How to Download and Install Linux for Windows 11
Linux is an operating system, similar to Windows, but available in many different versions due to its open source and fully customizable nature. To install Linux, you must choose an installation method and select a Linux distribution.
To install Linux:
- Choose an installation method: Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), bare metal Linux; or create a virtual machine (VM) to run locally or in the cloud Linux.
- Choose a Linux distribution: Ubuntu, Debian, Kali Linux, OpenSUSE, etc.
- Follow the steps for your preferred installation method:
- Use the install Linux command with Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- Create a Linux virtual machine (VM) in the cloud
- Create a Linux virtual machine (VM) on your local computer
- Create a bootable USB to install bare metal Linux
- After installing Linux: Get familiar with the distribution version of the package manager, update and upgrade available packages, and become familiar with Microsoft's other Linux resources, such as training courses, Linux versions of popular tools, news, and open source events.
Step 1 – Choose a method to install Linux
Choosing which method to use to install Linux depends on your needs and preferences.
- New to Linux? We recommend starting with Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) as it is the easiest way to get up and running.
- Working in a business environment with more complex needs related to scale or security? We recommend running Linux as a virtual machine (VM) in the cloud and looking at what support Azure has to offer. The same applies if you want to run Linux as a server.
- Just want to run Linux as your primary operating system? If you're good with the slightly more complicated installation process and don't need access to Windows tools (like Outlook, Teams, Word, PowerPoint, etc.), you can run Linux on bare metal to access the full potential of the hardware without the need for virtualization or emulation any overhead.
Learn more about these options below.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
For those of you using a Windows machine, this is the easiest way to install Linux. Just run the Linux installation command: to install the Ubuntu distribution. wsl --install
This method uses virtualization to integrate the Windows operating system (OS) with the Linux operating system (running on the actual Linux kernel). You can add as many different Linux distributions as you like and run your favorite Linux tools, including GUI applications, as well as your favorite Windows tools. You can also mix and match Bash and PowerShell commands on the same command line. The Linux file system hosts the project files, while a separate Windows file system hosts any developer tools that work with the files, such as VS Code. This method of running Linux is very efficient and performant. After you select a Linux distribution or choose to use the default Ubuntu distribution, follow the instructions for using the Install Linux command with the Windows Subsystem for Linux or learn more in the WSL documentation.
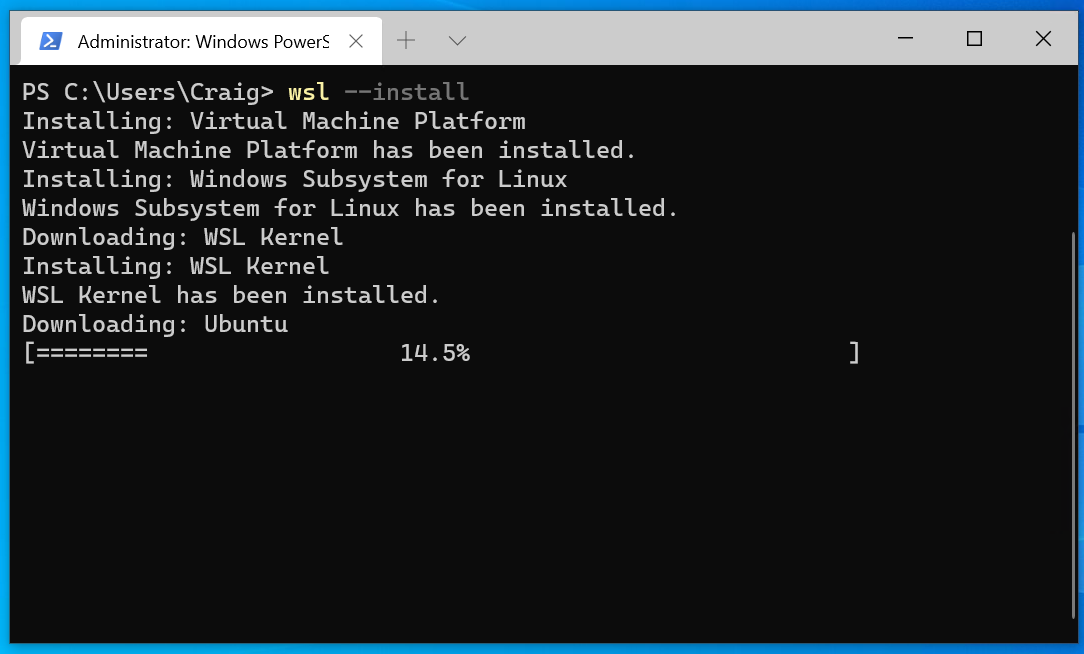
Create a virtual machine (VM)
Whether you are using a Windows-based or MacOS-based computer, everyone can use it, but if you are in the cloud If you create a VM in the VM, you need an Azure account, or if you create the VM directly on your computer (locally), you need virtualization software.
