 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 New title: Real-time rendering evolved! Innovative method of 3D reconstruction based on rays
New title: Real-time rendering evolved! Innovative method of 3D reconstruction based on rays
New title: Real-time rendering evolved! Innovative method of 3D reconstruction based on rays
 Pictures
Pictures
Paper link:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.19629
Code link:https://github.com/vLAR-group/RayDF
Homepage: The content that needs to be rewritten is: https://vlar-group.github.io/RayDF.html
Rewritten content: Implementation method:
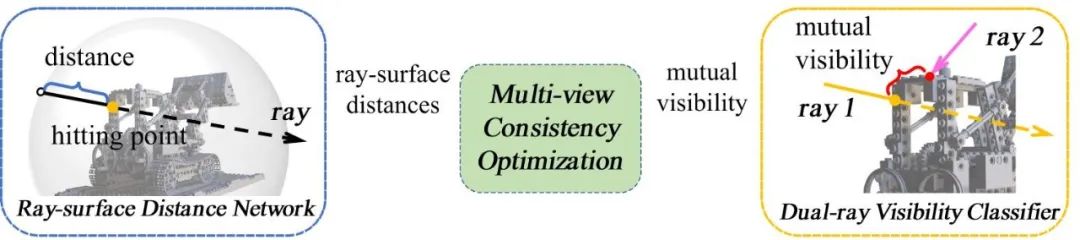
The overall process and components of RayDF are as follows (see Figure 1)
1. Introduction
In the machine Learning accurate and efficient 3D shape representation is very important in many cutting-edge applications in the fields of vision and robotics. However, existing implicit expressions based on 3D coordinates require expensive computational costs when representing 3D shapes or rendering 2D images; in contrast, ray-based methods can efficiently infer 3D shapes. However, existing ray-based methods do not take into account the geometric consistency under multiple viewing angles, making it difficult to recover accurate geometric shapes under unknown viewing angles.
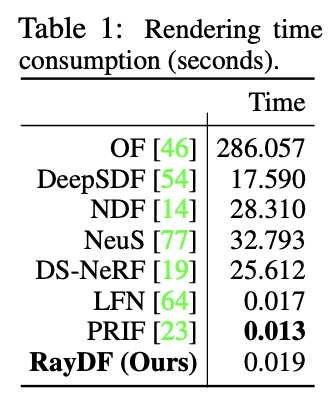
To address these problems, this paper proposes a new maintenance method. RayDF, a ray-based implicit expression method for multi-view geometric consistency. This method is based on a simple ray-surface distance field, by introducing a new dual-ray visibility classifier and a multi-view consistency optimization module. optimization module), learn to obtain a ray-surface distance that satisfies the geometric consistency of multiple viewing angles. Experimental results show that the modified method achieves superior 3D surface reconstruction performance on three data sets and achieves a rendering speed 1000 times faster than the coordinate-based method (see Table 1).
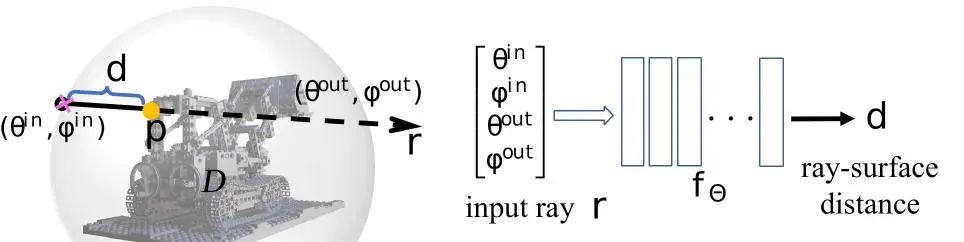
The following are the main contributions:
- Using ray-surface distance field to represent three-dimensional shape, this expression is better than Existing coordinate-based representations are more efficient.
