How to perform performance analysis of C++ code?

How to perform performance analysis of C code?
When developing C programs, performance is an important consideration. Optimizing the performance of your code can improve the speed and efficiency of your program. However, to optimize your code, you first need to understand where its performance bottlenecks are. To find the performance bottleneck, you first need to perform code performance analysis.
This article will introduce some commonly used C code performance analysis tools and techniques to help developers find performance bottlenecks in the code for optimization.
- Use Profiling tool
Profiling tool is one of the indispensable tools for code performance analysis. It can help developers find hot functions and time-consuming operations in the program.
A commonly used Profiling tool is gprof. It can generate a program's function call graph and the running time of each function. By analyzing this information, performance bottlenecks in the code can be found.
The steps to use gprof for performance analysis are as follows:
- When compiling the code, use the -g parameter to turn on debugging information.
- Run the program and record the running time.
- Use gprof to generate a report and execute the "gprof
> " command. - Analyze reports and find out time-consuming operations and hot functions.
In addition, there are some commercial and open source tools, such as Intel VTune and Valgrind, which provide more powerful and detailed performance analysis functions.
- Using the Timer and Profiler classes
In addition to using Profiling tools, developers can also perform performance analysis by writing code.
You can write a Timer class to measure the running time of code blocks in the program. At the beginning and end of the code block, record the current time and calculate the time difference. This will give you the running time of the code block.
For example:
class Timer {
public:
Timer() {
start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
}
~Timer() {
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(end - start).count();
std::cout << "Time taken: " << duration << " microseconds" << std::endl;
}
private:
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::high_resolution_clock> start;
};Add Timer instances before and after the code block that needs performance analysis to get the running time of the code block.
In addition to the Timer class, you can also write a Profiler class to analyze the running time of the function. The Profiler class can record the running time and number of calls of the function, and provides an interface for querying this information.
For example:
class Profiler {
public:
static Profiler& getInstance() {
static Profiler instance;
return instance;
}
void start(const std::string& functionName) {
functionTimes[functionName] -= std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
}
void end(const std::string& functionName) {
functionTimes[functionName] += std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
functionCalls[functionName]++;
}
void printReport() {
for (const auto& pair : functionTimes) {
std::cout << "Function: " << pair.first << " - Time taken: "
<< std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(pair.second).count()
<< " microseconds - Called " << functionCalls[pair.first] << " times" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::duration> functionTimes;
std::unordered_map<std::string, int> functionCalls;
Profiler() {}
~Profiler() {}
};At the beginning and end of the function that needs to be performance analyzed, call the start and end functions of the Profiler class respectively. Finally, by calling the printReport function, you can get the running time and number of calls of the function.
- Use built-in performance analysis tools
Some compilers and development environments provide built-in performance analysis tools that can be used directly in the code.
For example, the GCC compiler provides a built-in performance analysis tool-GCC Profiler. When compiling the code, add the -fprofile-generate parameter. After running the code, some .profile files will be generated. When compiling the code again, use the -fprofile-use parameter. Then rerun the code to get the performance analysis results.
Similarly, development environments such as Microsoft Visual Studio also provide performance analysis tools that can help developers find performance problems in the code.
- Use static analysis tools
In addition to the methods introduced above, you can also use static analysis tools to analyze the performance of the code.
Static analysis tools can find potential performance problems by analyzing the structure and flow of the code, such as redundant calculations in loops, memory leaks, etc.
Commonly used static analysis tools include Clang Static Analyzer, Coverity, etc. These tools can perform static analysis while compiling the code and generate corresponding reports.
In summary, performance analysis of C code is crucial to optimizing the performance of the code. By using Profiling tools, writing Timer and Profiler classes, using built-in performance analysis tools, and using static analysis tools, developers can help find performance bottlenecks and perform corresponding optimizations.
The above is the detailed content of How to perform performance analysis of C++ code?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
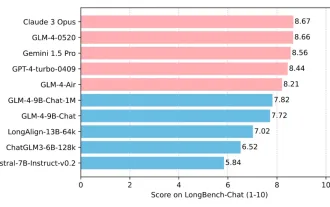 Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
Since the launch of ChatGLM-6B on March 14, 2023, the GLM series models have received widespread attention and recognition. Especially after ChatGLM3-6B was open sourced, developers are full of expectations for the fourth-generation model launched by Zhipu AI. This expectation has finally been fully satisfied with the release of GLM-4-9B. The birth of GLM-4-9B In order to give small models (10B and below) more powerful capabilities, the GLM technical team launched this new fourth-generation GLM series open source model: GLM-4-9B after nearly half a year of exploration. This model greatly compresses the model size while ensuring accuracy, and has faster inference speed and higher efficiency. The GLM technical team’s exploration has not
 The Mistral open source code model takes the throne! Codestral is crazy about training in over 80 languages, and domestic Tongyi developers are asking to participate!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 09:55 PM
The Mistral open source code model takes the throne! Codestral is crazy about training in over 80 languages, and domestic Tongyi developers are asking to participate!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 09:55 PM
Produced by 51CTO technology stack (WeChat ID: blog51cto) Mistral released its first code model Codestral-22B! What’s crazy about this model is not only that it’s trained on over 80 programming languages, including Swift, etc. that many code models ignore. Their speeds are not exactly the same. It is required to write a "publish/subscribe" system using Go language. The GPT-4o here is being output, and Codestral is handing in the paper so fast that it’s hard to see! Since the model has just been launched, it has not yet been publicly tested. But according to the person in charge of Mistral, Codestral is currently the best-performing open source code model. Friends who are interested in the picture can move to: - Hug the face: https
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...
 How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
The calculation of C35 is essentially combinatorial mathematics, representing the number of combinations selected from 3 of 5 elements. The calculation formula is C53 = 5! / (3! * 2!), which can be directly calculated by loops to improve efficiency and avoid overflow. In addition, understanding the nature of combinations and mastering efficient calculation methods is crucial to solving many problems in the fields of probability statistics, cryptography, algorithm design, etc.
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
std::unique removes adjacent duplicate elements in the container and moves them to the end, returning an iterator pointing to the first duplicate element. std::distance calculates the distance between two iterators, that is, the number of elements they point to. These two functions are useful for optimizing code and improving efficiency, but there are also some pitfalls to be paid attention to, such as: std::unique only deals with adjacent duplicate elements. std::distance is less efficient when dealing with non-random access iterators. By mastering these features and best practices, you can fully utilize the power of these two functions.
 How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
In C language, snake nomenclature is a coding style convention, which uses underscores to connect multiple words to form variable names or function names to enhance readability. Although it won't affect compilation and operation, lengthy naming, IDE support issues, and historical baggage need to be considered.




