How to use Workerman to implement a distributed computing system

Distributed computing system refers to a computing model that treats a group of computers as a single system to collaboratively complete computing tasks. In practice, distributed computing systems can increase the computing speed by increasing the number of computers, and at the same time can solve the problem of processing large amounts of data. Workerman is a framework that can implement distributed computing systems using PHP language. This article will introduce how to use Workerman to implement a simple distributed computing system and provide code examples.
- Install Workerman
First, we need to install Workerman. It can be installed through Composer. The specific command is as follows:
composer require workerman/workerman
- Create server program
We will create a server program named server.php and run With this program, the client can submit computing tasks to the server, and the server is responsible for assigning tasks to computing nodes for calculation and returning the final results to the client. The following is a code example of server.php:
<?php
use WorkermanWorker;
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
$worker = new Worker('text://0.0.0.0:2346');
$worker->count = 4;
$worker->onMessage = function($connection, $data){
$params = json_decode($data, true);
$worker_num = $params['worker_num'];
$task_data = $params['task_data'];
$task_id = md5($task_data);
$task_worker = new Task($task_id);
$task_worker->send([
'worker_num' => $worker_num,
'task_data' => $task_data
]);
$connection->send(json_encode([
'task_id' => $task_id
]));
};
class Task{
protected $task_id;
protected $worker_num;
protected $task_data;
public function __construct($task_id){
$this->task_id = $task_id;
}
public function send($data){
$task_data = json_encode([
'task_id' => $this->task_id,
'data' => $data
]);
$worker_num = $data['worker_num'];
$socket_name = "tcp://127.0.0.1:".(2347 + $worker_num);
$client = stream_socket_client($socket_name, $errno, $errstr);
fwrite($client, $task_data);
fclose($client);
}
}
Worker::runAll();In the above code, we use the server listening port to wait for the client to submit a task. When the server receives the task submitted by the client, the server will assign the task to a computing node for calculation and return the results to the client.
In the instance of the Worker class, we configured 4 processes to handle client requests. In the onMessage event callback, we first obtain worker_num and task_data from the JSON data submitted by the client, then create a new Task instance, send the task to the computing node, and wait for the calculation result to be returned.
In the Task class, we store the task ID (task_id), the node number to be calculated (worker_num) and the data to be calculated (task_data). The send() method is used to send tasks to the specified computing node. Here, we use the stream_socket_client() function to implement a TCP socket client for communicating with the specified computing node.
- Create a computing node program
Next, we create a computing node program named worker.php. The program will perform calculations after the server assigns the calculation tasks to it, and return the results to the server. The following is a code example for worker.php:
<?php
use WorkermanWorker;
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
$worker_num = intval($argv[1]);
$worker = new Worker("tcp://0.0.0.0:". (2347 + $worker_num));
$worker->onMessage = function($connection, $data){
$params = json_decode($data, true);
$task_id = $params['task_id'];
$task_data = $params['data'];
$result = strlen($task_data);
$connection->send(json_encode([
'task_id' => $task_id,
'result' => $result
]));
};
Worker::runAll();In the above code, we use a TCP socket to listen to a port and wait for the server to assign computing tasks. When there is a computing task that needs to be processed, we obtain the data that needs to be processed from the task data, perform calculations, and send the results to the server.
- Create client program
Finally, we need to create a client program named client.php to submit calculation tasks to the server and obtain calculations result. The following is a code example for client.php:
<?php
use WorkermanWorker;
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
$client = stream_socket_client("tcp://127.0.0.1:2346", $errno, $errstr);
$data = [
'worker_num' => 1,
'task_data' => 'Workerman is a high-performance PHP socket framework'
];
$json_data = json_encode($data);
fwrite($client, $json_data);
$result = fread($client, 8192);
fclose($client);
$result_data = json_decode($result, true);
$task_id = $result_data['task_id'];
foreach(range(0,3) as $worker_num){
$worker_client = stream_socket_client("tcp://127.0.0.1:". (2347 + $worker_num), $errno, $errstr);
fwrite($worker_client, json_encode([
'task_id' => $task_id,
'worker_num' => $worker_num
]));
$worker_result = fread($worker_client, 8192);
$worker_result_data = json_decode($worker_result, true);
if($worker_result_data['task_id'] == $task_id){
echo "Result: " . $worker_result_data['result'] . PHP_EOL;
break;
}
}
In the above code, we first create a TCP socket client to connect to the compute node. The fread() function is used here to obtain the return results of the calculation task from the server. Then we send task_id as a parameter to all computing nodes and wait for the results to be returned. Based on the task ID (task_id), we can identify which computing node returned the calculation result. Finally we can output the calculation results.