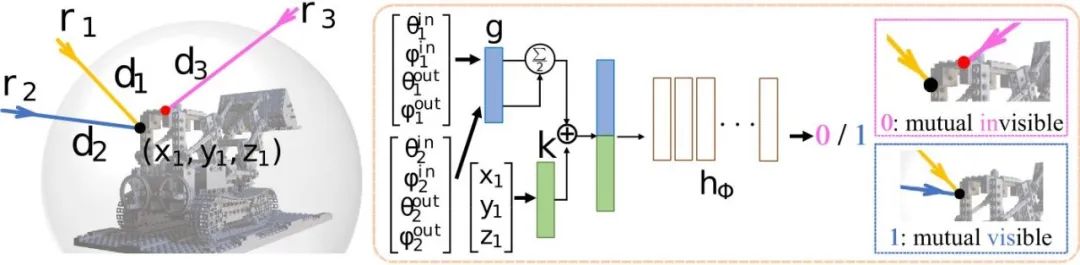
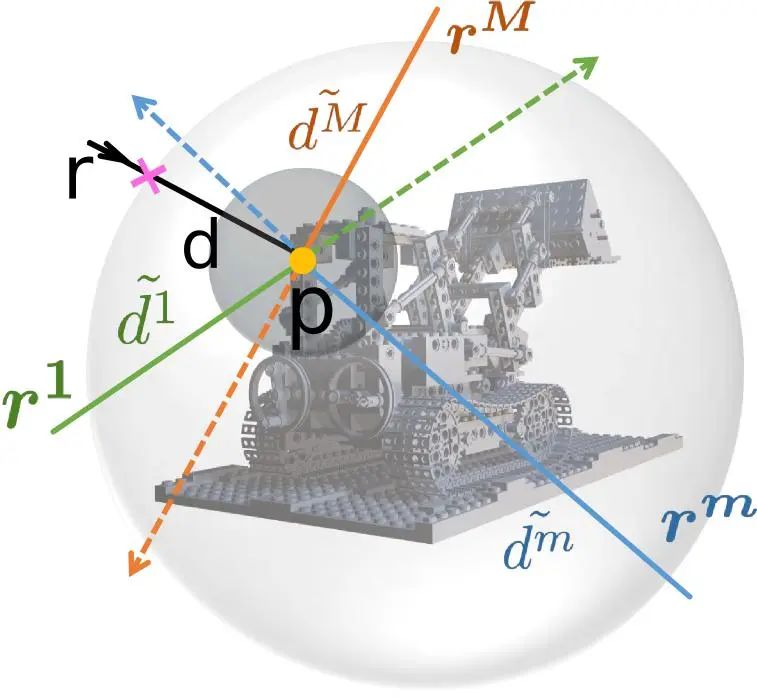
(1) First construct the ray pairs for training for the auxiliary network dual-ray visibility classifier. For a ray in a picture (corresponding to a pixel in the picture), the corresponding space surface point can be known through its ray-surface distance. Project it to the remaining viewing angles in the training set to obtain another ray; and this ray There is a corresponding ray-surface distance. The article sets a threshold of 10 mm to determine whether two rays are visible to each other.
(2) The second stage is to train the main network ray-surface distance network to make its predicted distance field meet multi-view consistency. As shown in Figure 4, for a main ray and its surface points, the surface point is uniformly sampled with the center of the sphere to obtain several multi-view rays. Pair the main ray with these multi-view rays one by one, and their mutual visibility can be obtained through the trained dual-ray visibility classifier. Then predict the ray-surface distance of these rays through the ray-surface distance network; if the main ray and a certain sampling ray are mutually visible, then the surface points calculated by the ray-surface distances of the two rays should be the same point; according to The corresponding loss function is designed and the main network is trained, which ultimately enables the ray-surface distance field to meet multi-view consistency.
2.4 Surface Normal Derivation and Outlier Points Removal
Since the depth value at the edge of the scene surface often has mutations (discontinuity), and neural The network is a continuous function. The above-mentioned ray-surface distance field can easily predict inaccurate distance values at the edge of the surface, resulting in noise on the geometric surface at the edge. Fortunately, the designed ray-surface distance field has a good feature, as shown in Figure 5. The normal vector of each estimated three-dimensional surface point can be easily found in closed form through automatic differentiation of the network. Therefore, the normal vector Euclidean distance of the surface point can be calculated during the network inference stage. If the distance value is greater than the threshold, the surface point is regarded as an outlier and eliminated, thereby obtaining a clean three-dimensional reconstructed surface.
