 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 1 token ends the LLM digital coding problem! Nine major institutions jointly released xVal: Numbers that are not included in the training set can also be predicted!
1 token ends the LLM digital coding problem! Nine major institutions jointly released xVal: Numbers that are not included in the training set can also be predicted!
1 token ends the LLM digital coding problem! Nine major institutions jointly released xVal: Numbers that are not included in the training set can also be predicted!
Although the performance of large language models (LLM) is very powerful on text analysis and generation tasks, when faced with problems containing numbers, such as multi-digit multiplication, due to the lack of unified and complete numbers within the model The word segmentation mechanism will cause LLM to be unable to understand the semantics of numbers and make up random answers.
Currently, one of the major obstacles that LLM has not been widely used in data analysis in the scientific field is the problem of digital encoding.
Recently, nine research institutions including the Flatiron Institute, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of Cambridge, New York University, and Princeton University jointly released a new digital encoding scheme xVal, only one token is needed to encode all numbers.

Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.02989.pdf
xVal By numerically scaling the embedding vector of a dedicated token ([NUM]) to represent the target true value, combined with a modified numerical inference method, the xVal strategy successfully enables the model to map from input string numbers to output numbers end-to-end. Continuous, more suitable for applications in scientific fields.
Evaluation results on synthetic and real-world datasets show that xVal not only performs better and is more token-efficient than existing numeric encoding schemes, but also exhibits better interpolation. Generalization properties.
New breakthrough in digital encoding
The standard LLM word segmentation scheme does not distinguish between numbers and text, so it is impossible to quantify values.
There has been previous work that mapped all numbers into a limited set of prototype numerals in the form of scientific notation, using 10 as the base, or calculated between number embeddings. The cosine distance reflects the numerical difference of the numbers themselves, and has been successfully used to solve linear algebra problems, such as matrix multiplication.
However, for continuous or smooth problems in the scientific field, the language model still cannot handle interpolation and out-of-distribution generalization problems well, because after encoding the numbers into text, LLM is encoding And the decoding stage is still discrete in nature and it is difficult to learn to approximate a continuous function.
xVal’s idea is to encode the numerical size multiplicatively and orient it in a learnable direction in the embedding space, which greatly changes the processing and interpretation in the Transformer architecture. Digital way.
xVal uses a single token for numerical encoding, which has the advantages of token efficiency and a minimal vocabulary footprint.
Combined with the modified numeric reasoning paradigm, the Transformer model value is continuous (smooth) when the mapping between input numbers and output string numbers is continuous (smooth) when the approximate function is continuous Or smoothing can bring better inductive bias.
xVal: Continuous number encoding
xVal does not use different tokens for different numbers, but directly embeds values along specific learnable directions in the embedding space.
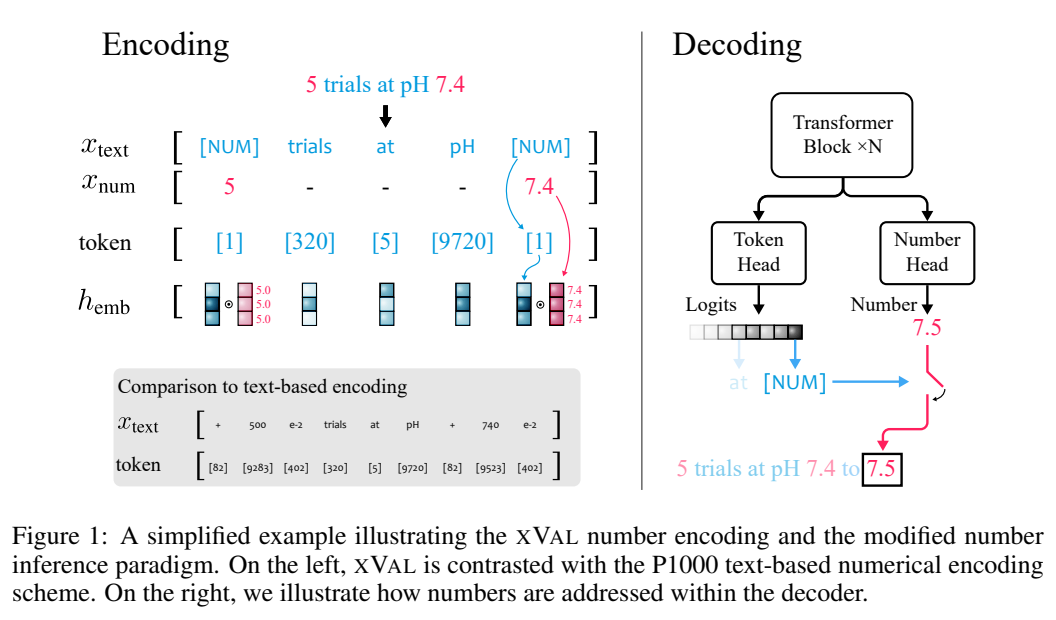
Assuming that the input string contains both numbers and text, the system will first parse the input, extract all the values, and then construct a A new string in which numbers are replaced with [NUM] placeholders, and the embedding vector of [NUM] is multiplied by its corresponding numeric value.