Summary
The above are the detailed steps on how to use Workerman to implement a distributed computing system, including creating server programs, computing node programs and client programs, and providing specific code examples. It is worth mentioning that the examples provided in this article only demonstrate the basic ideas of how to use Workerman to implement distributed computing systems. There are still some problems in practical applications, such as load balancing, task allocation strategies, etc. But all of these problems can be solved by carefully studying the Workerman framework and adjusting the code.
The above is the detailed content of How to use Workerman to implement a distributed computing system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
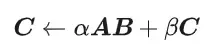 CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
CUDA's universal matrix multiplication: from entry to proficiency!
Mar 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) is a vital part of many applications and algorithms, and is also one of the important indicators for evaluating computer hardware performance. In-depth research and optimization of the implementation of GEMM can help us better understand high-performance computing and the relationship between software and hardware systems. In computer science, effective optimization of GEMM can increase computing speed and save resources, which is crucial to improving the overall performance of a computer system. An in-depth understanding of the working principle and optimization method of GEMM will help us better utilize the potential of modern computing hardware and provide more efficient solutions for various complex computing tasks. By optimizing the performance of GEMM
 How to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in word document
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
How to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in word document
Mar 19, 2024 pm 08:13 PM
WORD is a powerful word processor. We can use word to edit various texts. In Excel tables, we have mastered the calculation methods of addition, subtraction and multipliers. So if we need to calculate the addition of numerical values in Word tables, How to subtract the multiplier? Can I only use a calculator to calculate it? The answer is of course no, WORD can also do it. Today I will teach you how to use formulas to calculate basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in tables in Word documents. Let's learn together. So, today let me demonstrate in detail how to calculate addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in a WORD document? Step 1: Open a WORD, click [Table] under [Insert] on the toolbar, and insert a table in the drop-down menu.
 How to count the number of elements in a list using Python's count() function
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
How to count the number of elements in a list using Python's count() function
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:53 PM
How to use Python's count() function to calculate the number of an element in a list requires specific code examples. As a powerful and easy-to-learn programming language, Python provides many built-in functions to handle different data structures. One of them is the count() function, which can be used to count the number of elements in a list. In this article, we will explain how to use the count() function in detail and provide specific code examples. The count() function is a built-in function of Python, used to calculate a certain
 Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Implement file upload and download in Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
To implement file upload and download in Workerman documents, specific code examples are required. Introduction: Workerman is a high-performance PHP asynchronous network communication framework that is simple, efficient, and easy to use. In actual development, file uploading and downloading are common functional requirements. This article will introduce how to use the Workerman framework to implement file uploading and downloading, and give specific code examples. 1. File upload: File upload refers to the operation of transferring files on the local computer to the server. The following is used
 How to use the Math.Pow function in C# to calculate the power of a specified number
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How to use the Math.Pow function in C# to calculate the power of a specified number
Nov 18, 2023 am 11:32 AM
In C#, there is a Math class library, which contains many mathematical functions. These include the function Math.Pow, which calculates powers, which can help us calculate the power of a specified number. The usage of the Math.Pow function is very simple, you only need to specify the base and exponent. The syntax is as follows: Math.Pow(base,exponent); where base represents the base and exponent represents the exponent. This function returns a double type result, that is, the power calculation result. Let's
 Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Which one is better, swoole or workerman?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
Swoole and Workerman are both high-performance PHP server frameworks. Known for its asynchronous processing, excellent performance, and scalability, Swoole is suitable for projects that need to handle a large number of concurrent requests and high throughput. Workerman offers the flexibility of both asynchronous and synchronous modes, with an intuitive API that is better suited for ease of use and projects that handle lower concurrency volumes.
 How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
How to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:46 AM
Introduction to how to implement the basic usage of Workerman documents: Workerman is a high-performance PHP development framework that can help developers easily build high-concurrency network applications. This article will introduce the basic usage of Workerman, including installation and configuration, creating services and listening ports, handling client requests, etc. And give corresponding code examples. 1. Install and configure Workerman. Enter the following command on the command line to install Workerman: c
 Workerman development: How to implement real-time video calls based on UDP protocol
Nov 08, 2023 am 08:03 AM
Workerman development: How to implement real-time video calls based on UDP protocol
Nov 08, 2023 am 08:03 AM
Workerman development: real-time video call based on UDP protocol Summary: This article will introduce how to use the Workerman framework to implement real-time video call function based on UDP protocol. We will have an in-depth understanding of the characteristics of the UDP protocol and show how to build a simple but complete real-time video call application through code examples. Introduction: In network communication, real-time video calling is a very important function. The traditional TCP protocol may have problems such as transmission delays when implementing high-real-time video calls. And UDP