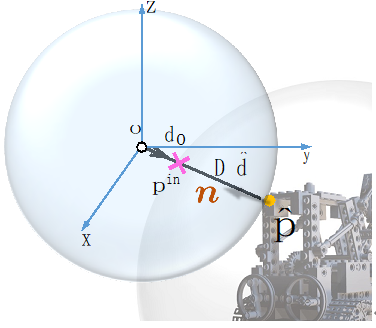
Figure 5 Surface normal calculation
3. Experiments
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, we performed experiments on three data sets Experiments were conducted on. The three data sets are the object-level synthetic data set Blender [1], the scene-level synthetic data set DM-SR [2], and the scene-level real data set ScanNet [3]. We selected seven baselines for performance comparison. Among them, OF [4]/DeepSDF [5]/NDF [6]/NeuS [7] are coordinate-based level-set methods, DS-NeRF [8] is a depth-supervised NeRF-based method, and LFN [9] and PRIF [10] are two ray-based baselines
Due to the ease of the RayDF method to directly add a radiance branch to learn textures, it can be compared with baseline models that support predicting radiance fields. Therefore, the comparative experiments of this paper are divided into two groups. The first group (Group 1) only predicts distance (geometry), and the second group (Group 2) predicts both distance and radiance (geometry and texture)
3.1 Evaluation on Blender Dataset
As can be seen from Table 2 and Figure 6, in Group 1 and 2, RayDF achieved better results in surface reconstruction, especially in the most important ADE indicator. Better than coordinate- and ray-based baselines. At the same time, in terms of radiance field rendering, RayDF also achieved performance comparable to DS-NeRF and better than LFN and PRIF.
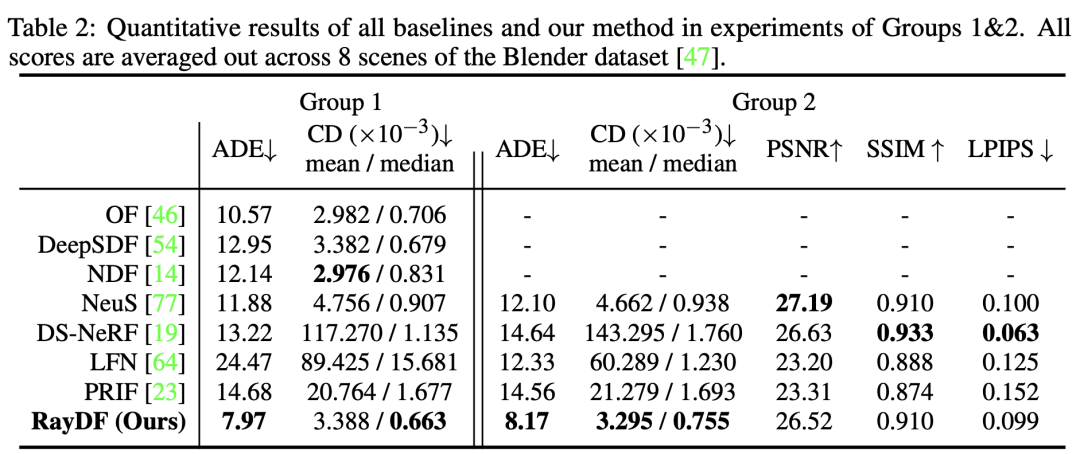
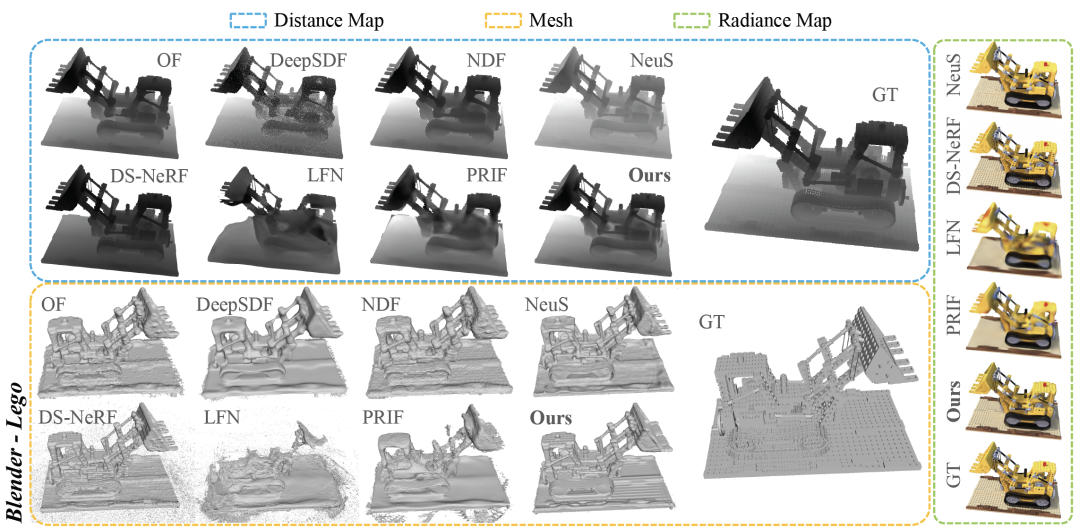
Figure 6 Visual comparison of Blender data set
3.2 Evaluation on DM-SR Dataset
As can be seen from Table 3, RayDF surpasses all baselines in the most critical ADE indicator. At the same time, in the Group 2 experiment, RayDF was able to obtain high-quality new view synthesis while ensuring that the accurate surface shape was restored (see Figure 7).
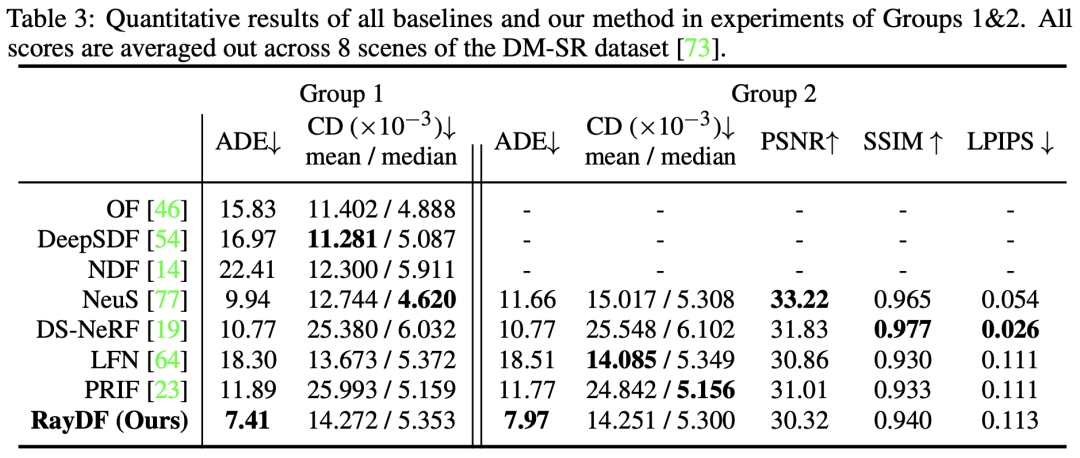
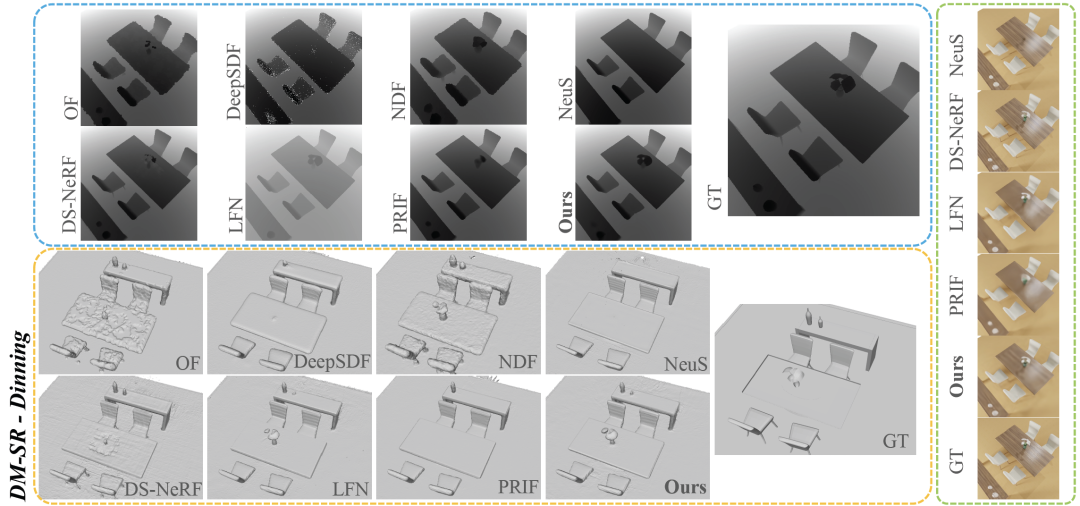