The entire encoding process can be used for mask language modeling (MLM) and autoregressive (AR) generation.
Implicit normalization via layer-norm based on layer normalization
In the specific implementation, first After the multiplicative embedding of xVal in each Transformer block, the position encoding vector and layer normalization (layer-norm) need to be added to normalize the embedding of each token based on the input sample.
When the position embedding is not collinear with the [NUM] tag embedding, the scalar value can be passed through the non-linear rescaling function (non-linear rescaling).
Assume u is the embedding of [NUM], p is the position embedding, and x is the encoded scalar value. To simplify the calculation, u · p=0 can be assumed, where ∥u∥ =∥p∥ = 1, you can get
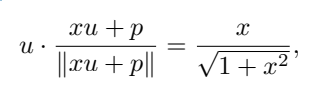
That is, the value of x is encoded in the same direction as u, and this attribute can still be maintained after training.
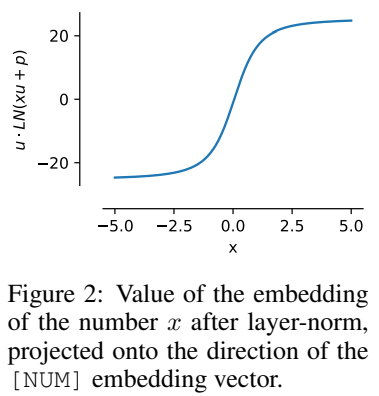
This normalization characteristic means that the dynamic range of xVal is smaller than that of other text-based encoding schemes. In the experiment, Set as [-5, 5] as a preprocessing step before training.
Numerical Reasoning
xVal defines a continuous embedding in the input value, but if a multi-classification task is used as the output and training algorithm, consider that from the input value to Mapping between output values, the model as a whole is not end-to-end continuous, and the numbers need to be processed separately in the output layer.
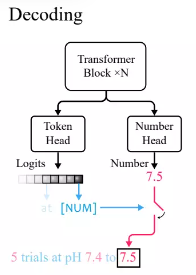
According to standard practice in the Transformer language model, the researchers defined a token head that outputs the probability distribution of vocabulary tokens.
Because xVal uses [NUM] to replace numbers, the head does not carry any information about the numerical value, so a new number head with scalar output needs to be introduced, through the mean square error (MSE) loss is trained to recover the specific numerical value associated with [NUM].
After given the input, first observe the output of the token head. If the generated token is [NUM], then look at the number head to fill in the value of the token.
In experiments, because the Transformer model is end-to-end continuous when inferring values, it performs better when interpolating to unseen values.
Experimental part
Comparison with other digital encoding methods
The researchers compared the performance of XVAL with Four other digital encodings were compared. These methods all need to first process the numbers into the form of ±ddd E±d, and then call single or multiple tokens according to the format to determine the encoding.
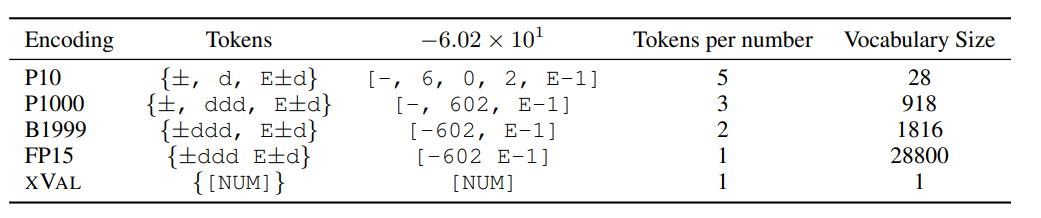
Different methods have very different numbers of tokens and vocabularies required to encode each number, but overall, xVal The encoding efficiency is the highest and the vocabulary size is the smallest.
