacks.
Set an access whitelist: Only IP addresses in the whitelist are allowed to access the cloud server, and access to other IP addresses is denied. This can effectively reduce unnecessary access requests and reduce the risk of DDoS Risk of attack.
Set an access blacklist: Add IP addresses that have launched DDoS attacks to the blacklist and prohibit these IP addresses from accessing the cloud server. This avoids repeated attacks.
3. Use cloud server DDoS protection function
Most cloud server providers provide DDoS protection function, and users can choose the appropriate protection strategy according to their own needs. Cloud server DDoS protection functions can be divided into the following types:
Basic protection: Basic protection functions provided for free, which can deal with small-scale DDoS attacks.
Professional protection: The professional protection function provided for a fee can deal with large-scale DDoS attacks and ensure the stable operation of the business.
Customized protection: Provide customized DDoS protection solutions according to the special needs of users.
4. Deploy cloud server defense tools
In addition to the DDoS protection functions provided by cloud server providers, users can also deploy some cloud server defense tools to improve defense capabilities . Common cloud server defense tools include the following:
Traffic cleaning: Use traffic cleaning equipment to identify and filter DDoS attack traffic to ensure that normal traffic can access the cloud server normally.
Distributed defense: By deploying multiple cloud servers, a distributed defense network is formed to improve defense capabilities.
Intelligent defense: Through artificial intelligence technology, real-time monitoring and analysis of DDoS attacks is performed, and defense strategies are automatically adjusted to improve defense efficiency.
5. Strengthen cloud server security protection
In addition to the above methods, users should also strengthen cloud server security protection to reduce the risk of DDoS attacks. Specific measures include:
Regularly update system patches: timely update operating system and application patches, patch security vulnerabilities, and reduce the risk of attacks.
Install security software: Install anti-virus software, firewall and other security software to improve the defense capabilities of the cloud server.
Strengthen password security: Set a more complex password and change it regularly to avoid password cracking.
Restrict port scanning: Close unnecessary services and ports, limit port scanning, and reduce the risk of DDoS attacks.
In short, cloud server defense against DDoS Attacks need to start from multiple aspects and take a variety of measures to improve defense capabilities. When choosing a cloud server provider, you must fully consider factors such as its network resources, defense capabilities, and after-sales services to ensure the stable operation of the business.
The above is the detailed content of How to defend cloud servers against DDoS attacks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 How to deploy SpringBoot project to cloud server
May 13, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
How to deploy SpringBoot project to cloud server
May 13, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
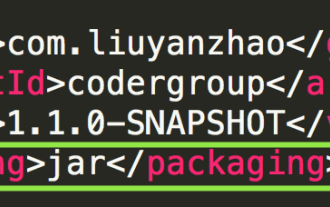
1. Set the Maven packaging type here to jar. According to my experience, packaging into a war is a pitfall, and you need to follow Tomcat, and you will encounter many problems when deploying for the first time. By packaging it into a jar, you don’t need to install Tomcat. You can start the project with just one command: java-jarcodergroup-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar. 2. Packaging the SpringBoot project. I use IntelliJIDEA here. Directly in the Maven plug-in, click package. Then you can see in the target of the project that the jar file is uploaded to the server. 3. Install MySQL and JDK for convenience
 How to manually configure DNS for Linux cloud server
May 16, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
How to manually configure DNS for Linux cloud server
May 16, 2023 pm 03:22 PM
Configuring the DNS service of the cloud server is indispensable for the cloud server to access the public domain name. DNS is the record of the domain name pointing to the IP. Only by setting up the DNS server can the public network resolution record of the domain name be obtained. The local DNS server configuration information is stored in the file /etc/resolv.conf. Write the following DNS configuration nameserver8.8.8.8nameserver114.114.114.114 in the configuration information. This will successfully set up two default dns servers, which will take effect immediately after saving. If you need to specify the resolution record of a certain domain name, you need to use the /etc/hosts file and write the ip address, space, and domain name in the configuration information to manually specify it.
 Which cloud server is cheaper?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Which cloud server is cheaper?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Cost-effective cloud server service providers include Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Amazon AWS and Huawei Cloud. These service providers provide rich product lines, affordable prices, complete ecosystems and technical support. When choosing, in addition to price, you should also consider stability, performance, security, customer service, etc., and choose the service provider that best suits your needs after a comprehensive evaluation.
 What is the difference between lightweight application server and cloud server?
Jul 27, 2023 am 10:12 AM
What is the difference between lightweight application server and cloud server?
Jul 27, 2023 am 10:12 AM
The differences between lightweight application servers and cloud servers are: 1. Lightweight application servers have smaller hardware configurations and resource consumption, while cloud servers have larger hardware configurations and resources; 2. Cloud servers provide more functions and services , while lightweight application servers do not; 3. Lightweight application servers are usually simpler and easier to use, while cloud servers require more technical knowledge and management experience; 4. Lightweight application servers are relatively cheap, while cloud servers cost more Higher.
 How to deploy Java projects to cloud servers
May 11, 2023 am 10:58 AM
How to deploy Java projects to cloud servers
May 11, 2023 am 10:58 AM
1. When purchasing a cloud server and installing the system, you usually choose which operating system to install. I usually use CentOS, either 6.x or 7.x. 2. Installing the Pagoda Panel is the same on any server, but different operating systems may have different commands. 1. The account and password for ssh connection to the server are usually set when purchasing the server, and can be modified later. If ssh cannot connect, make sure port 22 is allowed. 2. Type the installation command Centos installation script yuminstall-ywget&&wget-Oinstall.shhttp://download.bt.cn/install/install_6
 How much does it cost to rent a cloud server for one year?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:51 AM
How much does it cost to rent a cloud server for one year?
Mar 21, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Cloud server rental costs vary according to service providers and configuration plans. Key influencing factors include server configuration, bandwidth and data center location. For example, Alibaba Cloud's cloud server rentals range from a few hundred yuan to tens of thousands of yuan per year, depending on the configuration. Providers such as Amazon AWS, Tencent Cloud and Huawei Cloud also have their own pricing plans. Users can select configurations and service providers based on their needs, and calculate annual rent based on pricing. Some service providers provide discounts or discounts, and users can pay attention to get better prices.
 How to change the hostname of Linux cloud server
May 18, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
How to change the hostname of Linux cloud server
May 18, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
CentOS61, remote login system. 2. Use the hostname command. hostnamezhaomu.com3. Edit the /etc/hosts file. Replace the old hostname with the new hostname. 4. Edit /etc/sysconfig/network. Change the value of the HOSTNAME parameter to the new hostname. 5. Use the hostname command to check whether it takes effect. CentOS7/Ubuntu1, remote login system. 2. Use the hostnamectl command. hostnamectlset-hostnamezhaomu.com3. Use the hostname command to check
 How to change the remote port of Linux cloud server
May 15, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
How to change the remote port of Linux cloud server
May 15, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
Step 1: Configure SSH. Edit the SSH configuration file: vi/etc/ssh/sshd_config. Find the Port line and change the default 22 to the desired port, such as 2124. Port2124 Step 2: Update the firewall If you are not using a firewall, this step can be ignored. If the firewall is enabled and the firewall is not updated after changing the remote port, remote access will not be possible. CentOS6iptables-IINPUT-ptcp--dport2124--syn-jACCEPTserviceiptablessavesemanageport-a-tssh_port_t-ptcp2124Cen