A VM is a digital version of a physical computer and is used in environments where expanded hardware support levels (required memory and processing power) and security levels (anti-malware, encryption, backups, policy management, etc.) may be required Common options for running Linux.
Like WSL, you can create as many VM instances of different Linux distributions as you need and run them in an isolated environment without any conflicts, perfect for software development testing. While the performance of running a Linux distribution on WSL is slightly faster, Linux VMs are easier to clone or migrate. You can use virtualization software (also called a hypervisor) to create a virtual machine on a cloud service (such as Azure) or on your local computer.
Creating a VM on Azure means it is hosted in the cloud, on Microsoft's servers. Essentially renting computing resources from Microsoft and using them to run VMs. This is convenient if you need to provision new VMs quickly, or if you need to run workloads that require more computing resources than your local machine can provide. Larger enterprises with more complex needs often choose to run Linux VMs on Azure because of its scalability, control, and rich functionality. Learn more about the architecture, workflow, and considerations for running Linux VMs on Azure.
Creating a VM on a local computer requires virtualization using a hypervisor. Windows includes a "Type 1" hypervisor called Hyper-V that runs virtualization directly on the device hardware. There are also "type 2" hypervisors that run on top of the operating system, such as VirtualBox or VMware. If you are using a Mac, the most commonly recommended hypervisor is "Parallels Desktop", although this is a paid service. See Install a Linux VM on a Mac with an Apple M-series chip. VirtualBox also supports Windows and MacOS. For more information about how to design and run a custom Linux guest on an Apple silicon or Intel-based Mac, see Create and run a Linux virtual machine.
You are responsible for managing your virtual machines when using a hypervisor, including allocating resources such as memory and disk space, and ensuring that they are secure and up to date. This requires more technical expertise than some other options and may not be scalable or fault-tolerant.
After you select your distribution and decide whether you want to run your VM locally using a hypervisor or in the cloud using Azure, follow Create a Linux virtual machine in the cloud or Create a Linux virtual machine locally using a hypervisor Instructions for operating a virtual machine
Bare Metal Linux
Bare Metal Linux simply means Linux runs directly on the device hardware. This installation method requires you to create a bootable USB drive by downloading the iso installation file from the site hosting your chosen Linux distribution. You'll need to use a Windows computer (or any desktop device with an existing operating system) to create this drive.
Many users choose the traditional method of installing bare-metal Linux on a device that is also running Windows and uses the "dual boot" method. To dual-boot Linux and Windows, you need to partition your hard drive to create separate spaces for the Linux and Windows operating systems. Performance speeds between WSL, virtual machines, and bare metal Linux have become so close that few developers choose this approach because of the need to reboot (reboot) every time you want to switch between operating systems Equipment overhead. If you choose the bare-metal Linux installation route, you may also need to deal with potential driver issues or hardware compatibility issues that Linux may have on certain devices.
You can find a list of Popular Linux Distributions available for download on Linux.org. Once you've chosen a distro, follow the instructions to Create a bootable USB to install bare-metal Linux.
Step 2 – Choose a Linux Distribution
Different versions of Linux are called “distros” (sometimes abbreviated to “releases”). So there isn't really a way to "install Linux", you first need to choose the distribution of the Linux kernel you want to download and install. There are more than 600 active Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Debian, Kali Linux, OpenSUSE, etc. There are many factors to consider when choosing a distribution, such as:
Required Linux Experience
If you are new to Linux, you may want to start with Ubuntu. This is one of the most common starting points for Linux users due to the level of support and ease of use. Ubuntu is available in both desktop and server versions, depending on how you plan to use it. The specific tasks that the operating system will be responsible for can help you decide which distribution to use. Arch Linux is a popular choice for those who want a highly customizable, do-it-yourself approach that remains stable and well-supported by a large user base. This is a more complex starting point, but can help you better understand how Linux works due to the amount of custom configuration.
System Requirements
Minimal or "lightweight" distribution means a small footprint and low memory and processing speed requirements. Alpine Linux is a popular option and users will find that most features are disabled by default or not installed, but still has everything needed for containerized applications. Security needs: Some Linux users may have specific security issues to consider. Kali Linux is an example of a distribution designed for security tasks, such as penetration testing, security research, computer forensics, and reverse engineering.