The researchers also evaluated xVal on three data sets, including synthetic arithmetic operation data, global temperature data and planetary orbit simulation data.
Learning arithmetic
Even for the largest LLM, "multiple digit multiplication" is still a Extremely challenging tasks, such as GPT-4, can only achieve a zero-shot accuracy of 59% on three-digit multiplication problems, and even only 4% and 0% accuracy on four-digit and five-digit multiplication problems.
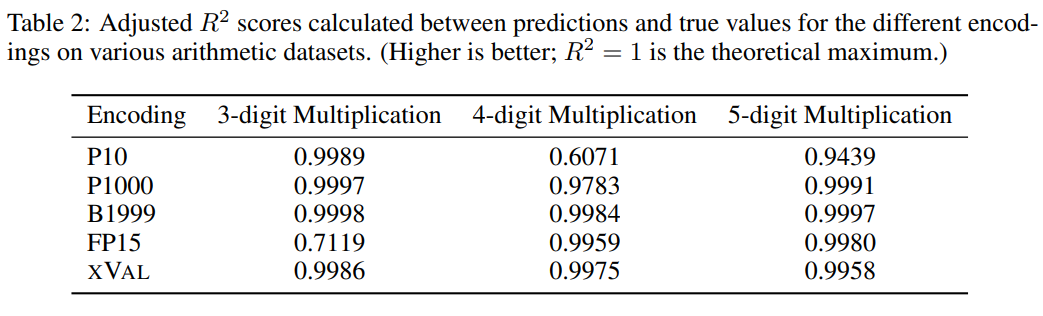
From comparative experiments, other digital encodings can usually solve multi-digit multiplication problems well, but the prediction results of xVal are compared to P10 and FP15 are more stable and will not produce abnormal prediction values.
In order to improve the difficulty of the task, the researchers used random binary trees to construct a fixed number of operands (2, 3 or 4) using binary operators of addition, subtraction and multiplication. A data set where each sample is an arithmetic expression such as ((1.32 * 32.1) (1.42-8.20)) = 35.592
and then based on the encoding scheme of each number Processing requires processing of samples, and the task goal is to calculate the expression on the left side of the equation, that is, the right side of the equation is the mask.
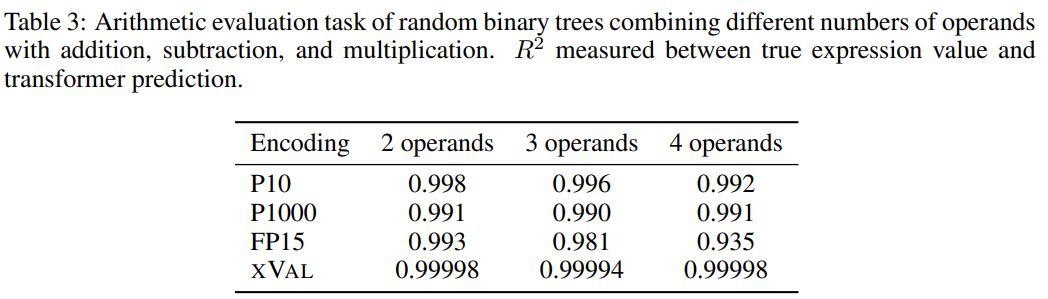
Judging from the results, xVal performed very well on this task, but arithmetic experiments alone are not enough to fully evaluate the mathematical capabilities of the language model, because the samples in arithmetic operations are usually short sequences and the underlying data flow Since the shape is low-dimensional, these problems do not break through the computational bottleneck of LLMs, and the applications in the real world are more complex.
Temperature prediction
The researchers used a subset of the ERA5 global climate data set with For evaluation, for simplicity, the experiment only focuses on surface temperature data (T2m in ERA5), and then divides the samples, where each sample includes 2-4 days of surface temperature data (with unit variance after normalization) and data from 60 - Latitude and longitude of 90 randomly selected reporting stations.
Encode the sine of the latitude and the sine and cosine of the longitude of the coordinates, thus maintaining the periodicity of the data, and then use the same operation to encode the position in the 24-hour and 365-day periods.