Figure 7 Visual comparison of DM-SR data set
3.3 Evaluation on ScanNet Dataset
Table 4 compares the performance of RayDF and baselines in challenging real-world scenarios. In the first and second groups, RayDF significantly outperforms baselines in almost all evaluation metrics, showing clear advantages in recovering complex real-world 3D scenes
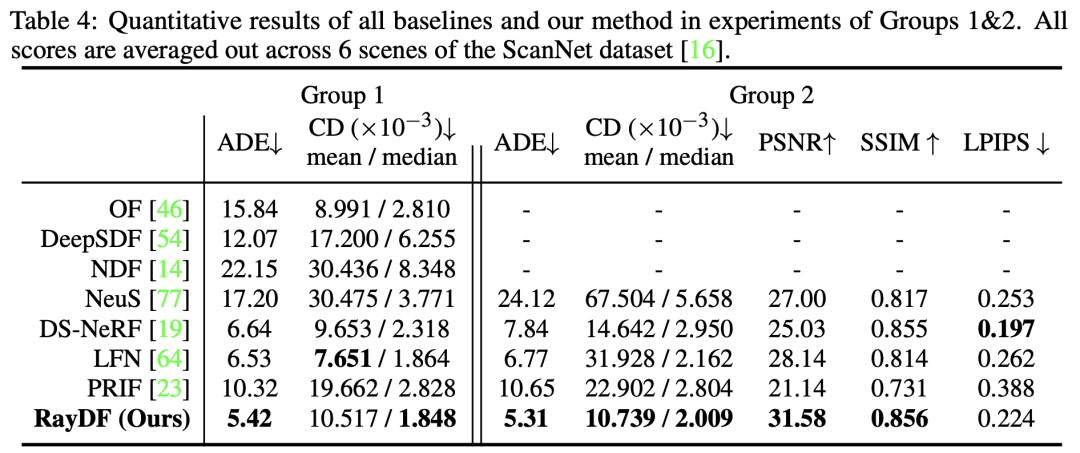
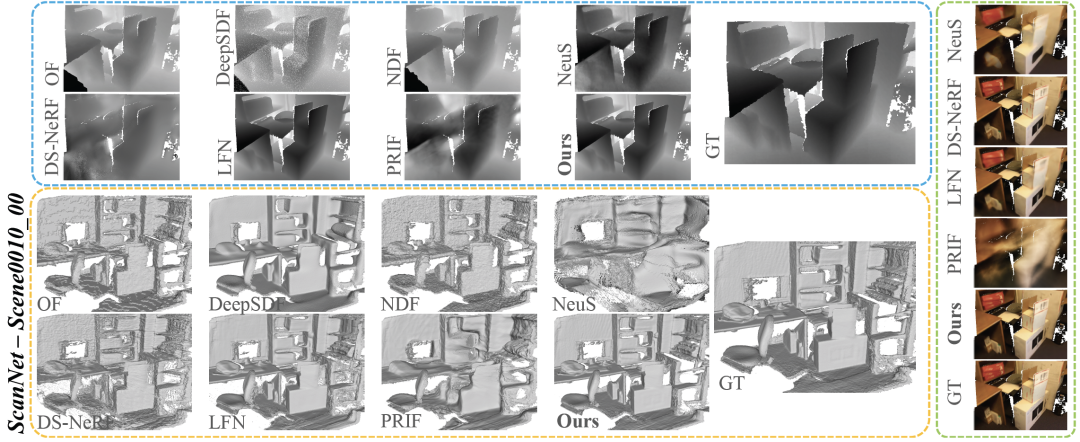
The following is a rewrite of the visual comparison of Figure 8 ScanNet dataset: In Figure 8, we show the visual comparison results of the ScanNet dataset
3.4 Ablation Study
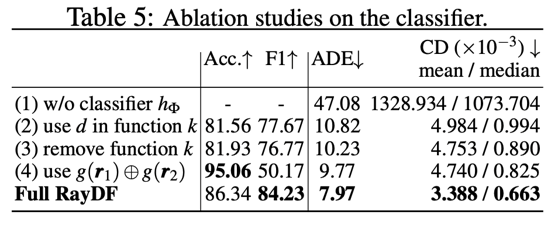
We conducted an ablation experiment on the Blender dataset. Table 5 in the paper shows the key The ablation experimental results of the dual-ray visibility classifier
- are shown in Table 5 (1). Without the help of the dual-ray visibility classifier, the ray-surface distance field will not be able to detect the new angle of view. The rays predict reasonable distance values (see Figure 9).
- In the input of the classifier, the input surface point coordinates are selected as auxiliary, as shown in Table 5 (2) and (3), if the surface point distance value is selected as auxiliary or not Providing auxiliary information, the classifier will obtain lower accuracy and F1 score, resulting in insufficient visibility information provided for the ray-surface distance network, thereby predicting incorrect distance values.
- As shown in Table 5 (4), by inputting a pair of rays in an asymmetric manner, the trained classifier has a higher accuracy but a lower F1 score. This shows that this classifier is significantly less robust than a classifier trained with symmetric input rays.
Other resection operations can be viewed in the paper and the paper appendix

need to be re- The written content is: Figure 9 shows the visual comparison of using a classifier and not using a classifier
4. Conclusion
