 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 The speed and accuracy exceed that of humans. AI alone created 41 new materials in just 17 days.
The speed and accuracy exceed that of humans. AI alone created 41 new materials in just 17 days.
The speed and accuracy exceed that of humans. AI alone created 41 new materials in just 17 days.
"Nature" published two blockbuster studies on November 30: The latest artificial intelligence-driven platform GNoME (Graphic Network for Materials Exploration) can already discover and synthesize new inorganic compounds on its own, including the discovery of more than 2.2 million With a stable structure, he created 41 new materials on his own in 17 days, with speed and accuracy far exceeding that of humans.
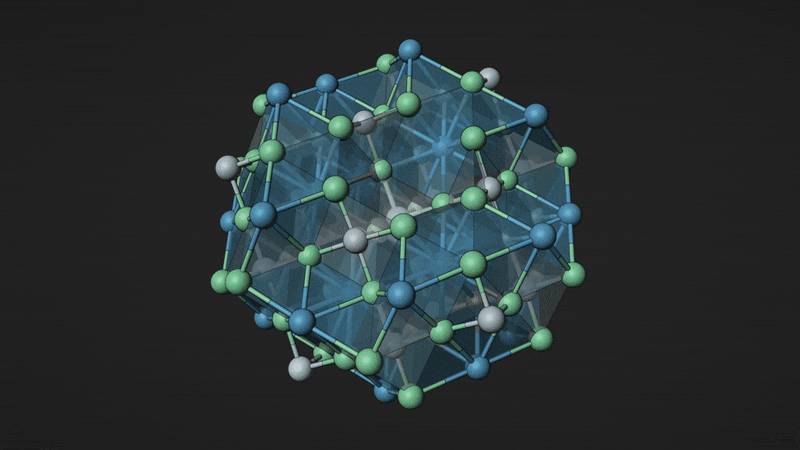
This compound (Ba6Nb7O21) is one of the new materials calculated by GNoME. It contains barium (blue), niobium (white) and oxygen (green). Image source: Berkeley Lab Materials Program
Advances in technology have improved the ability of computer programs to identify new materials, but a major obstacle faced in the process is how learning algorithms adapt to results that are contrary to what they have learned. This is because new discoveries are essentially the ability to understand data in new, creative ways
The "Deep Thinking" team proposed a computing model this time that can improve the efficiency of material discovery through large-scale active learning. The program is trained using existing literature to generate a diverse set of candidate structures for potential compounds, which are then continuously refined through a series of learnings. GNoME discovered more than 2.2 million stable structures, improving the accuracy of structural stability predictions to over 80% and, in predicting composition, to 33% accuracy per 100 trials, compared with this figure in previous work. Only 1%.
In a second study, a UC Berkeley research team developed an automated laboratory (A-Lab) system. This A-Lab system is trained on existing scientific literature, combined with active learning, and can create up to five preliminary synthetic recipes for proposed compounds. It can then perform experiments with a robotic arm to synthesize the compound in powder form. If the yield of a recipe falls below 50%, A-Lab will adjust the recipe and continue experimenting until the goal is successfully achieved or all possible recipes are exhausted. After 17 days of continuous experimentation and 355 experiments, A-Lab successfully synthesized 41 of the 58 proposed compounds (71%). In comparison, human researchers would spend months guessing and experimenting
The training of AI demonstrated by the two research institutes combines the rapid development of computing power with existing literature. It proves that the use of learning algorithms to assist in the discovery and synthesis of inorganic compounds has extremely broad prospects. In the future, autonomous laboratories will be able to Discover new materials at the fastest speed with the least manpower.
(Source: Science and Technology Daily)
The above is the detailed content of The speed and accuracy exceed that of humans. AI alone created 41 new materials in just 17 days.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
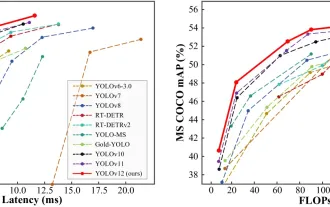 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 Guide to Uber's H3 for Spatial Indexing
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:54 AM
Guide to Uber's H3 for Spatial Indexing
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:54 AM
In today’s data-driven world, efficient geospatial indexing is crucial for applications ranging from ride-sharing and logistics to environmental monitoring and disaster response. Uber’s H3, a powerful open-source spat