Coords, start and data correspond to reporting station coordinates, time of first sample and normalized temperature data, and then use the MLM method to train the language model.
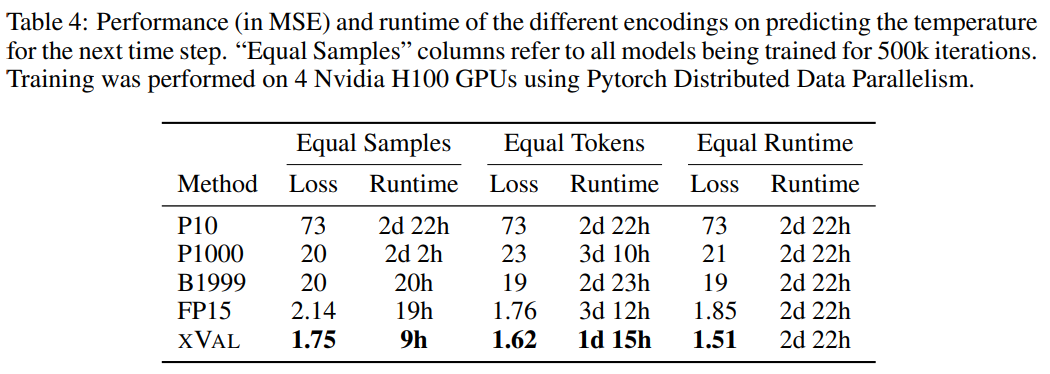
From the results, xVal has the best performance, and the calculation time is also significantly reduced.
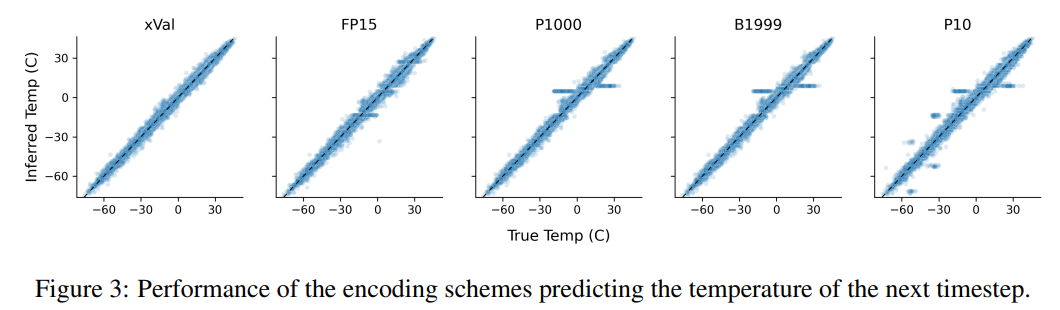
This task also illustrates the shortcomings of text-based encoding schemes, where the model can exploit spurious correlations in the data, namely P10, P1000 and B1999 There is a tendency to predict the normalized temperature ±0.1, mainly because this number appears most frequently in the data set.
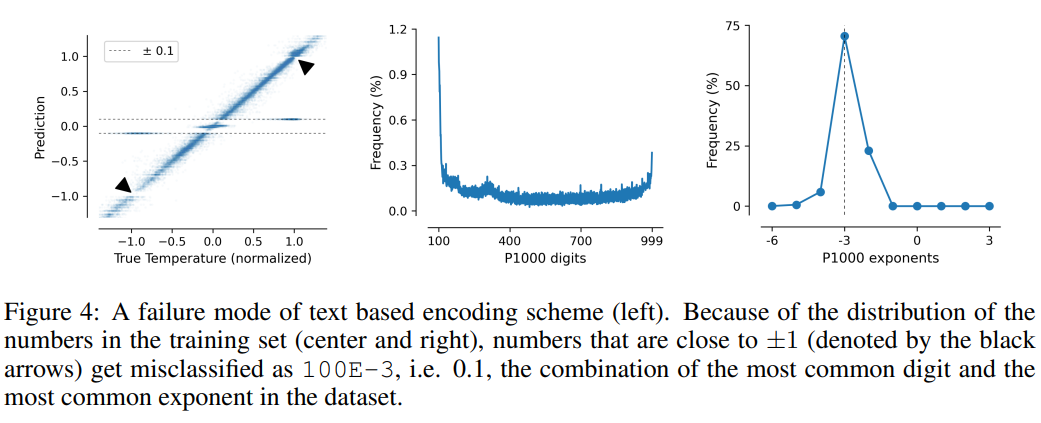
For the P1000 and P10 schemes, the average encoding output of the two schemes is about 8000 and 5000 tokens respectively (in comparison, FP15 and xVal averages about 1800 tokens), the poor performance of the model may be due to long-distance modeling issues.
