 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 NVIDIA slaps AMD in the face: With software support, H100's AI performance is 47% faster than MI300X!
NVIDIA slaps AMD in the face: With software support, H100's AI performance is 47% faster than MI300X!
NVIDIA slaps AMD in the face: With software support, H100's AI performance is 47% faster than MI300X!

According to news on December 14, AMD launched its most powerful AI chip Instinct MI300X earlier this month. The AI performance of its 8-GPU server is 60% higher than that of Nvidia H100 8-GPU. In this regard, NVIDIA recently released a set of the latest performance comparison data between H100 and MI300X, showing how H100 can use the right software to provide faster AI performance than MI300X.
According to data previously released by AMD, the FP8/FP16 performance of MI300X has reached 1.3 times that of NVIDIA H100, and the speed of running Llama 2 70B and FlashAttention 2 models is 20% faster than H100. In the 8v8 server, when running the Llama 2 70B model, MI300X is 40% faster than H100; when running the Bloom 176B model, MI300X is 60% faster than H100.
However, it should be noted that when comparing MI300X with NVIDIA H100, AMD used the optimization library in the latest ROCm 6.0 suite (which can support the latest computing formats such as FP16, Bf16 and FP8, including Sparsity etc.) to get these numbers. In contrast, the NVIDIA H100 was not tested without the use of optimization software such as NVIDIA's TensorRT-LLM.
AMD's implicit statement on the NVIDIA H100 test shows that using vLLM v.02.2.2 inference software and the NVIDIA DGX H100 system, the Llama 2 70B query has an input sequence length of 2048 and an output sequence length of 128
The latest test results released by NVIDIA for DGX H100 (with 8 NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs, with 80 GB HBM3) show that the public NVIDIA TensorRT LLM software is used, of which v0.5.0 is used for Batch-1 Test, v0.6.1 for latency threshold measurements. Test workload details are the same as previously conducted AMD tests
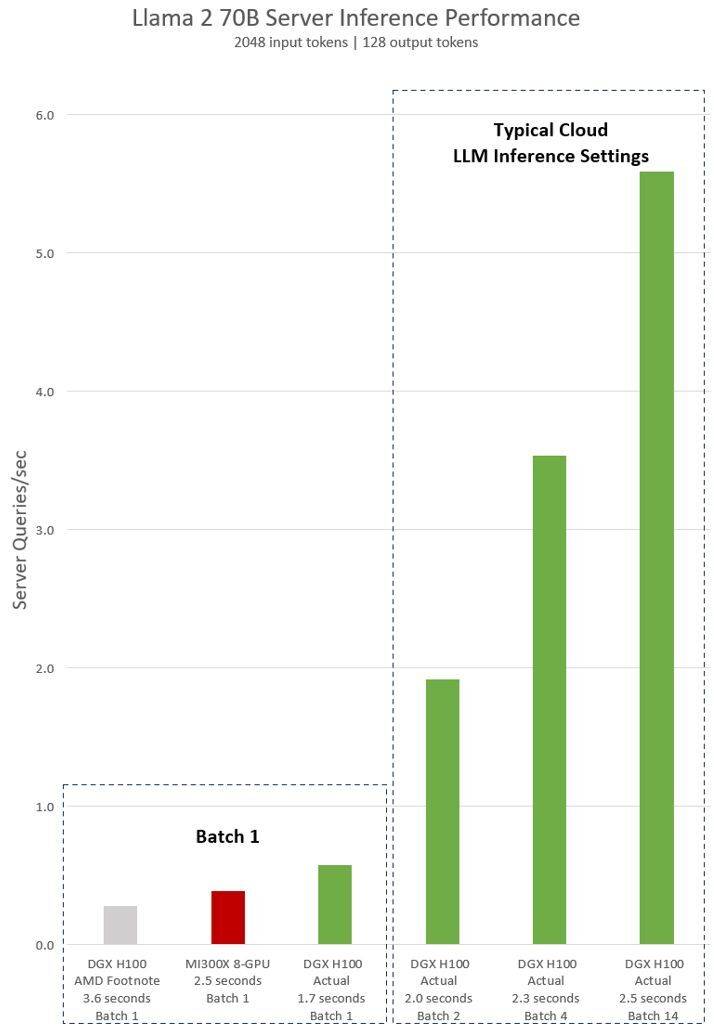
According to the results, after using optimized software, the performance of the NVIDIA DGX H100 server has increased by more than 2 times, and is 47% faster than the MI300X 8-GPU server displayed by AMD
DGX H100 can handle a single inference task in 1.7 seconds. In order to optimize response time and data center throughput, cloud services set fixed response times for specific services. This allows them to combine multiple inference requests into larger "batches", thereby increasing the overall number of inferences per second on the server. Industry standard benchmarks such as MLPerf also use this fixed response time metric to measure performance
Slight tradeoffs in response time can create uncertainty in the number of inference requests the server can handle in real time. Using a fixed 2.5 second response time budget, the NVIDIA DGX H100 server can handle more than 5 Llama 2 70B inferences per second, while Batch-1 handles less than one per second.
Obviously, it is relatively fair for Nvidia to use these new benchmarks. After all, AMD also uses its optimized software to evaluate the performance of its GPUs, so why not do the same when testing the Nvidia H100?