When using the ray-based multi-view consistency framework for research, the paper A conclusion is drawn that three-dimensional shape representations can be learned efficiently and accurately through this method. In the paper, a simple ray-surface distance field is used to represent the geometry of three-dimensional shapes, and a novel dual-ray visibility classifier is used to further achieve multi-view geometric consistency. Experiments on multiple data sets have proven that the RayDF method has extremely high rendering efficiency and excellent performance. Further extensions to the RayDF framework are welcome. You can view more visualization results on the homepage
The content that needs to be rewritten is: https://vlar-group.github.io/RayDF.html

The content that needs to be rewritten is: Original link: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dsrSHKT4NfgdDPYcKOhcOA
The above is the detailed content of New title: Real-time rendering evolved! Innovative method of 3D reconstruction based on rays. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
StableDiffusion3’s paper is finally here! This model was released two weeks ago and uses the same DiT (DiffusionTransformer) architecture as Sora. It caused quite a stir once it was released. Compared with the previous version, the quality of the images generated by StableDiffusion3 has been significantly improved. It now supports multi-theme prompts, and the text writing effect has also been improved, and garbled characters no longer appear. StabilityAI pointed out that StableDiffusion3 is a series of models with parameter sizes ranging from 800M to 8B. This parameter range means that the model can be run directly on many portable devices, significantly reducing the use of AI
 Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