Business and Enterprise Requirements
Business, corporate, or academic environments may have unique concerns than consumer environments. Both Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and Oracle Linux offer 24/7 global support and subscription-based services. CentOS is another popular enterprise distribution that is community supported yet still compatible with RHEL.
Community Support
A large community of users who consistently contribute to the distribution, fixing bugs, adding features, helping with issues, etc. is another good consideration. Ubuntu is one of the most popular distributions. OpenSUSE has been around longer than most other distributions and still receives active updates. Many other distributions quickly became popular as the needs and preferences of the user community changed. The Linux.org website provides resources to help you evaluate what is available, well supported, or growing in popularity.
Step 3 – Follow the installation instructions
Installing Linux using Windows Subsystem for Linux
To install on a Windows PC For Linux, use the install Linux command.
- In Administrator ModeOpen PowerShell or Windows Command Prompt by right-clicking and selecting "Run as administrator."
- Enter the Linux installation command:.
wsl --install - Restart the computer.
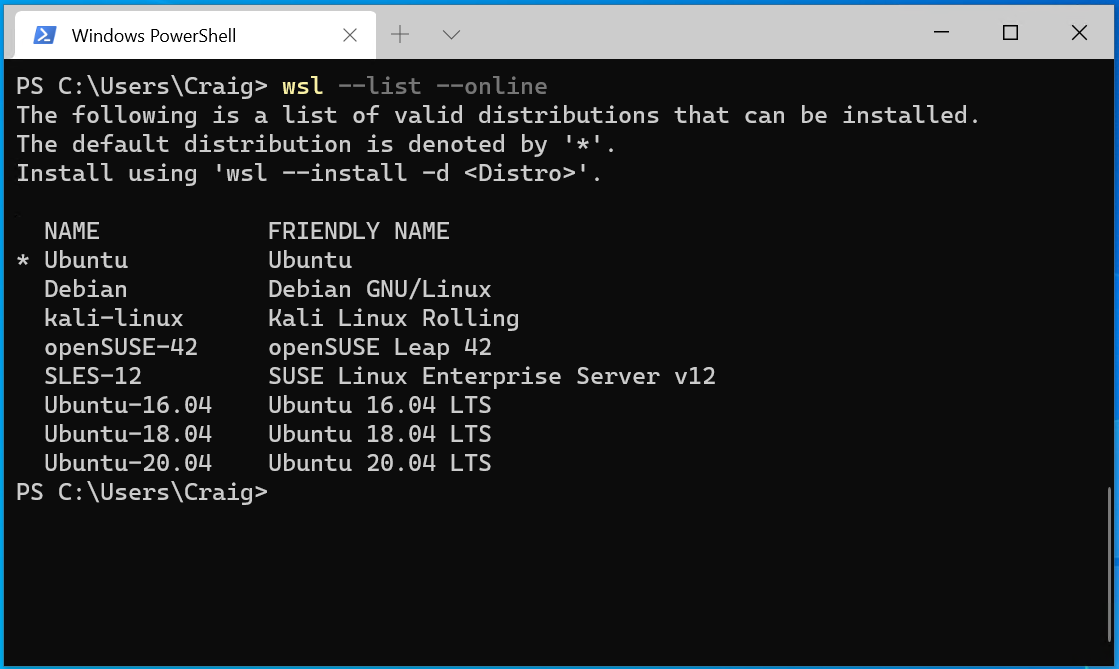
Install Linux Command Options
By default, the install command will use the Ubuntu distribution of Linux. You can view other allocations available in Microsoft Store by entering the following command: . If you want to install a distribution other than Ubuntu, just add the name of the distribution you want to install to the command: wsl -l -o-d
wsl --install -d <Distro Name>
If the distribution you want to install is not available in the Microsoft store, see the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) documentation to learn how to import any Linux distribution for use with WSL.
Details on how to use VS Code, Git, databases, Docker, GUI apps, GPU acceleration, NodesJS, USB devices or mount disks, build custom distributions, manage disk space, or set up WSL for enterprise business, See the WSL documentation.
Create a Linux virtual machine in the cloud
To create a Linux virtual machine (VM) hosted in the cloud on Azure, log in to the Azure portal and select Create virtual machine machine” service. Then follow the instructions to create a username, project, instance, SSH key, port, and copy IP address.
Azure supports various options for setting up Linux VMs in the cloud. For a quick start guide on how to set up a Linux VM, choose your preferred method:
- Azure Portal
- Azure CLI
- Azure PowerShell
- terraform
- One Bicep File
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Template
If you don’t have an Azure subscription, create a free account before starting. If you're new to using Azure to create Linux VMs, you can learn more about VMs or check out the online training course: Create a Linux virtual machine in Azure.