The above is the detailed content of 1 token ends the LLM digital coding problem! Nine major institutions jointly released xVal: Numbers that are not included in the training set can also be predicted!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 phpmyadmin creates data table
Apr 10, 2025 pm 11:00 PM
phpmyadmin creates data table
Apr 10, 2025 pm 11:00 PM
To create a data table using phpMyAdmin, the following steps are essential: Connect to the database and click the New tab. Name the table and select the storage engine (InnoDB recommended). Add column details by clicking the Add Column button, including column name, data type, whether to allow null values, and other properties. Select one or more columns as primary keys. Click the Save button to create tables and columns.
 How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
Creating an Oracle database is not easy, you need to understand the underlying mechanism. 1. You need to understand the concepts of database and Oracle DBMS; 2. Master the core concepts such as SID, CDB (container database), PDB (pluggable database); 3. Use SQL*Plus to create CDB, and then create PDB, you need to specify parameters such as size, number of data files, and paths; 4. Advanced applications need to adjust the character set, memory and other parameters, and perform performance tuning; 5. Pay attention to disk space, permissions and parameter settings, and continuously monitor and optimize database performance. Only by mastering it skillfully requires continuous practice can you truly understand the creation and management of Oracle databases.
 How to create oracle database How to create oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
How to create oracle database How to create oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
To create an Oracle database, the common method is to use the dbca graphical tool. The steps are as follows: 1. Use the dbca tool to set the dbName to specify the database name; 2. Set sysPassword and systemPassword to strong passwords; 3. Set characterSet and nationalCharacterSet to AL32UTF8; 4. Set memorySize and tablespaceSize to adjust according to actual needs; 5. Specify the logFile path. Advanced methods are created manually using SQL commands, but are more complex and prone to errors. Pay attention to password strength, character set selection, tablespace size and memory
 How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
The core of Oracle SQL statements is SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE, as well as the flexible application of various clauses. It is crucial to understand the execution mechanism behind the statement, such as index optimization. Advanced usages include subqueries, connection queries, analysis functions, and PL/SQL. Common errors include syntax errors, performance issues, and data consistency issues. Performance optimization best practices involve using appropriate indexes, avoiding SELECT *, optimizing WHERE clauses, and using bound variables. Mastering Oracle SQL requires practice, including code writing, debugging, thinking and understanding the underlying mechanisms.
 How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
Field operation guide in MySQL: Add, modify, and delete fields. Add field: ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY] [AUTO_INCREMENT] Modify field: ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY]
 Detailed explanation of nested query instances in MySQL database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Detailed explanation of nested query instances in MySQL database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Nested queries are a way to include another query in one query. They are mainly used to retrieve data that meets complex conditions, associate multiple tables, and calculate summary values or statistical information. Examples include finding employees above average wages, finding orders for a specific category, and calculating the total order volume for each product. When writing nested queries, you need to follow: write subqueries, write their results to outer queries (referenced with alias or AS clauses), and optimize query performance (using indexes).
 What are the integrity constraints of oracle database tables?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
What are the integrity constraints of oracle database tables?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
The integrity constraints of Oracle databases can ensure data accuracy, including: NOT NULL: null values are prohibited; UNIQUE: guarantee uniqueness, allowing a single NULL value; PRIMARY KEY: primary key constraint, strengthen UNIQUE, and prohibit NULL values; FOREIGN KEY: maintain relationships between tables, foreign keys refer to primary table primary keys; CHECK: limit column values according to conditions.
 What does oracle do
Apr 11, 2025 pm 06:06 PM
What does oracle do
Apr 11, 2025 pm 06:06 PM
Oracle is the world's largest database management system (DBMS) software company. Its main products include the following functions: relational database management system (Oracle database) development tools (Oracle APEX, Oracle Visual Builder) middleware (Oracle WebLogic Server, Oracle SOA Suite) cloud service (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure) analysis and business intelligence (Oracle Analytics Cloud, Oracle Essbase) blockchain (Oracle Blockchain Pla



