 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP7
PHP7
 Object-oriented programming in PHP7: How to improve code maintainability and scalability?
Object-oriented programming in PHP7: How to improve code maintainability and scalability?
Object-oriented programming in PHP7: How to improve code maintainability and scalability?

Object-oriented programming in PHP7: How to improve the maintainability and scalability of the code?
Abstract:
With the introduction of PHP7, object-oriented programming (OOP) has become more important in PHP development. This article will introduce how to use the new features of PHP7 to improve the maintainability and scalability of your code, and provide some specific code examples to illustrate these concepts.
Introduction:
Object-oriented programming is a method of encapsulating data and logic in classes. This programming style can make the code more modular and reusable, providing better maintainability and scalability. The introduction of PHP7 brings some new features and improvements to object-oriented programming, helping us write more efficient and reliable code.
1. Application of encapsulation and inheritance
1.1 Encapsulation
Encapsulation is one of the core concepts of object-oriented programming. Through encapsulation, we can encapsulate data and related methods in a class, avoiding code duplication and improving code maintainability. The following is a simple encapsulation example:
class User {
private $name;
private $age;
public function getName() {
return $this->name;
}
public function getAge() {
return $this->age;
}
public function setName($name) {
$this->name = $name;
}
public function setAge($age) {
$this->age = $age;
}
}
$user = new User();
$user->setName("John Doe");
$user->setAge(25);
echo $user->getName() . " is " . $user->getAge() . " years old.";Through encapsulation, we can save the user's name and age in private member variables and provide public access methods to control access and modification of data.
1.2 Inheritance
Inheritance is another important OOP concept. Through inheritance, we can derive a new class from an existing class and retain the characteristics and methods of the parent class in the new class. This improves code reusability and scalability. The following is a simple inheritance example:
class Animal {
protected $name;
public function __construct($name) {
$this->name = $name;
}
public function getName() {
return $this->name;
}
public function makeSound() {
// 默认实现
echo "The animal makes a sound.";
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public function makeSound() {
echo "The dog barks.";
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public function makeSound() {
echo "The cat meows.";
}
}
$dog = new Dog("Fido");
echo $dog->getName() . " says ";
$dog->makeSound();
$cat = new Cat("Whiskers");
echo $cat->getName() . " says ";
$cat->makeSound();Through inheritance, we can create different kinds of animal classes and override methods in the base class to achieve specific behaviors. This way we can easily add new animal classes without modifying existing code.
2. Improvement of code reuse and scalability
2.1 Polymorphism
Polymorphism is another core concept of OOP. It allows us to use a reference variable pointing to the parent class to access the object of the subclass, thereby achieving dynamic binding at runtime. The following is an example of polymorphism:
class Shape {
protected $color;
public function __construct($color) {
$this->color = $color;
}
public function getInfo() {
return "This is a shape.";
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private $radius;
public function __construct($color, $radius) {
parent::__construct($color);
$this->radius = $radius;
}
public function getInfo() {
return parent::getInfo() . " It is a circle with radius " . $this->radius . ".";
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private $width;
private $height;
public function __construct($color, $width, $height) {
parent::__construct($color);
$this->width = $width;
$this->height = $height;
}
public function getInfo() {
return parent::getInfo() . " It is a rectangle with width " . $this->width . " and height " . $this->height . ".";
}
}
$shape1 = new Circle("red", 5);
$shape2 = new Rectangle("blue", 10, 20);
$shapes = [$shape1, $shape2];
foreach ($shapes as $shape) {
echo $shape->getInfo() . " ";
}Through polymorphism, we can handle different types of objects through a unified calling interface. In the above example, although $shape1 and $shape2 are both instances of the Shape class, based on their actual types, the methods of their respective subclasses are called.
2.2 Interfaces and abstract classes
Interfaces and abstract classes are tools used to define methods and properties in OOP. An interface defines the specification of a set of methods, while an abstract class provides partial implementation of the methods. The following is an example of an interface and abstract class:
interface Logger {
public function log($message);
}
abstract class AbstractLogger implements Logger {
protected $name;
public function __construct($name) {
$this->name = $name;
}
public function log($message) {
echo $this->name . ": " . $message;
}
}
class FileLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public function log($message) {
parent::log($message);
// 具体的实现逻辑
file_put_contents("log.txt", $message, FILE_APPEND);
}
}
class DatabaseLogger extends AbstractLogger {
public function log($message) {
parent::log($message);
// 具体的实现逻辑
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=localhost;dbname=test", "root", "");
$pdo->query("INSERT INTO logs (message) VALUES ('$message')");
}
}
$logger1 = new FileLogger("FileLogger");
$logger1->log("Log message 1");
$logger2 = new DatabaseLogger("DatabaseLogger");
$logger2->log("Log message 2");Through interfaces and abstract classes, we can define a common set of methods to constrain the implementation of subclasses. In the above example, both the FileLogger and DatabaseLogger classes implement the Logger interface and provide their respective specific implementations.
Conclusion:
PHP7 introduces many new features and improvements, making object-oriented programming more powerful and flexible. Through the proper application of encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, interfaces, and abstract classes, we can improve the maintainability and scalability of our code, making it easier to read, understand, and modify.