The first pilot and key article mainly introduces several commonly used coordinate systems in autonomous driving technology, and how to complete the correlation and conversion between them, and finally build a unified environment model. The focus here is to understand the conversion from vehicle to camera rigid body (external parameters), camera to image conversion (internal parameters), and image to pixel unit conversion. The conversion from 3D to 2D will have corresponding distortion, translation, etc. Key points: The vehicle coordinate system and the camera body coordinate system need to be rewritten: the plane coordinate system and the pixel coordinate system. Difficulty: image distortion must be considered. Both de-distortion and distortion addition are compensated on the image plane. 2. Introduction There are four vision systems in total. Coordinate system: pixel plane coordinate system (u, v), image coordinate system (x, y), camera coordinate system () and world coordinate system (). There is a relationship between each coordinate system,
 This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
Trajectory prediction plays an important role in autonomous driving. Autonomous driving trajectory prediction refers to predicting the future driving trajectory of the vehicle by analyzing various data during the vehicle's driving process. As the core module of autonomous driving, the quality of trajectory prediction is crucial to downstream planning control. The trajectory prediction task has a rich technology stack and requires familiarity with autonomous driving dynamic/static perception, high-precision maps, lane lines, neural network architecture (CNN&GNN&Transformer) skills, etc. It is very difficult to get started! Many fans hope to get started with trajectory prediction as soon as possible and avoid pitfalls. Today I will take stock of some common problems and introductory learning methods for trajectory prediction! Introductory related knowledge 1. Are the preview papers in order? A: Look at the survey first, p
 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.