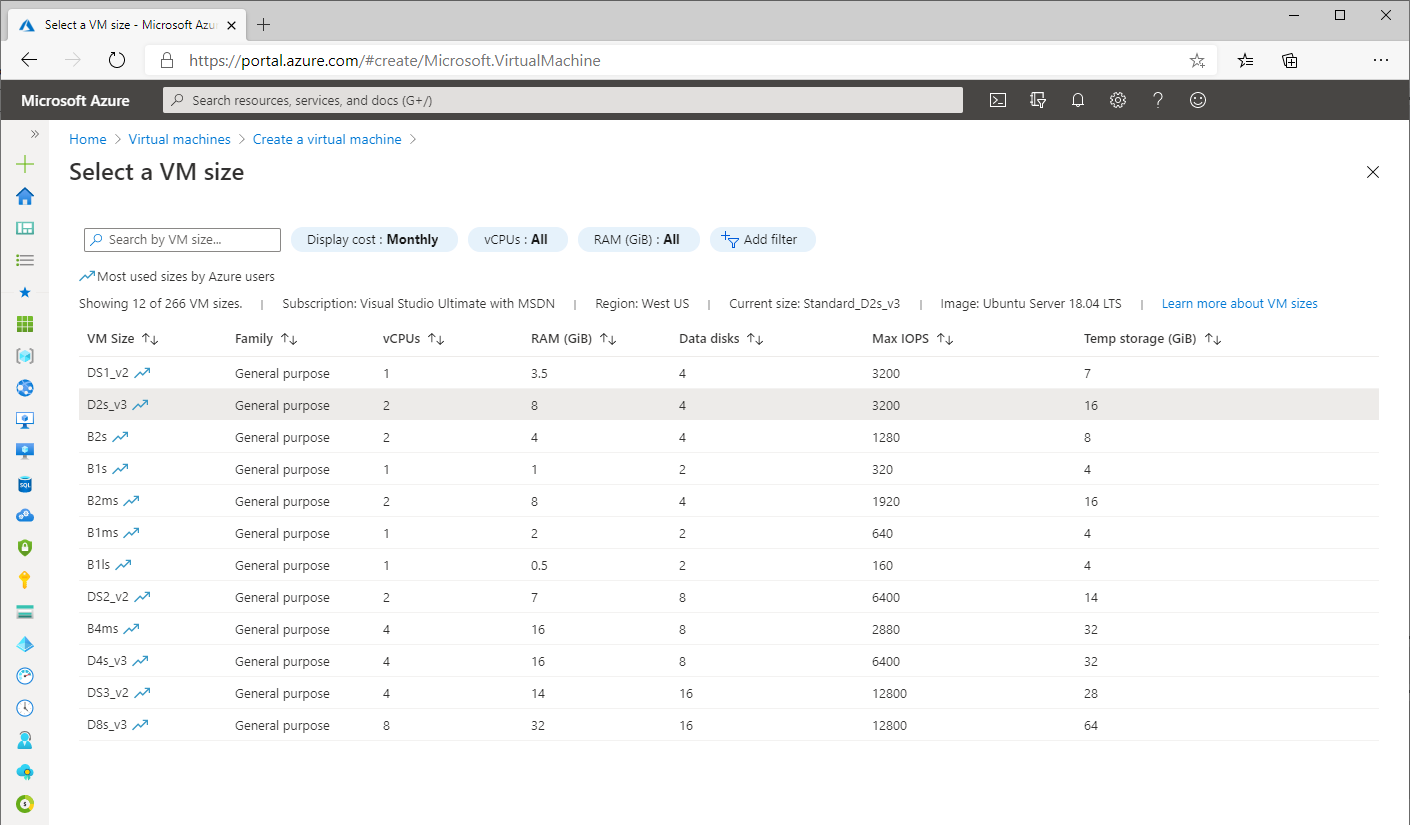
Create a Linux virtual machine locally using a hypervisor
To create a Linux VM hosted on your local computer using a hypervisor, you can Using:
- Winesows Super V
- Virtual Box
- VMware
You need to check the hardware requirements for your chosen hypervisor . After you enable or install the hypervisor, you need to select the type of operating system you want to install and the installation source (this is usually an .iso or .vhdx file). You need to name the VM, select the directory where you want to host the files, select the amount of memory you want to allocate to the VM, and the size of the virtual hard drive where the files will be stored (you can usually choose between a fixed or dynamically allocated amount of drive space). Integration with Linux virtual machines can sometimes be tricky due to display drivers and other hardware dependencies, but most hypervisors have an active user community that can help. If you want your VM to be connected to the Internet, you may also need to set up a virtual network.