The above is the detailed content of Object-oriented programming in PHP7: How to improve code maintainability and scalability?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
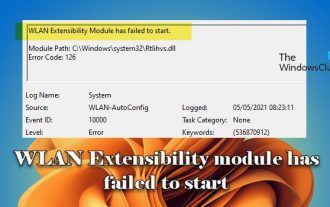 WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
This article details methods to resolve event ID10000, which indicates that the Wireless LAN expansion module cannot start. This error may appear in the event log of Windows 11/10 PC. The WLAN extensibility module is a component of Windows that allows independent hardware vendors (IHVs) and independent software vendors (ISVs) to provide users with customized wireless network features and functionality. It extends the capabilities of native Windows network components by adding Windows default functionality. The WLAN extensibility module is started as part of initialization when the operating system loads network components. If the Wireless LAN Expansion Module encounters a problem and cannot start, you may see an error message in the event viewer log.
 Optimizing PHP PDO queries: improving performance and scalability
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Optimizing PHP PDO queries: improving performance and scalability
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Using Prepared Statements Prepared statements in PDO allow the database to precompile queries and execute them multiple times without recompiling. This is essential to prevent SQL injection attacks, and it can also improve query performance by reducing compilation overhead on the database server. To use prepared statements, follow these steps: $stmt=$pdo->prepare("SELECT*FROMusersWHEREid=?");Bind ParametersBind parameters are a safe and efficient way to provide query parameters that can Prevent SQL injection attacks and improve performance. By binding parameters to placeholders, the database can optimize query execution plans and avoid performing string concatenation. To bind parameters, use the following syntax:
 How to design a maintainable MySQL table structure to implement online shopping cart functionality?
Oct 31, 2023 am 09:34 AM
How to design a maintainable MySQL table structure to implement online shopping cart functionality?
Oct 31, 2023 am 09:34 AM
How to design a maintainable MySQL table structure to implement online shopping cart functionality? When designing a maintainable MySQL table structure to implement the online shopping cart function, we need to consider the following aspects: shopping cart information, product information, user information and order information. This article details how to design these tables and provides specific code examples. Shopping cart information table (cart) The shopping cart information table is used to store the items added by the user in the shopping cart. The table contains the following fields: cart_id: shopping cart ID, as the main
 Best practices for readability and maintainability of golang functions
Apr 28, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Best practices for readability and maintainability of golang functions
Apr 28, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To improve the readability and maintainability of Go functions, follow these best practices: keep function names short, descriptive, and reflective of behavior; avoid abbreviated or ambiguous names. The function length is limited to 50-100 lines. If it is too long, consider splitting it. Document functions using comments to explain complex logic and exception handling. Avoid using global variables, and if necessary, name them explicitly and limit their scope.
 How scalable and maintainable are Java functions in large applications?
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
How scalable and maintainable are Java functions in large applications?
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Java functions provide excellent scalability and maintainability in large applications due to the following features: Scalability: statelessness, elastic deployment and easy integration, allowing easy adjustment of capacity and scaling of deployment. Maintainability: Modularity, version control, and complete monitoring and logging simplify maintenance and updates. By using Java functions and serverless architecture, more efficient processing and simplified maintenance can be achieved in large applications.
 Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
WebLogic and Tomcat are two commonly used Java application servers. They have some differences in scalability and functionality. This article will analyze the scalability of these two servers and compare the differences between them. First, let's take a look at WebLogic's scalability. WebLogic is a highly scalable Java application server developed by Oracle. It provides many advanced features, including transaction management, JDBC connection pooling, distributed caching, etc. WebLogic support
 The ultimate guide to PHP documentation: PHPDoc from beginner to proficient
Mar 01, 2024 pm 01:16 PM
The ultimate guide to PHP documentation: PHPDoc from beginner to proficient
Mar 01, 2024 pm 01:16 PM
PHPDoc is a standardized documentation comment system for documenting PHP code. It allows developers to add descriptive information to their code using specially formatted comment blocks, thereby improving code readability and maintainability. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to help you from getting started to mastering PHPDoc. Getting Started To use PHPDoc, you simply add special comment blocks to your code, usually placed before functions, classes, or methods. These comment blocks start with /** and end with */ and contain descriptive information in between. /***Calculate the sum of two numbers**@paramint$aThe first number*@paramint$bThe second number*@returnintThe sum of two numbers*/functionsum
 Java and Kubernetes know each other well: the perfect companion for microservices
Feb 29, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
Java and Kubernetes know each other well: the perfect companion for microservices
Feb 29, 2024 pm 02:31 PM
Java is a popular programming language for developing distributed systems and microservices. Its rich ecosystem and powerful concurrency capabilities provide the foundation for building robust, scalable applications. Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that manages and automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It simplifies the management of microservices environments by providing features such as orchestration, service discovery, and automatic failure recovery. Advantages of Java and Kubernetes: Scalability: Kubernetes allows you to scale your application easily, both in terms of horizontal and vertical scaling. Resilience: Kubernetes provides automatic failure recovery and self-healing capabilities to ensure that applications remain available when problems arise. Agility