 The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Some of the author’s personal thoughts In the field of autonomous driving, with the development of BEV-based sub-tasks/end-to-end solutions, high-quality multi-view training data and corresponding simulation scene construction have become increasingly important. In response to the pain points of current tasks, "high quality" can be decoupled into three aspects: long-tail scenarios in different dimensions: such as close-range vehicles in obstacle data and precise heading angles during car cutting, as well as lane line data. Scenes such as curves with different curvatures or ramps/mergings/mergings that are difficult to capture. These often rely on large amounts of data collection and complex data mining strategies, which are costly. 3D true value - highly consistent image: Current BEV data acquisition is often affected by errors in sensor installation/calibration, high-precision maps and the reconstruction algorithm itself. this led me to
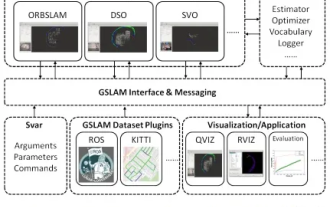 GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Suddenly discovered a 19-year-old paper GSLAM: A General SLAM Framework and Benchmark open source code: https://github.com/zdzhaoyong/GSLAM Go directly to the full text and feel the quality of this work ~ 1 Abstract SLAM technology has achieved many successes recently and attracted many attracted the attention of high-tech companies. However, how to effectively perform benchmarks on speed, robustness, and portability with interfaces to existing or emerging algorithms remains a problem. In this paper, a new SLAM platform called GSLAM is proposed, which not only provides evaluation capabilities but also provides researchers with a useful way to quickly develop their own SLAM systems.
 'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
Please note that this square man is frowning, thinking about the identities of the "uninvited guests" in front of him. It turned out that she was in a dangerous situation, and once she realized this, she quickly began a mental search to find a strategy to solve the problem. Ultimately, she decided to flee the scene and then seek help as quickly as possible and take immediate action. At the same time, the person on the opposite side was thinking the same thing as her... There was such a scene in "Minecraft" where all the characters were controlled by artificial intelligence. Each of them has a unique identity setting. For example, the girl mentioned before is a 17-year-old but smart and brave courier. They have the ability to remember and think, and live like humans in this small town set in Minecraft. What drives them is a brand new,
 More than just 3D Gaussian! Latest overview of state-of-the-art 3D reconstruction techniques
Jun 02, 2024 pm 06:57 PM
More than just 3D Gaussian! Latest overview of state-of-the-art 3D reconstruction techniques
Jun 02, 2024 pm 06:57 PM
Written above & The author’s personal understanding is that image-based 3D reconstruction is a challenging task that involves inferring the 3D shape of an object or scene from a set of input images. Learning-based methods have attracted attention for their ability to directly estimate 3D shapes. This review paper focuses on state-of-the-art 3D reconstruction techniques, including generating novel, unseen views. An overview of recent developments in Gaussian splash methods is provided, including input types, model structures, output representations, and training strategies. Unresolved challenges and future directions are also discussed. Given the rapid progress in this field and the numerous opportunities to enhance 3D reconstruction methods, a thorough examination of the algorithm seems crucial. Therefore, this study provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in Gaussian scattering. (Swipe your thumb up