If you are new to hypervisors and want to learn more, try the free online training module: Configuring and Managing Hyper-V Virtual Machines.
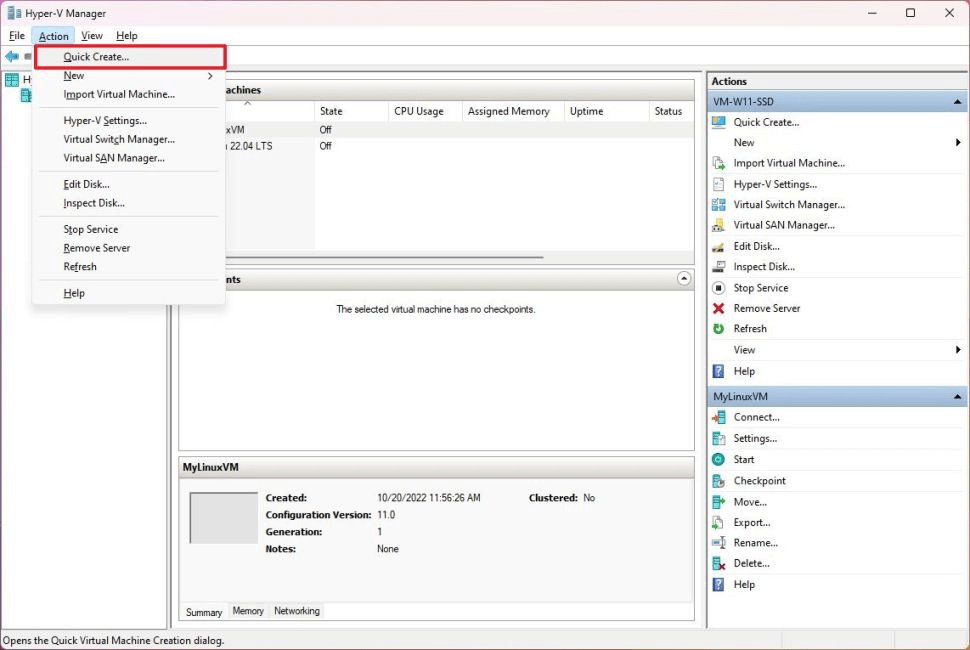
Create a bootable USB drive to install bare-metal Linux
If you want bare-metal Linux, whether running the distro on its own on the device or dual-booting between the distro and Windows, here are the steps:
- Download the image file of the selected Linux distribution. This is usually an ISO file. For example, you can find image files for the latest version of Ubuntu in Download Ubuntu Desktop . Some Linux distributions may require you to verify the image signature before downloading.
- Create a bootable USB drive. You usually need a USB drive with at least 16GB of space. You'll also need software to create a bootable drive. There are many options (like balenaEtcher, Rufus, UNetbootin, etc.). Typically, the download site for your chosen Linux distribution will recommend the boot disk creator software to use.
- Boot the device from the USB drive. When restarting your device, you need to enter the boot menu. This is usually done by holding down the F12 key during startup. You can then select the USB drive that contains the Linux distribution ISO from which you want to install.
- Select installation options. Typically, the installer for a Linux distribution will include a set of installation steps that will involve options to choose whether to include certain features, third-party packages, etc. You may also want to specify whether to wipe the disk if this Linux distribution is the only operating system, or use partitions if you plan to run multiple operating systems. You may also be asked if you want to enable encryption.
- Finally, as with any Linux installation, you will be asked to create a username and password.
Step 4 – After Installing Linux
After successfully installing the Linux distribution, there are a few more important steps:
- Become familiar with the preferred package manager used by your chosen Linux distribution. Linux uses a package manager to download and update any software you plan to use. For example, Ubuntu uses Advanced Packaging Tool (APT).
- Use your distribution's package manager to update and upgrade your distribution. Packages in stable versions of Linux distributions are often out of date. It is recommended to run updates regularly. You may also want to run an upgrade to install newer versions of any packages you have installed. For example, if you are using Ubuntu, run: .
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Learn more about Linux resources available at Microsoft, such as Linux-specific versions of Microsoft tools like Visual Studio Code, .NET, and PowerShell , free Linux-related training courses available in the Learn directory, as well as information about events, news, and the ongoing partnership between Linux organizations and Microsoft, including support for Microsoft's Mariner distribution.
The above is the detailed content of How to Download and Install Linux for Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
VS Code To switch Chinese mode: Open the settings interface (Windows/Linux: Ctrl, macOS: Cmd,) Search for "Editor: Language" settings Select "Chinese" in the drop-down menu Save settings and restart VS Code