You must know that NVIDIA's software stack revolves around the CUDA ecosystem, and after years of hard work and development, it has a very strong position in the artificial intelligence market, while AMD's ROCm 6.0 is new and has not yet been tested in real-world scenarios.
According to information previously disclosed by AMD, it has reached a large part of the deal with large companies such as Microsoft and Meta. These companies regard its MI300X GPU as a replacement for Nvidia's H100 solution.
AMD’s latest Instinct MI300X is expected to be shipped in large quantities in the first half of 2024. However, NVIDIA’s more powerful H200 GPU will also be shipped by then, and NVIDIA will also launch a new generation of Blackwell B100 in the second half of 2024. In addition, Intel will also launch its new generation AI chip Gaudi 3. Next, competition in the field of artificial intelligence seems to become more intense.
Editor: Xinzhixun-Rurounijian
The above is the detailed content of NVIDIA slaps AMD in the face: With software support, H100's AI performance is 47% faster than MI300X!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 ASUS unveils Adol Book 14 Air with AMD Ryzen 9 8945H and curious incense dispenser
Aug 01, 2024 am 11:12 AM
ASUS unveils Adol Book 14 Air with AMD Ryzen 9 8945H and curious incense dispenser
Aug 01, 2024 am 11:12 AM
ASUS already offers various 14-inch laptops, including the Zenbook 14 OLED (curr. $1,079.99 on Amazon). Now, it has decided to introduce the Adol Book 14 Air, which looks like a typical 14-inch laptop on the face of it. However, an inconspicuous meta
 AMD Radeon RX 7800M in OneXGPU 2 outperforms Nvidia RTX 4070 Laptop GPU
Sep 09, 2024 am 06:35 AM
AMD Radeon RX 7800M in OneXGPU 2 outperforms Nvidia RTX 4070 Laptop GPU
Sep 09, 2024 am 06:35 AM
OneXGPU 2 is the first eGPUto feature the Radeon RX 7800M, a GPU that even AMD hasn't announced yet. As revealed by One-Netbook, the manufacturer of the external graphics card solution, the new AMD GPU is based on RDNA 3 architecture and has the Navi
 Ryzen AI software gets support for new Strix Halo and Kraken Point AMD Ryzen processors
Aug 01, 2024 am 06:39 AM
Ryzen AI software gets support for new Strix Halo and Kraken Point AMD Ryzen processors
Aug 01, 2024 am 06:39 AM
AMD Strix Point laptopshave just hit the market, and the next-gen Strix Halo processors are expected to be released sometime next year. However, the company has already added support for the Strix Halo and Krackan Point APUs to its Ryzen AI software.
 AMD Z2 Extreme chip for handheld consoles tipped for an early 2025 launch
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:38 AM
AMD Z2 Extreme chip for handheld consoles tipped for an early 2025 launch
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:38 AM
Even though AMD tailor-made the Ryzen Z1 Extreme (and its non-Extreme variant) for handheld consoles, the chip only ever found itself in two mainstream handhelds, the Asus ROG Ally (curr. $569 on Amazon) and Lenovo Legion Go (three if you count the R
 AMD announces 'Sinkclose' high-severity vulnerability, affecting millions of Ryzen and EPYC processors
Aug 10, 2024 pm 10:31 PM
AMD announces 'Sinkclose' high-severity vulnerability, affecting millions of Ryzen and EPYC processors
Aug 10, 2024 pm 10:31 PM
According to news from this site on August 10, AMD officially confirmed that some EPYC and Ryzen processors have a new vulnerability called "Sinkclose" with the code "CVE-2023-31315", which may involve millions of AMD users around the world. So, what is Sinkclose? According to a report by WIRED, the vulnerability allows intruders to run malicious code in "System Management Mode (SMM)." Allegedly, intruders can use a type of malware called a bootkit to take control of the other party's system, and this malware cannot be detected by anti-virus software. Note from this site: System Management Mode (SMM) is a special CPU working mode designed to achieve advanced power management and operating system independent functions.
 First Minisforum mini PC with Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 rumored to launch with high price tag
Sep 29, 2024 am 06:05 AM
First Minisforum mini PC with Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 rumored to launch with high price tag
Sep 29, 2024 am 06:05 AM
Aoostar was among the first to announce a Strix Point mini PC, and later, Beelink launched the SER9with a soaring starting price tag of $999. Minisforum joined the party by teasingthe EliteMini AI370, and as the name suggests, it will be the company'
 Beelink SER9: Compact AMD Zen 5 mini-PC announced with Radeon 890M iGPU but limited eGPU options
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:16 PM
Beelink SER9: Compact AMD Zen 5 mini-PC announced with Radeon 890M iGPU but limited eGPU options
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:16 PM
Beelink continues to introduce new mini-PCs and accompanying accessories at a rate of knots. To recap, little over a month has passed since it released the EQi12, EQR6 and the EX eGPU dock. Now, the company has turned its attention to AMD's new Strix
 Deal | Lenovo ThinkPad P14s Gen 5 with 120Hz OLED, 64GB RAM and AMD Ryzen 7 Pro is 60% off right now
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:31 AM
Deal | Lenovo ThinkPad P14s Gen 5 with 120Hz OLED, 64GB RAM and AMD Ryzen 7 Pro is 60% off right now
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:31 AM
Many students are going back to school these days, and some may notice that their old laptop isn't up to the task anymore. Some college students might even be in the market for a high-end business notebook with a gorgeous OLED screen, in which case t



